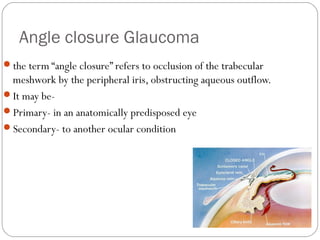
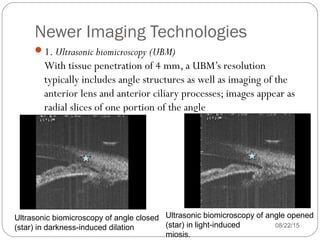
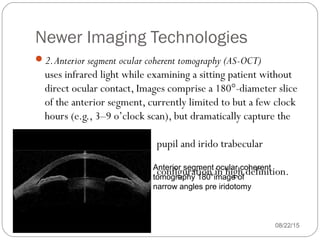
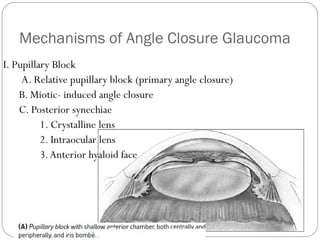
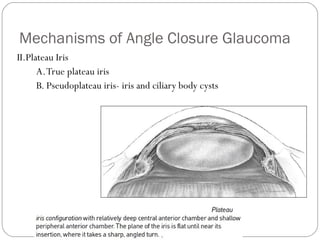
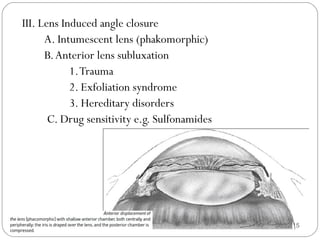
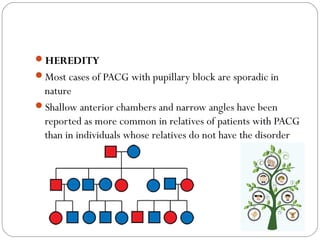
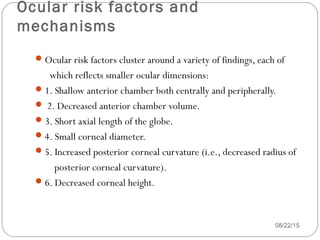
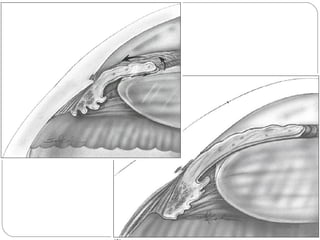
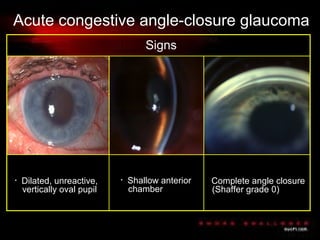
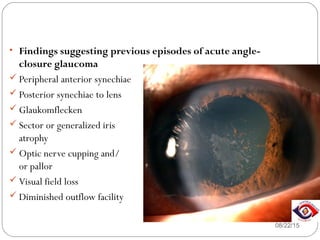
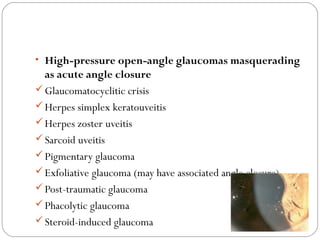
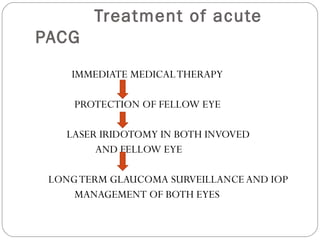
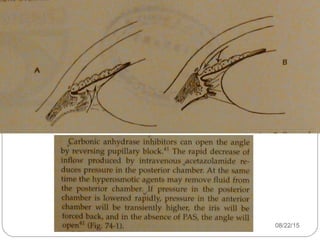
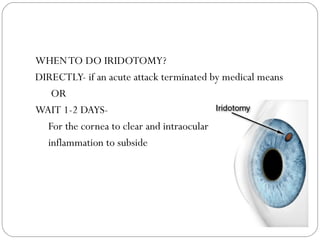
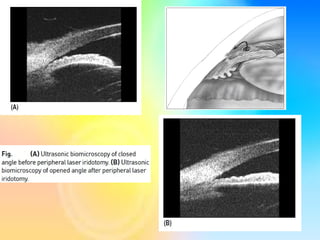
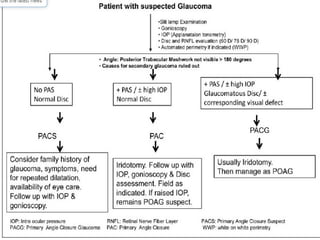
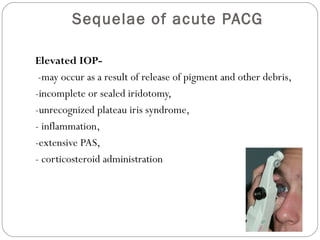
