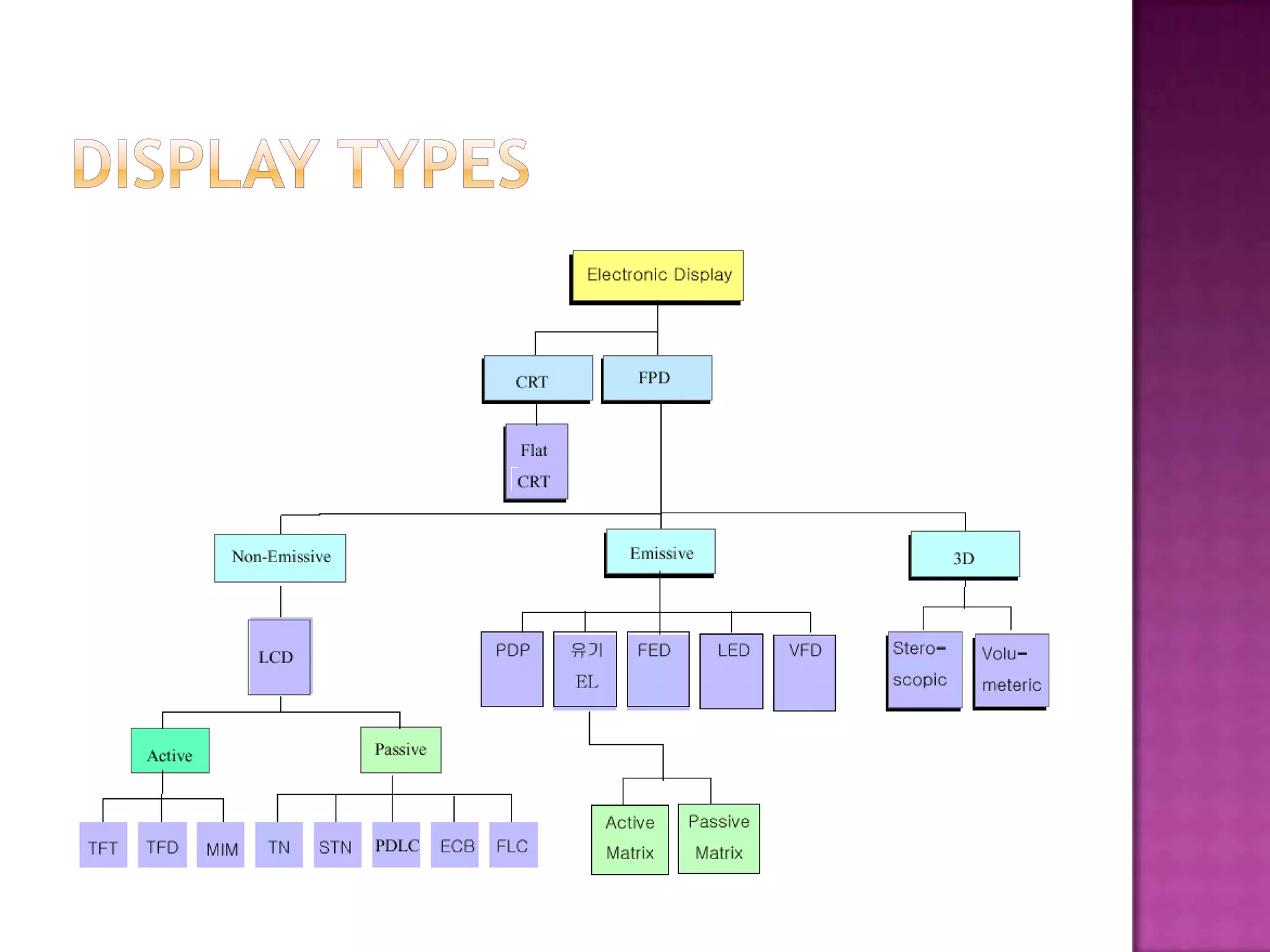
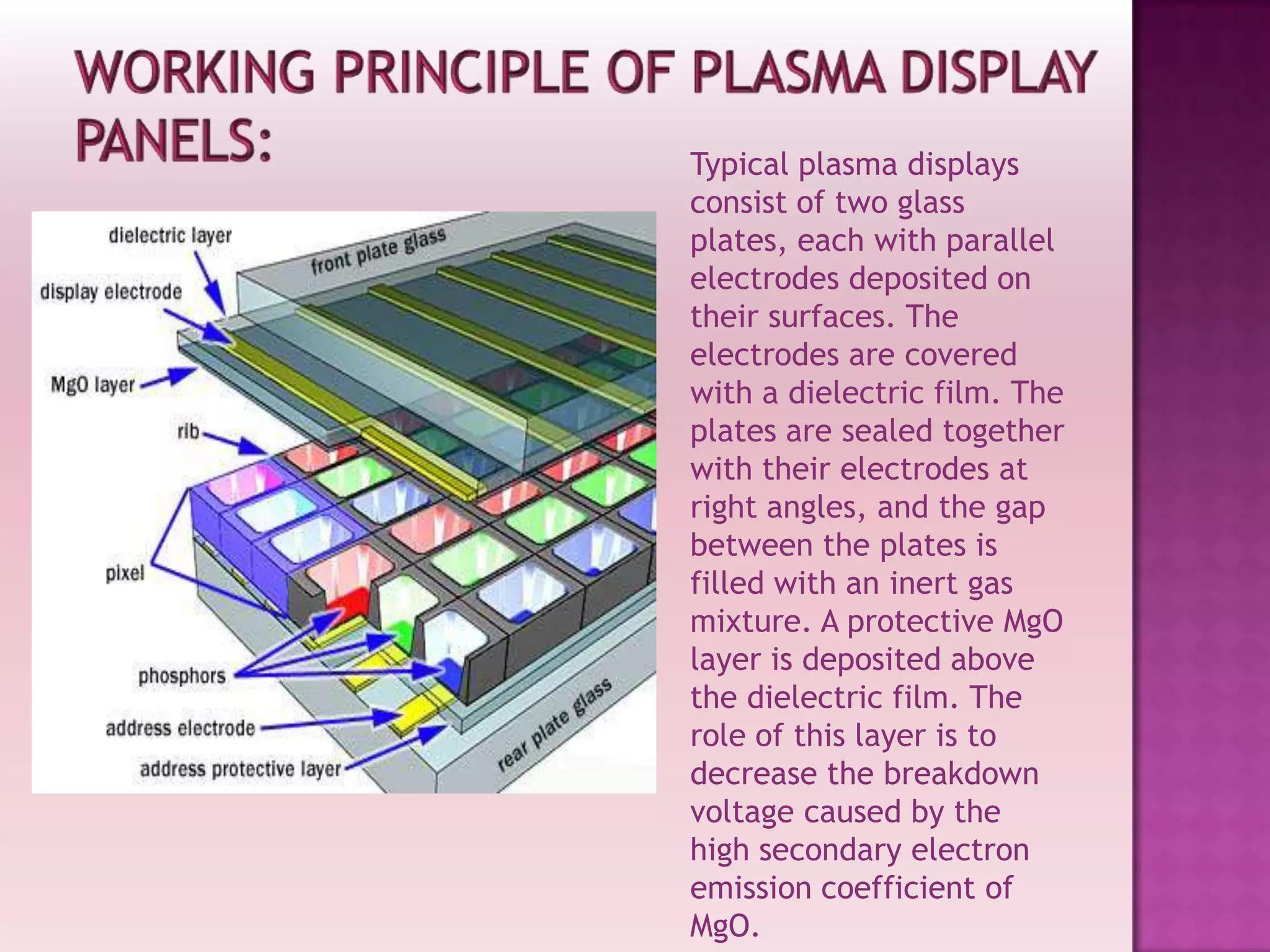
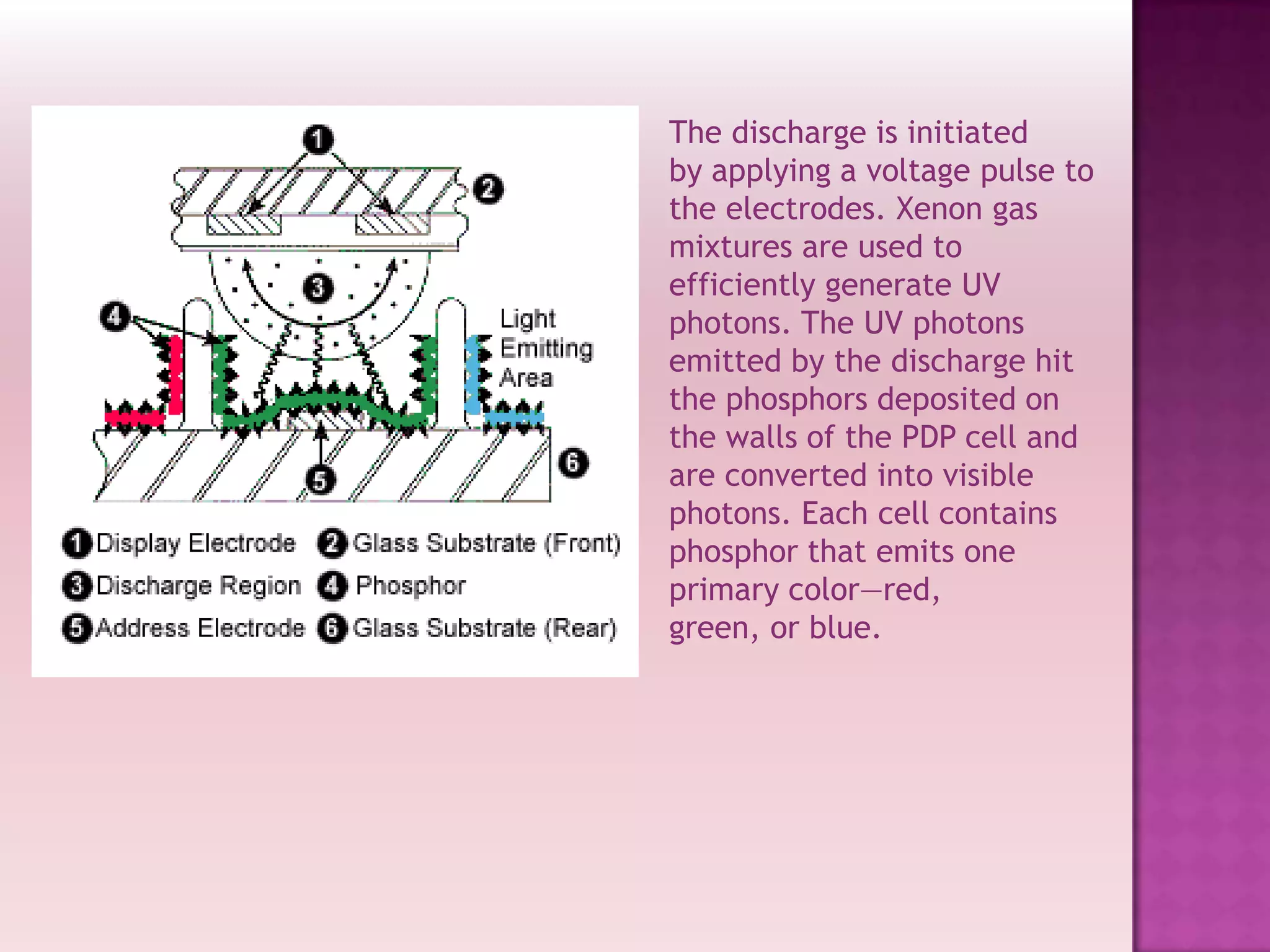
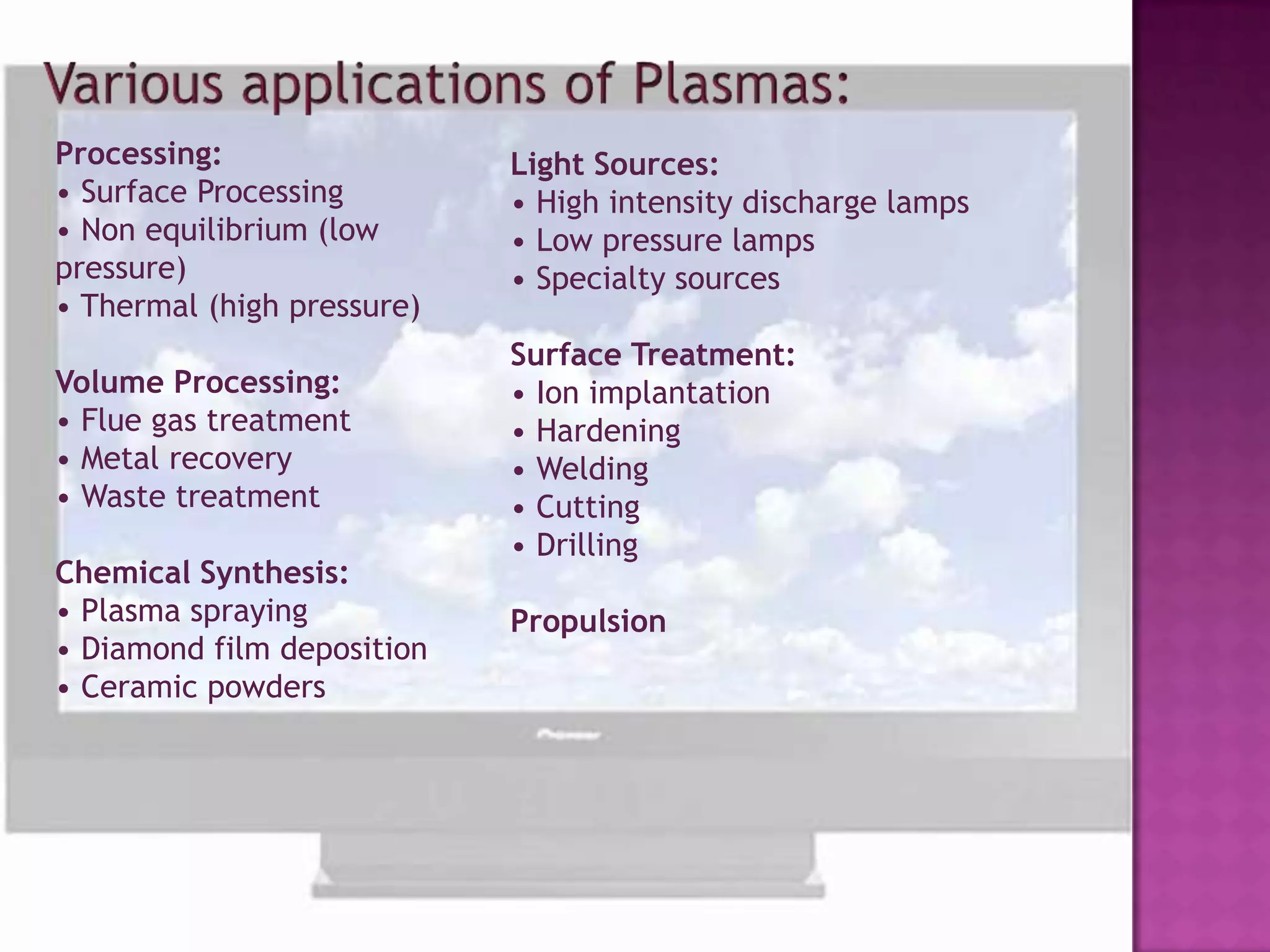
