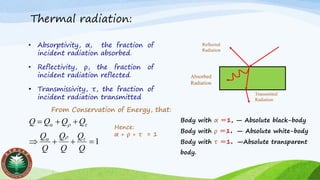
Thermal radiation is emitted by all objects due to the vibrational and rotational movements of molecules and atoms. It is transported via electromagnetic waves and can propagate through a vacuum. All objects emit radiation at any temperature above absolute zero according to their emissivity.
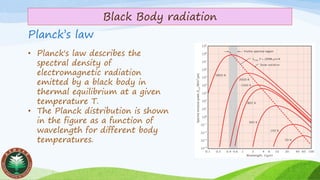
Blackbody radiation follows Planck's law, with a continuous frequency spectrum that depends only on temperature. It has a peak wavelength defined by Wien's displacement law. The total power output of blackbody radiation is described by Stefan-Boltzmann law.
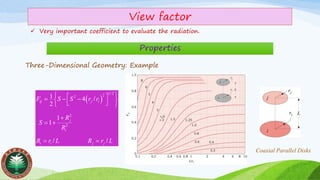
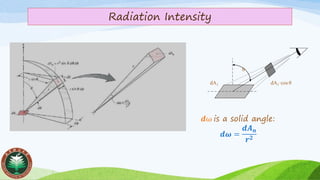
The view factor is used to account for incomplete radiation exchange between surfaces, describing the fraction of radiation leaving one surface that is received by another. It is essential for calculating radiation heat transfer between surfaces.







![Plank’s Law
• The Planck law describes
theoretical spectral
distribution for the emissive
power of a black body.
• 𝐸𝜆,𝑏 =
𝐶1
𝜆5[exp
𝐶2
𝜆𝑇
−1]
• where C1=3.742x108
(W.mm4/m2) and
C2=1.439x104 (m m.K) are
two constants.
• 𝑰 𝝀,𝒃 𝝀, 𝑻 =
𝟐𝒉𝒄 𝒐
𝟐
𝝀 𝟓[𝒆𝒙𝒑
𝒉𝒄 𝒐
𝝀𝒌 𝑩 𝑻
−𝟏]
• Where ℎ = 6.626 × 10−34
𝐽 ∙ 𝑠 and
𝑘 𝐵 = 1.381 × 10−23
𝐽/𝐾 are the
universal Plank and
Boltzmann constants,
respectively.
• 𝑐 𝑜 = 2.998 × 108 𝑚/𝑠 is the speed
of light in vacuum, and T is
the absolute temperature of
the blackbody(K).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thermalradiationpresentation-180520122340/85/Thermal-radiation-presentation-12-320.jpg)




![Black Body radiation
The Stefan- Boltzmann law
The total intensity associated with blackbody emission is 𝑰 𝒃 =
𝑬 𝒃
𝝅
𝑬 𝒃 = න
𝟎
∞
𝑪 𝟏
𝝀 𝟓[𝒆𝒙𝒑
𝑪 𝟐
𝝀𝑻
− 𝟏]
𝒅𝝀 Performing the integration, it may be shown that
𝐸 𝑏 = 𝜎𝑇4 The result is termed the Stefan–Boltzmann law. It
can be stated as “The emissive power of a black body
(per unit area per unit time) is directly proportional
to the fourth power of its absolute temperature”.
Where the unit is :
W/m2. ( b means
black body)
𝜎 is Proportionality constant called Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
𝜎= 5.676 x 10-8 W/m2-K4 unit is:W/m2K4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thermalradiationpresentation-180520122340/85/Thermal-radiation-presentation-17-320.jpg)