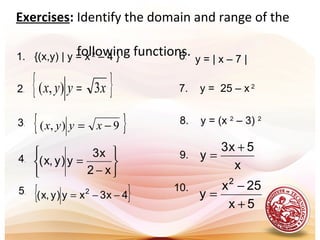
The document defines functions and discusses:
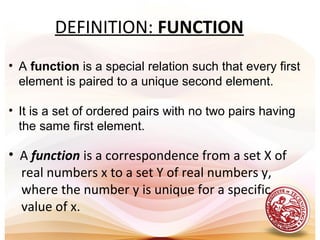
- Functions are sets of ordered pairs with each first element paired to a unique second element.
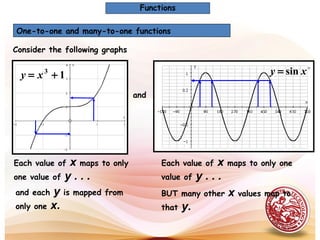
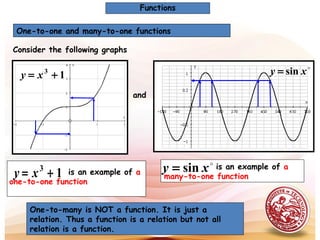
- Functions can be one-to-one or many-to-one.
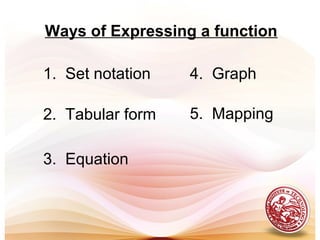
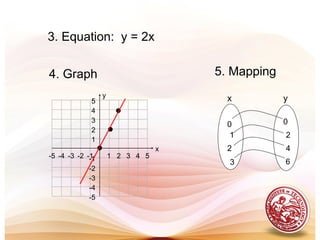
- Functions are represented in set notation, tabular form, as equations, and as graphs.
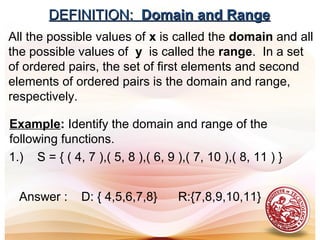
- The domain of a function is the set of first elements and the range is the set of second elements.









![EXAMPLE:
Evaluate each function value.
1. If f ( x ) = x + 9 , what is the value of f ( x 2
) ?
2. If g ( x ) = 2x – 12 , what is the value of g (– 2 )?
3. If h ( x ) = x 2
+ 5 , find h ( x + 1 ).
4.If f(x) = x – 2 and g(x) = 2x2
– 3 x – 5 ,
Find: a) f(g(x)) b) g(f(x))
[ ] [ ]222
)(,)(),1(),(),0(),3( hafafafafff ++
5. If find each of the following1)( 2
−= xxf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1functionsdomainrange-151022203830-lva1-app6891/85/L1-functions-domain-amp-range-15-320.jpg)






![B. Given the function f defined by f(x) = 2x2
+ 3x – 1,
find:
a. f(0) f. f(3 – x2
)
b. f(1/2) g. f(2x3
)
c. f(-3) h. f(x) + f(h)
d.f(k + 1) i. [f(x)]2
– [f(2)]2
e. f(h – 1) j. 0h;
h
)x(f)hx(f
≠
−+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1functionsdomainrange-151022203830-lva1-app6891/85/L1-functions-domain-amp-range-24-320.jpg)