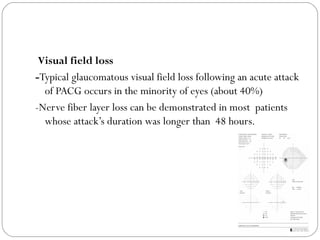
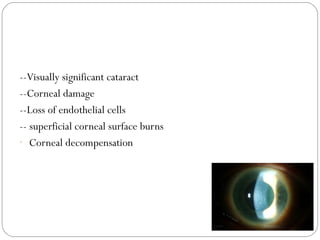
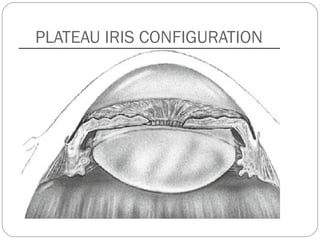
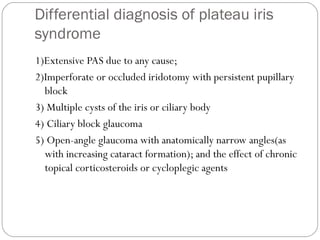
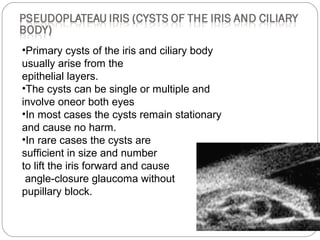
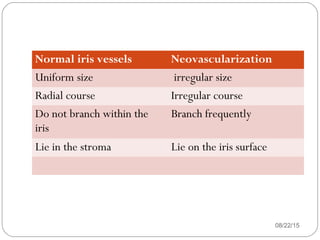
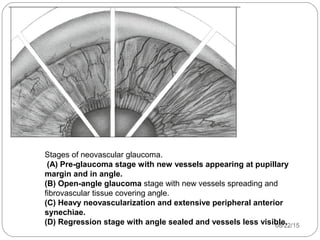
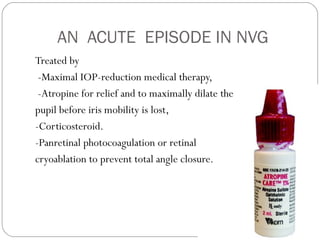
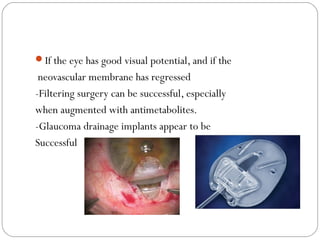
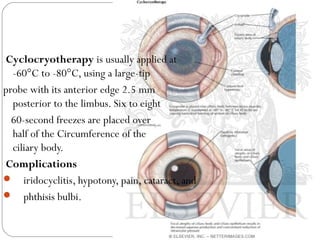
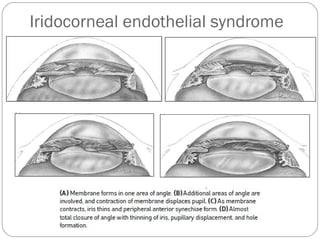
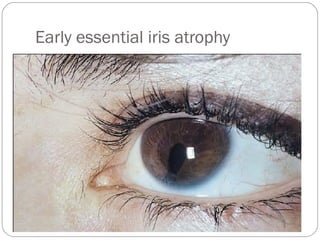
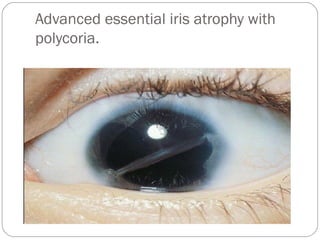
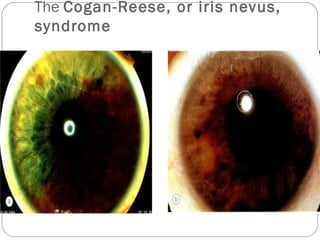
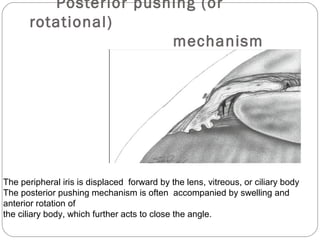
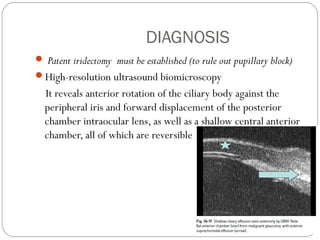
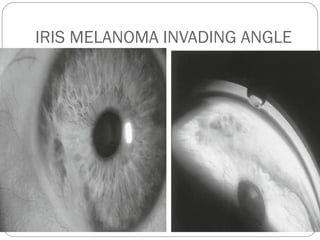
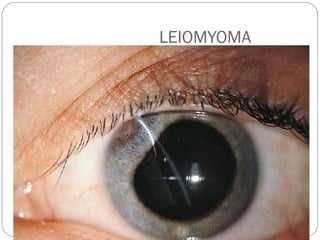
