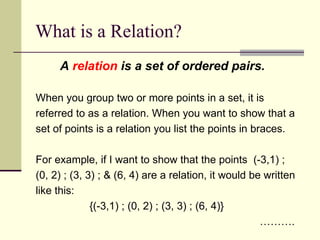
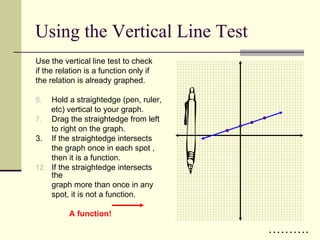
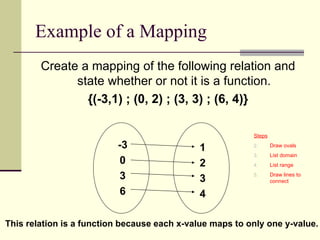
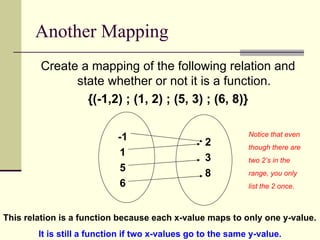
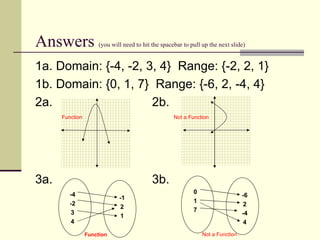
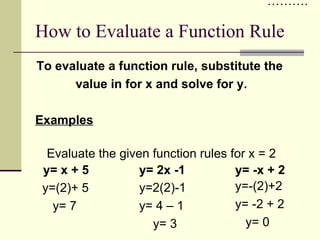
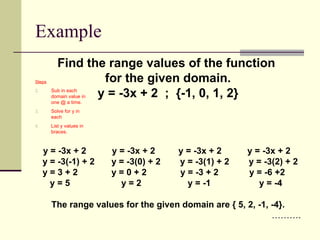
The document defines relations and functions. A relation is a set of ordered pairs, while a function is a special type of relation where each x-value is mapped to only one y-value. The domain is the set of x-values and the range is the set of y-values. Functions can be identified using the vertical line test or by mapping the relation to check if any x-values are mapped to multiple y-values. Evaluating functions involves substituting domain values into the function rule to find the corresponding range values.