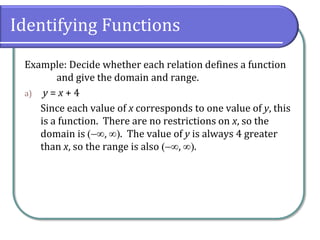
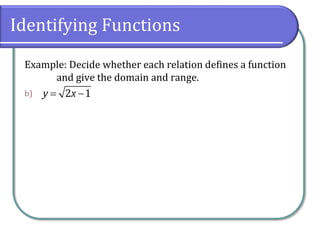
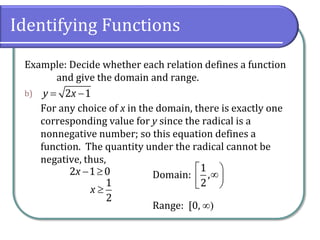
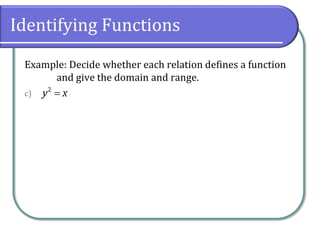
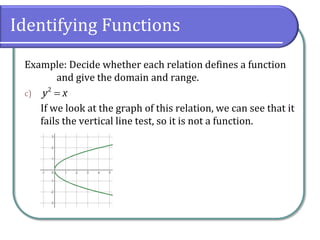
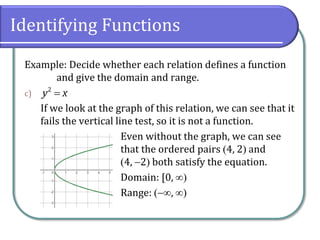
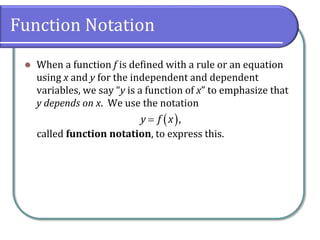
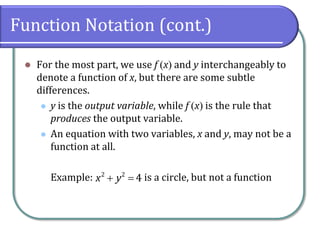
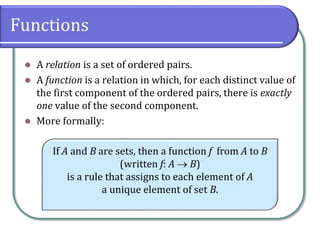
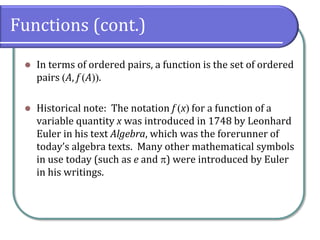
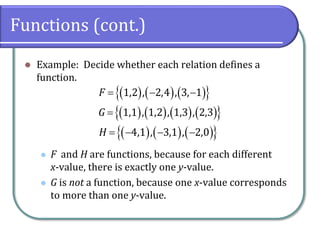
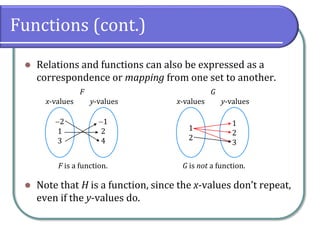
This document defines and discusses functions. It begins by defining a relation and function, noting that a function is a special type of relation where each input is mapped to exactly one output. It introduces function notation and discusses the domain, codomain, and range of a function. Examples are provided to illustrate determining if a relation defines a function. The document also covers identifying functions from equations or graphs, and the vertical line test. It concludes with a discussion of function notation and classwork assignments.


![Domain and Range From Graphs
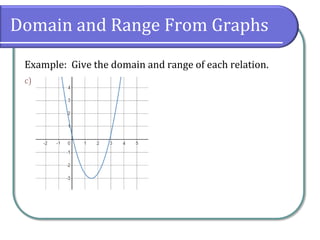
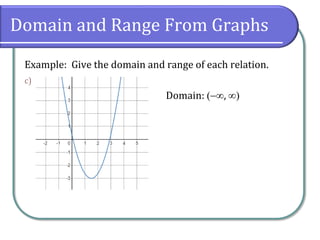
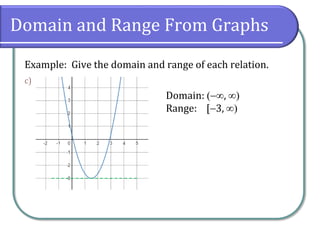
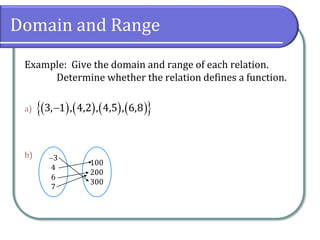
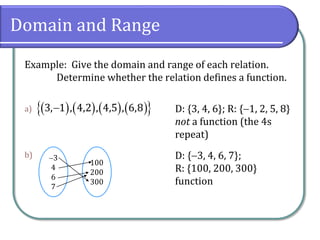
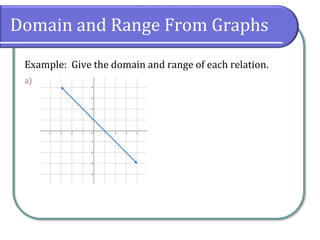
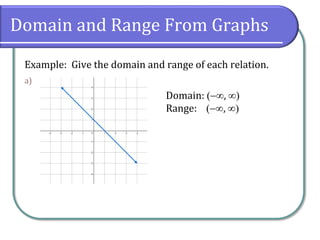
Example: Give the domain and range of each relation.
b)
Domain: [4, 4]
Domain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-201112174424/85/2-3-Functions-14-320.jpg)
![Domain and Range From Graphs
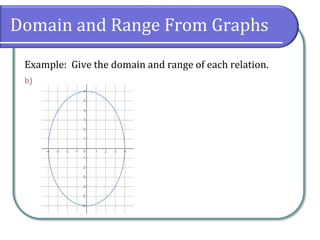
Example: Give the domain and range of each relation.
b)
Domain: [4, 4]
Range: [6, 6]
Domain
Range](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-201112174424/85/2-3-Functions-15-320.jpg)