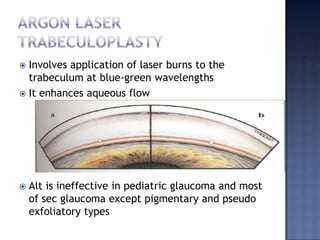
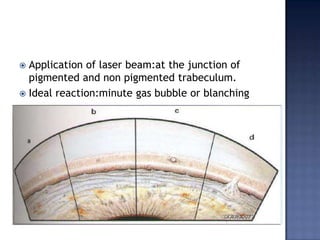
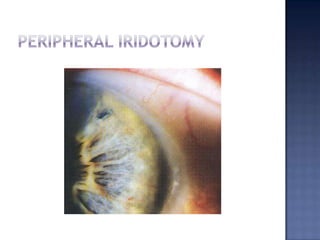
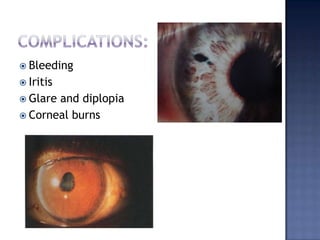
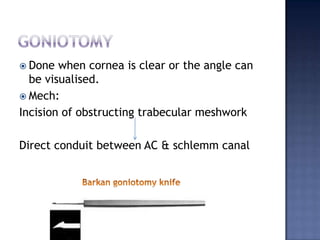
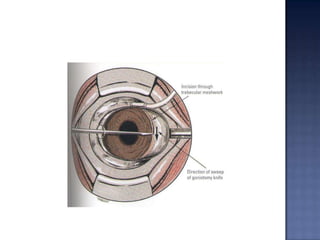
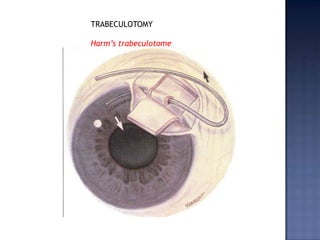
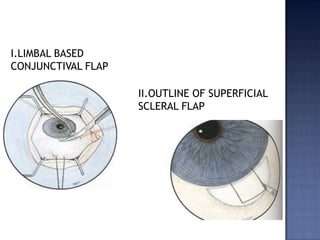
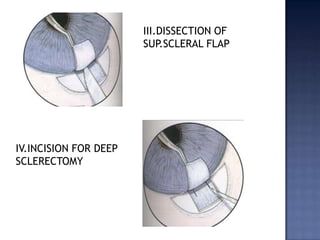
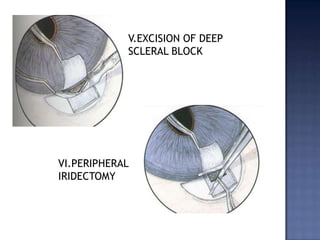
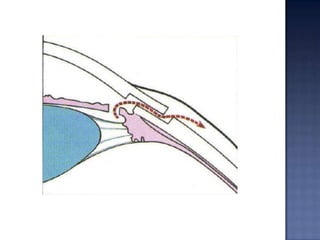
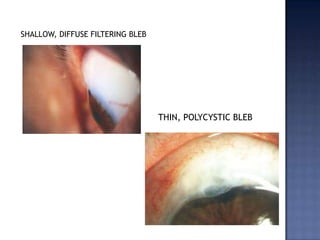
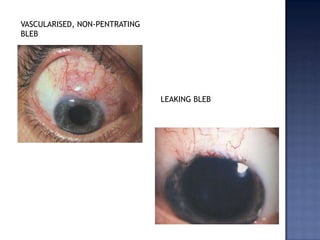
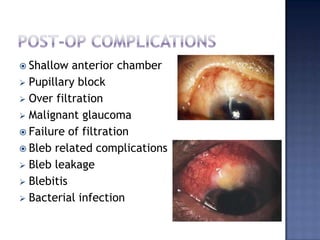
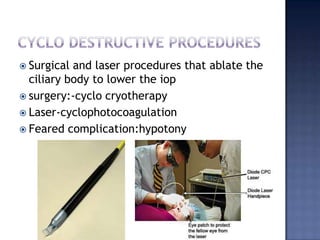
Surgical management of glaucoma includes various laser surgeries, filtering surgeries like trabeculectomy, and other procedures. Laser surgeries like argon laser trabeculoplasty and selective laser trabeculoplasty use laser energy to increase drainage by altering the trabecular meshwork. Trabeculectomy involves creating a small hole in the eye to allow drainage of fluid into a filtering bleb under the conjunctiva. Other options include non-penetrating surgeries, artificial drainage implants, and cyclo destructive procedures to ablate the ciliary body. The goal of all these surgeries is to lower intraocular pressure and slow glaucoma progression.