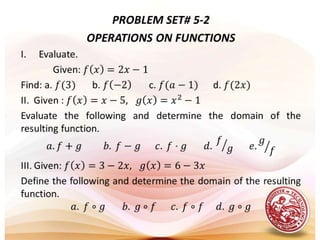
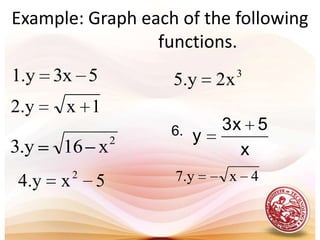
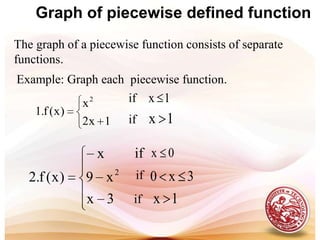
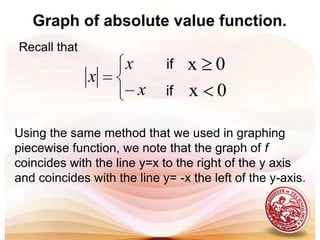
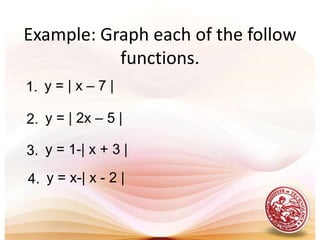
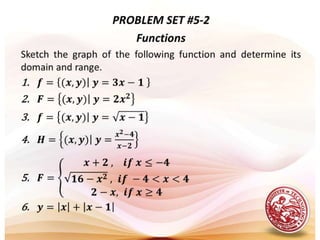
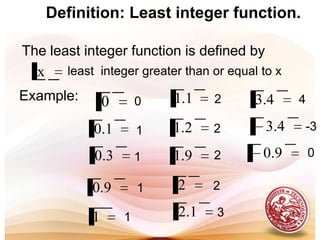
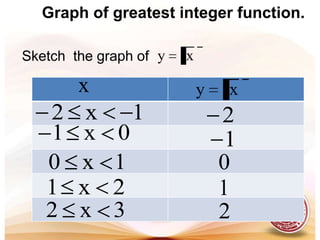
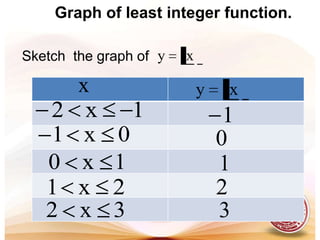
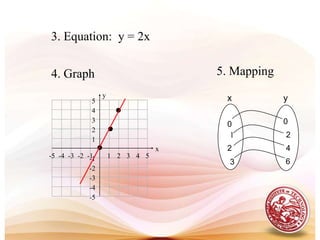
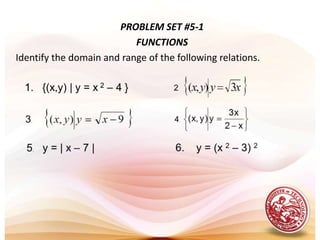
This document defines functions and relations. It discusses identifying the domain and range of functions and relations, evaluating functions, and performing operations on functions such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition. It also covers graphing functions, including piecewise functions, absolute value functions, greatest and least integer functions. Key examples are provided to illustrate how to identify domains and ranges, evaluate functions, perform operations on functions, and graph different types of functions.
















![DEFINITION: Operations on FunctionsIf f (x) and g (x) are two functions, thenSum and Difference ( f + g ) ( x ) = f(x) + g(x) Product( f g ) ( x ) = [ f(x) ] [ g(x) ] Quotient( f / g ) ( x ) = f(x) / g(x) d) Composite ( f ◦ g ) ( x ) = f (g(x))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-functions-110908064649-phpapp02/85/7-functions-22-320.jpg)