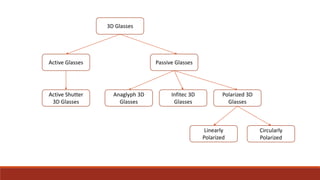
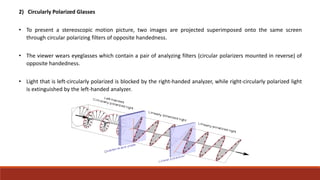
The document discusses various types of 3D glasses used for viewing stereoscopic images, including active, passive, anaglyph, infitec, and polarized glasses. Each type employs different technologies to deliver specific images to each eye, enhancing the perception of depth. The history and applications of these technologies are also highlighted, including their use in theaters, medical imaging, and early 3D films.