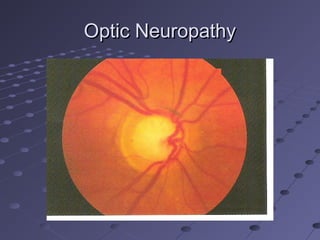
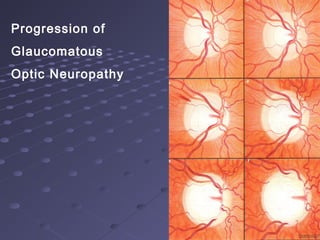
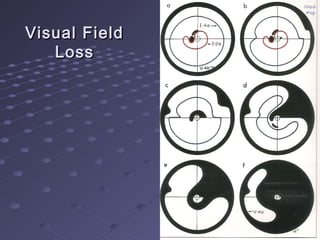
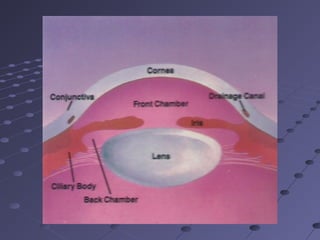
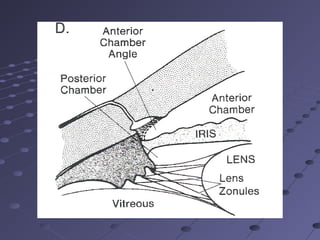
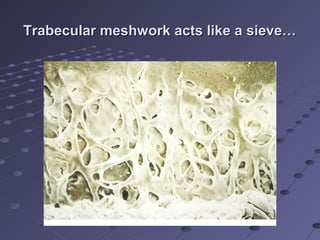
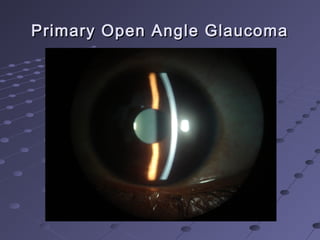
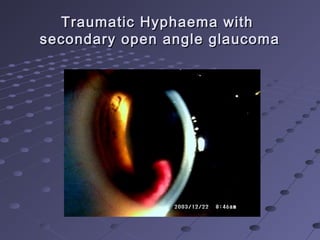
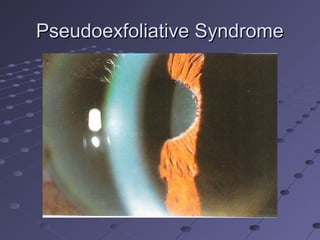
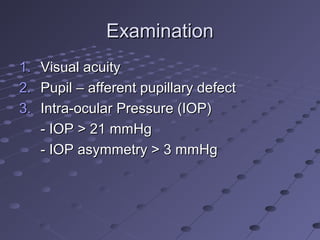
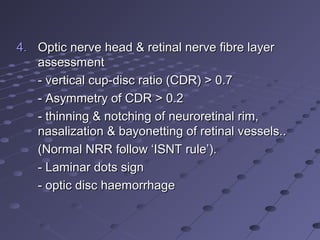
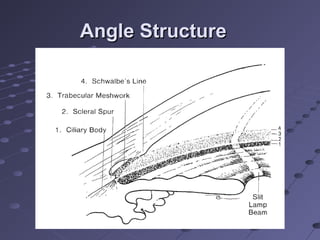
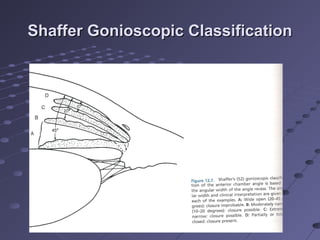
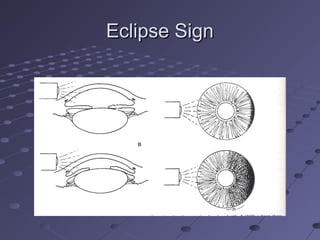
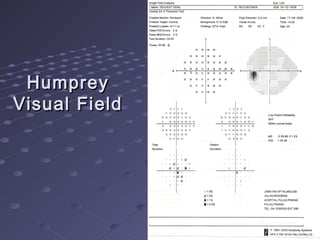
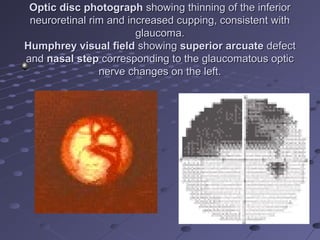
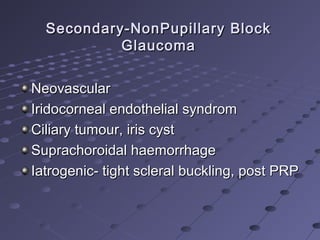
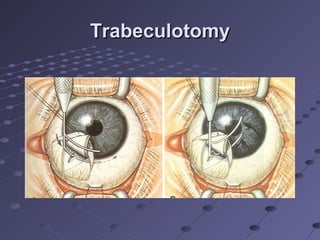
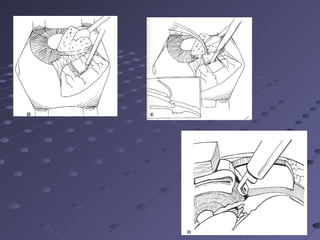
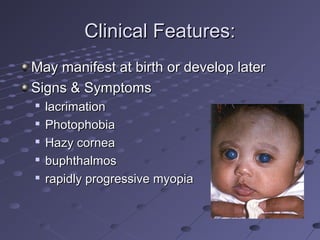
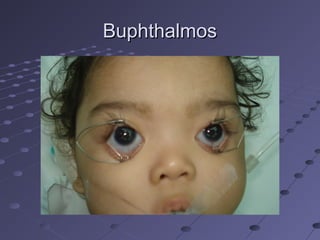
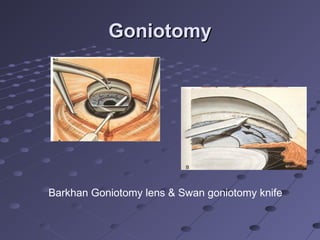
This document provides information about glaucoma, including definitions, classifications, risk factors, clinical features, examination findings, and management strategies. It discusses primary open angle glaucoma as the most common type, which can cause progressive, painless vision loss if intraocular pressure is not controlled. It also covers primary angle closure glaucoma and congenital glaucoma. Surgical treatments like trabeculectomy may be used if medical therapy with eye drops is insufficient to stop disease progression. Early detection and treatment are important to prevent irreversible vision loss from this sight-threatening condition.