Embed presentation
Downloaded 68 times

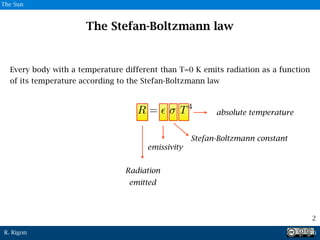


![R. Rigon
Planck’s Law
•Planck’s law is the general law for electromagnetic emission from the
surface of a blackbody*:
W =
2⇡c2
h 5
e
ch
KT 1
[Wm 2
µm 1
]
14
7
The Sun
* Stefan-Boltzmann law is just the integration of Plank’s law over wavelengths](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-c-radiation-stefanboltzman-170216045128/85/6-c-radiation-stefan-boltzman-7-320.jpg)

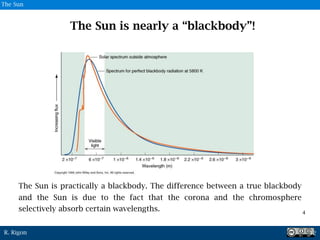
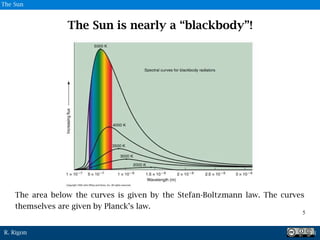
The document discusses the Stefan-Boltzmann law and its application to solar radiation, noting that all bodies emit radiation based on temperature, and highlights the sun's behavior as nearly a blackbody. It explains that the sun emits a significant amount of energy, approximating a blackbody spectrum, despite some absorption by its corona and chromosphere. The document also refers to Planck's law as crucial for understanding electromagnetic emissions from blackbodies.






![R. Rigon
Planck’s Law
•Planck’s law is the general law for electromagnetic emission from the
surface of a blackbody*:
W =
2⇡c2
h 5
e
ch
KT 1
[Wm 2
µm 1
]
14
7
The Sun
* Stefan-Boltzmann law is just the integration of Plank’s law over wavelengths](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-c-radiation-stefanboltzman-170216045128/85/6-c-radiation-stefan-boltzman-7-320.jpg)