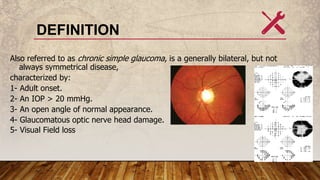
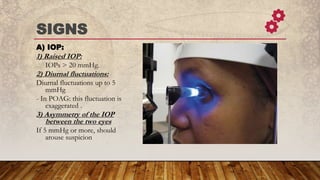
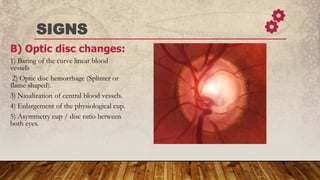
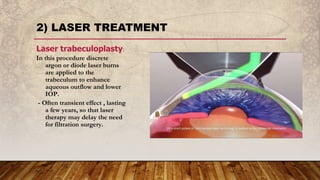
Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is a common, irreversible optic neuropathy characterized by adult onset, elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) greater than 20 mmHg, and progressive visual field loss. It typically affects those over 40, with a higher incidence in individuals of African descent, and has both genetic and environmental risk factors. Treatment focuses on lowering IOP through medical, laser, or surgical methods to prevent vision impairment.