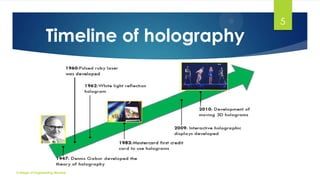
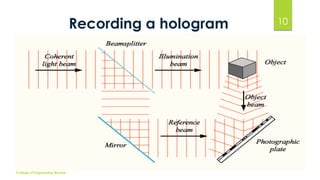
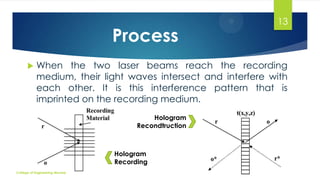
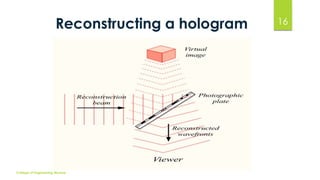
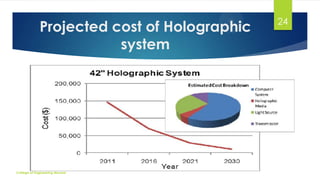
The document discusses 3D holographic projection technology, including its definition, types, how holograms work, and their recording and reconstruction processes. It highlights advancements in holography, applications in various fields such as education and entertainment, and predicts that holographic displays will eventually replace traditional screens. The technology offers high-resolution, interactive, and life-like images without the need for glasses or projection screens.