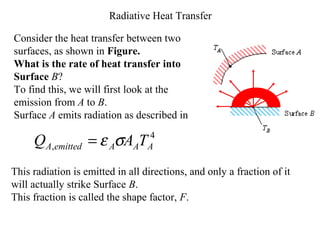
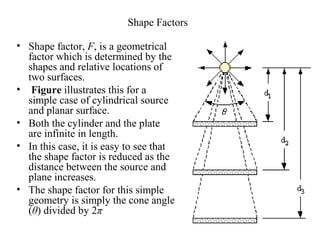
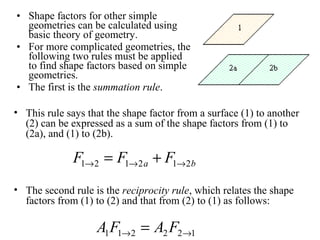
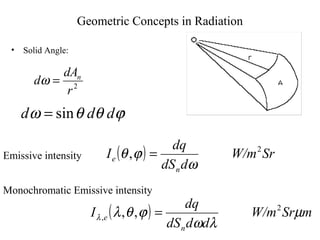
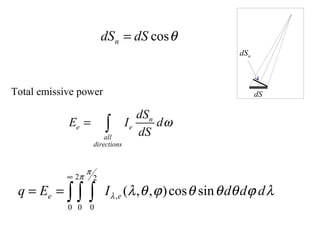
- Radiation heat transfer occurs through electromagnetic waves emitted by surfaces due to their temperature. All real surfaces emit less than ideal blackbodies.
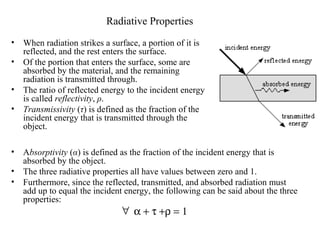
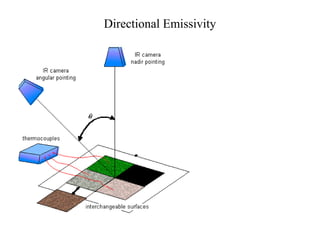
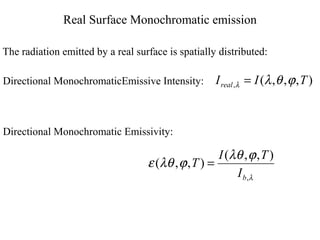
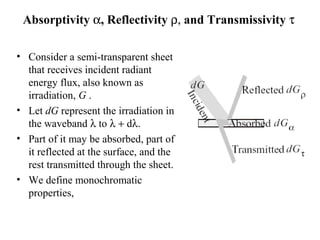
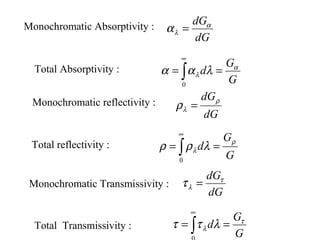
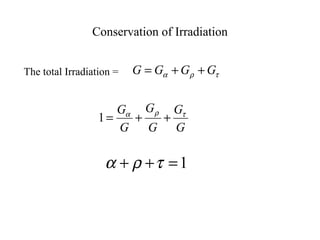
- The key radiative properties are emissivity ε, absorptivity α, reflectivity ρ, and transmissivity τ. For opaque surfaces, α + ρ = 1.
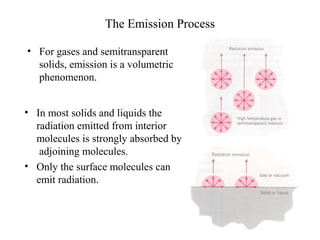
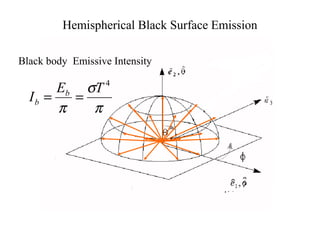
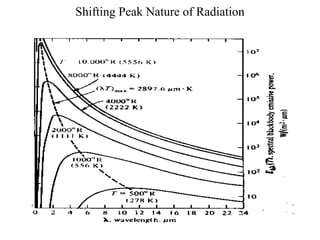
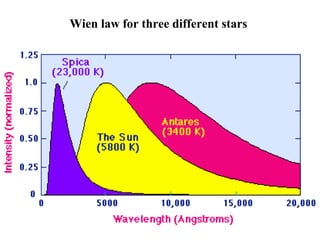
- Blackbodies have ε = 1 and emit thermal radiation described by Planck's law. Real surfaces emit radiation according to their emissivity and temperature.
- The rate of radiative heat transfer between two surfaces depends on their temperatures and emissivities, the shape factor F between their orientations, and the absorptivity of the receiving surface.