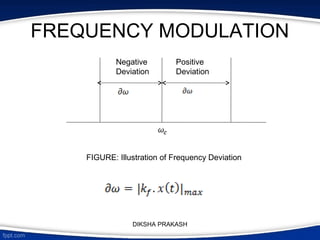
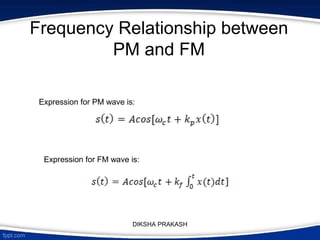
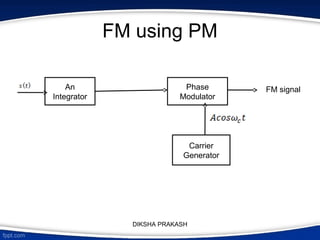
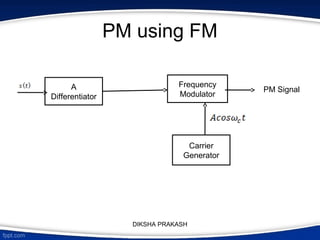
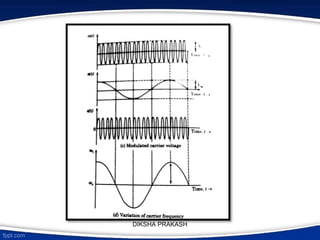
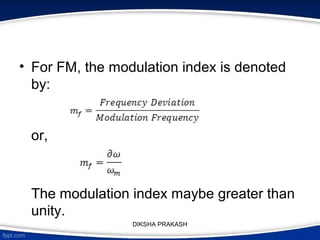
The document covers the concept of angle modulation, focusing on definitions of phase modulation (PM) and frequency modulation (FM), along with their relationship and applications in various communication technologies such as radio broadcasting and cellular communication. It outlines how the phase angle of the carrier wave varies according to the modulating signal while keeping amplitude constant. Additionally, it discusses the mathematical representation and implications of frequency deviation in FM and PM.