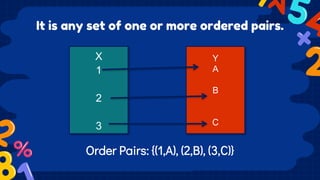
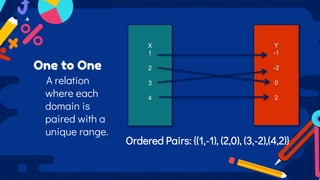
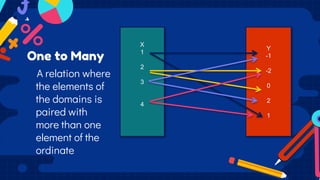
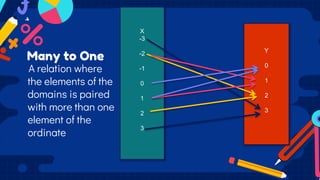
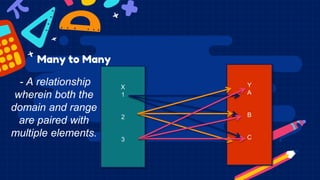
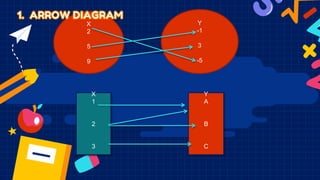
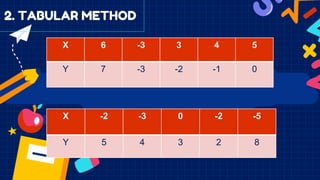
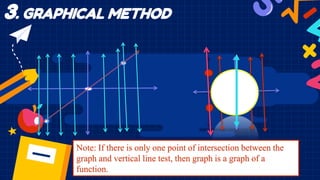
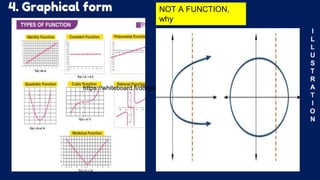
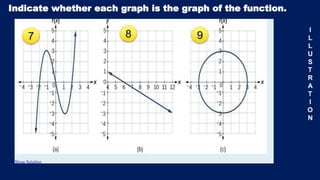
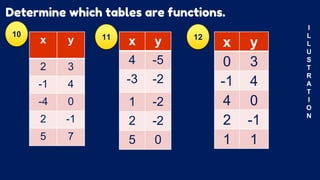
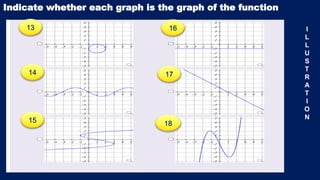
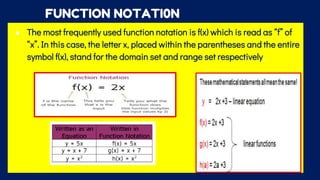
This document discusses functions and relations. It defines a relation as a set of ordered pairs and provides examples. It then defines a function as a special type of relation where each element of the domain corresponds to exactly one element of the range, meaning no two ordered pairs can have the same first element. The document discusses different types of relations including one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many. It also discusses how functions can be presented using arrow diagrams, tables, graphs, and ordered pairs. Finally, it discusses function notation and evaluating functions by substituting values into the function.