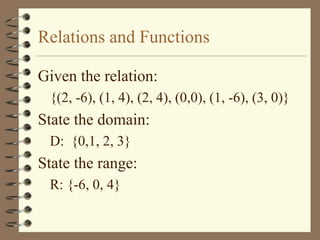
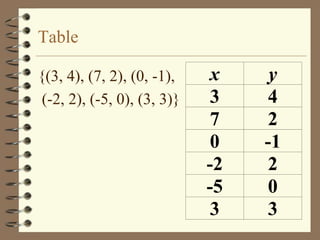
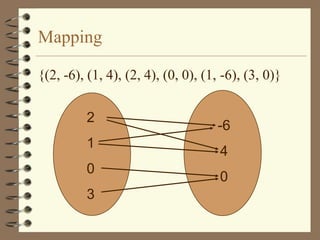
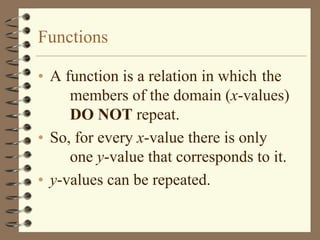
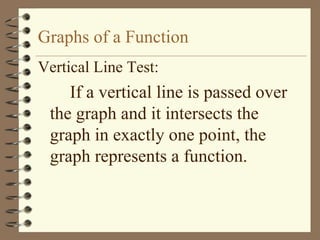
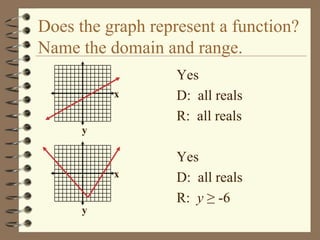
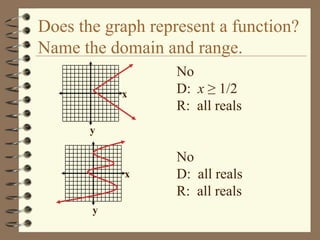
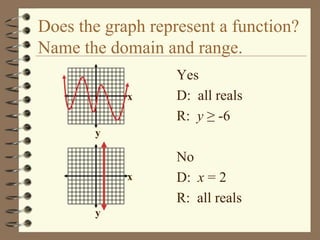
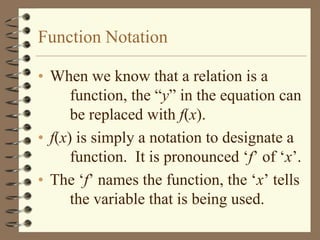
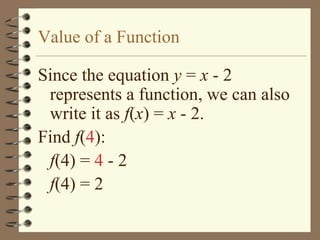
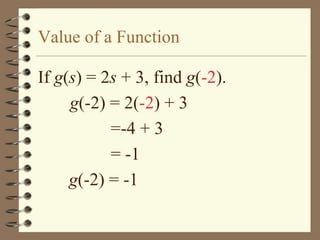
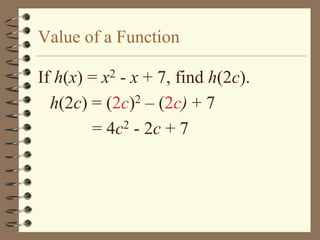
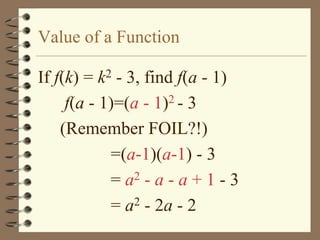
The document provides an overview of linear relations and functions. It defines relations as sets of ordered pairs and functions as relations where each x-value corresponds to only one y-value. It discusses representing relations as ordered pairs, tables, mappings, and graphs. Key aspects of functions covered include discrete vs continuous functions, the vertical line test, function notation such as f(x), and evaluating functions by finding values such as f(4) given f(x) = x - 2.