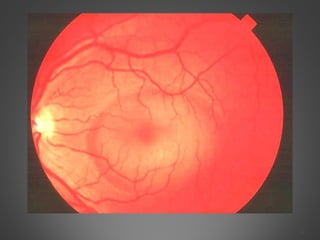
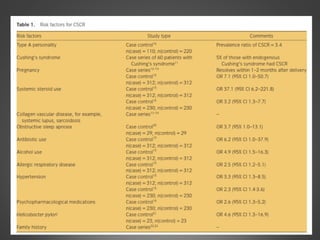
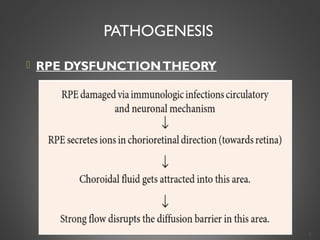
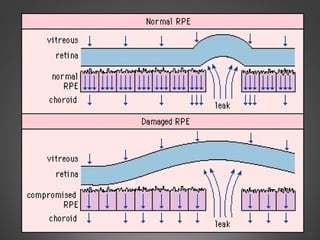
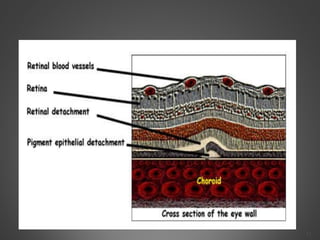
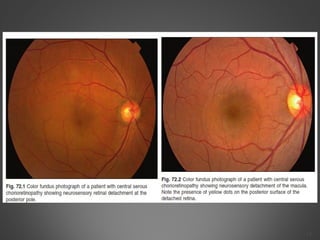
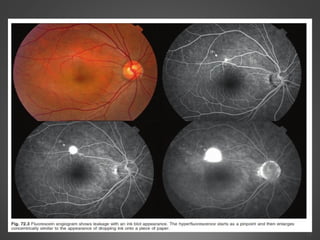
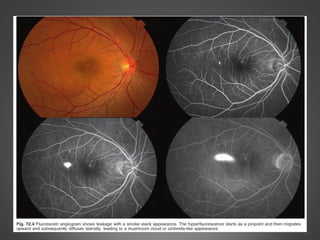
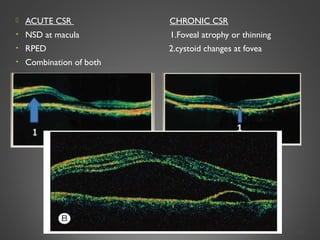
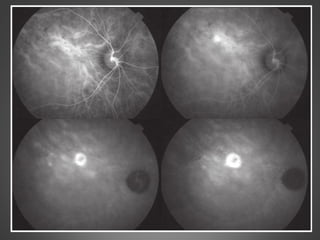
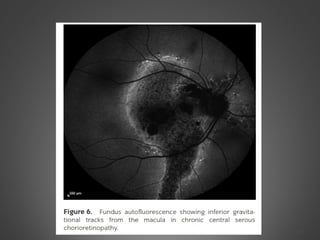
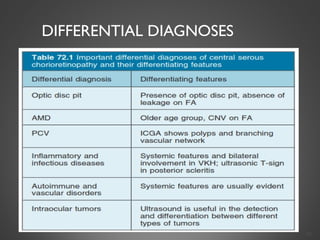
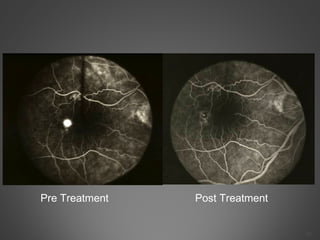
This document provides an overview of central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC), including its pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, course and treatment. CSC is characterized by a localized serous retinal detachment in the macula due to leakage of fluid from the choroid. It typically affects men ages 30-50 and can be associated with stress, corticosteroid use, hypertension and type A personality. Diagnosis is usually clinical but can be confirmed with fluorescein angiography showing characteristic leakage patterns or optical coherence tomography identifying subretinal fluid. While most cases resolve spontaneously, laser photocoagulation or photodynamic therapy may be used in persistent or recurrent cases to seal leaking sites and accelerate resolution.