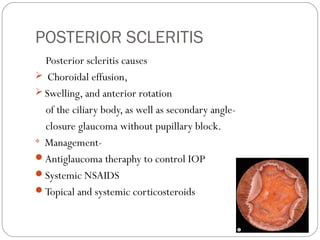
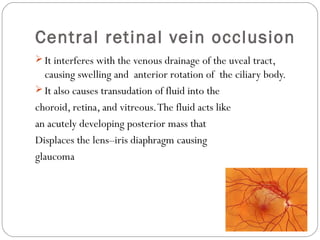
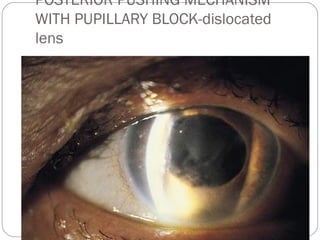
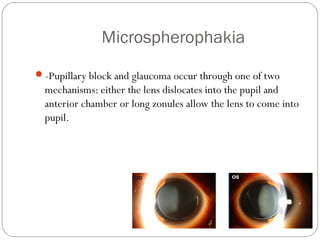
Angle closure glaucoma is caused by occlusion of the trabecular meshwork by the peripheral iris, obstructing aqueous outflow. It is classified as primary, relating to anatomical predisposition, or secondary, due to another ocular condition. The main mechanisms are pupillary block, where the iris bows forward and closes the angle, and plateau iris syndrome, where the iris is positioned anteriorly. Risk factors include shallow anterior chamber, older age, female sex, and hyperopia. Pupillary block occurs more commonly in winter due to lower light levels causing miosis.