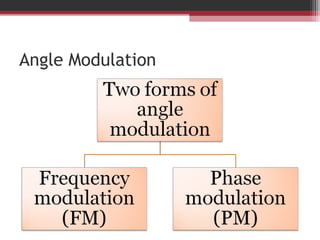
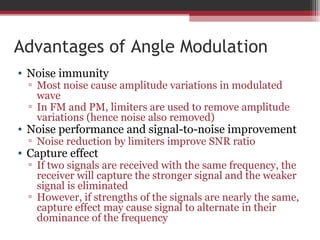
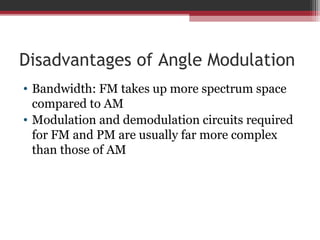
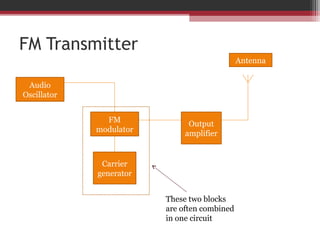
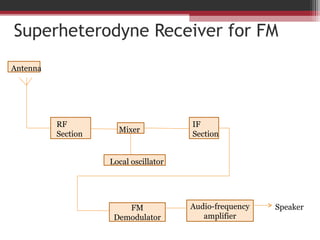
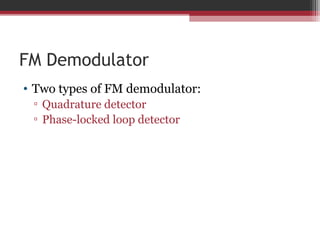
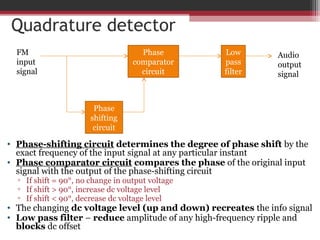
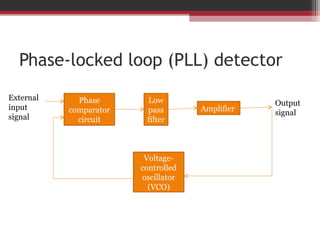
This document discusses angle modulation techniques, including frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM). It explains that FM directly varies the carrier frequency while PM directly varies the carrier phase. Both FM and PM occur simultaneously. It also describes the advantages of angle modulation, such as noise immunity, and the disadvantages, such as increased bandwidth compared to amplitude modulation. The key components of FM transmitters and receivers are outlined, including the FM modulator and demodulator. Two common types of FM demodulators are the quadrature detector and phase-locked loop detector.