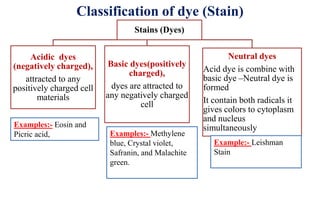
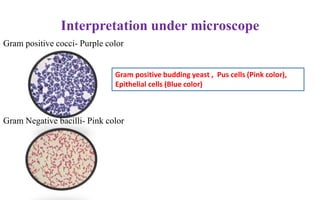
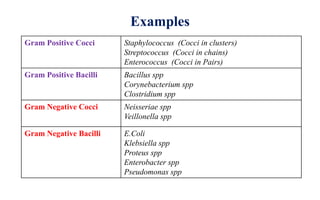
Gram staining is a differential staining technique used to classify bacteria into two groups - Gram positive and Gram negative. It works by using a primary stain (crystal violet), a mordant (iodine), a decolorizer (alcohol or acetone), and a counterstain (safranin). Gram positive bacteria retain the crystal violet dye after decolorization, appearing purple or blue under the microscope. Gram negative bacteria lose the crystal violet and take up the pink safranin counterstain instead. The difference is due to the thicker peptidoglycan layer in Gram positive bacteria, which prevents the dye from being washed away. Gram staining is useful for bacterial identification and determining appropriate empirical treatment.