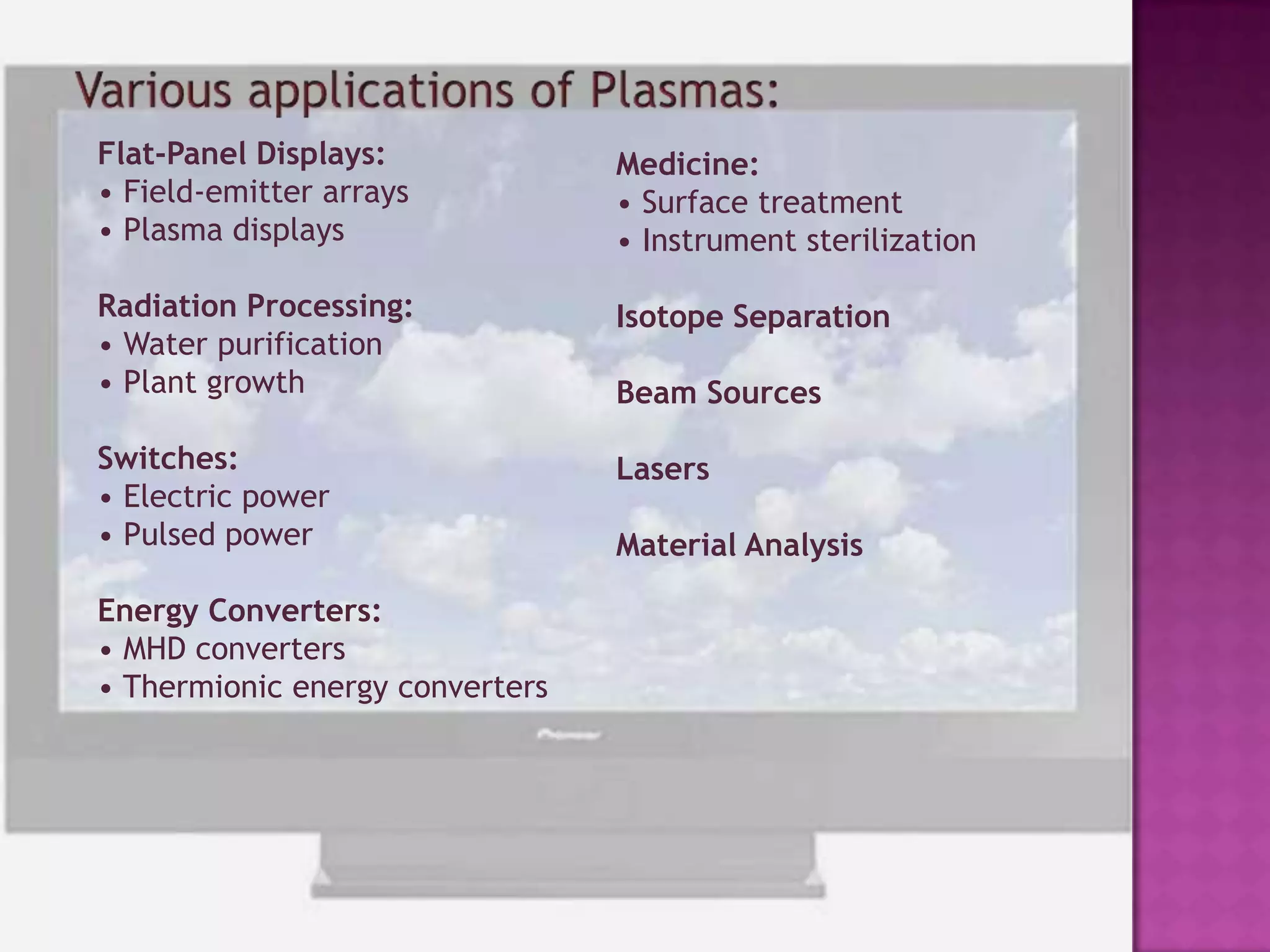
Plasma display panels (PDPs) use plasma technology to provide a flat panel display option. PDPs contain two glass plates separated by an inert gas that is ionized by an electrical current to produce visible light. This allows each pixel to emit red, green, or blue light independently. PDPs offer advantages over other displays like fast response time, wide viewing angles, low weight, and simple manufacturing. They are well-suited for applications like HDTV monitors. However, PDPs also have disadvantages compared to liquid crystal displays like higher power consumption and narrower viewing angles.