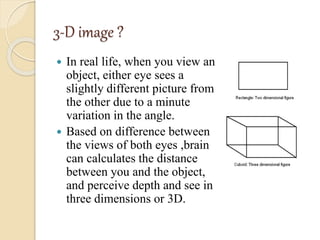
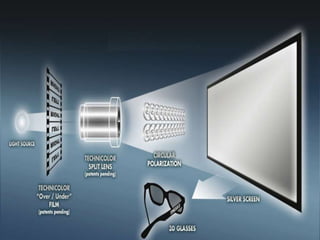
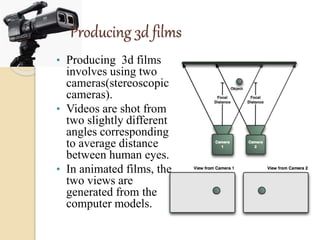
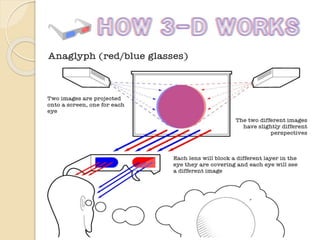
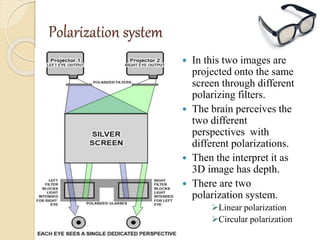
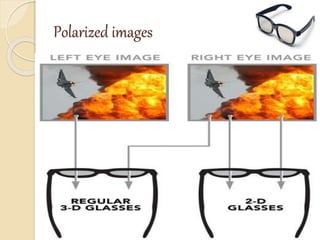
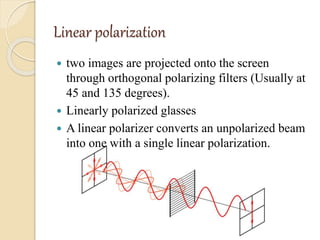
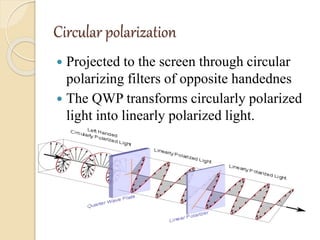
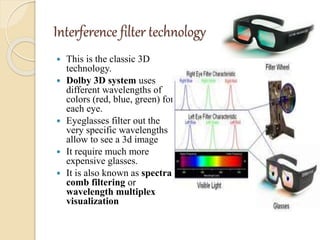
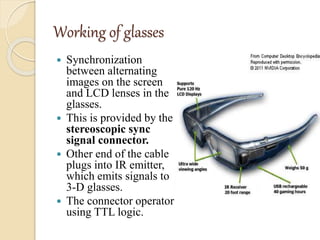
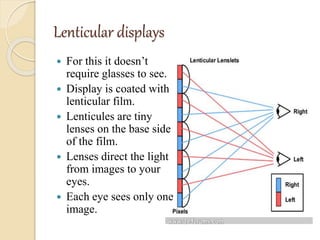
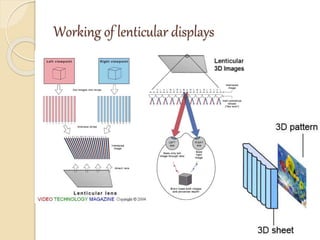
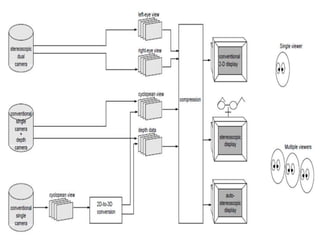
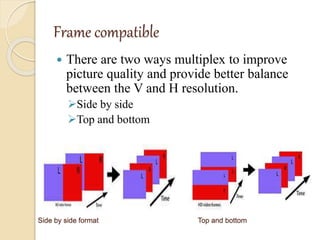
3D films and TVs provide depth perception by showing two slightly different perspectives that are interpreted by the brain as a 3D image. There are several technologies for producing and displaying 3D content, including anaglyph, polarization, and interference filtering systems. 3D TVs use technologies like eclipse filtering glasses or lenticular displays to show different images to each eye and create the 3D effect without glasses in some cases. Broadcasting 3D content involves generating, compressing, transmitting, and displaying the left and right perspectives in an alternating sequence.