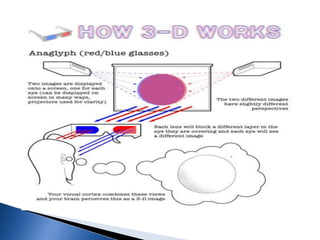
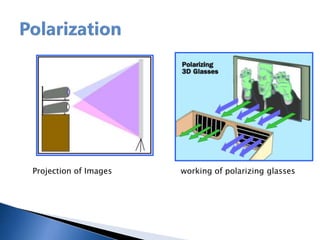
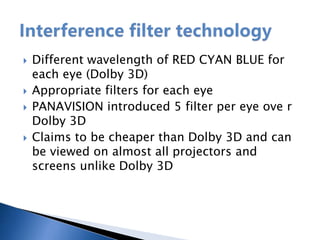
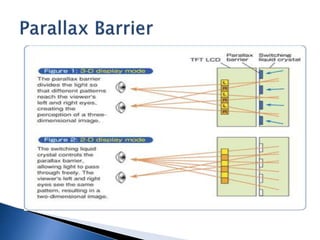
The document provides a history of 3D technology, beginning with William Friese Greene's 1880 patent and continuing through developments like Frederic Eugene Ives' 1900 3D camera and the 1922 premiere of the first 3D film. It discusses various 3D display methods including anaglyph, polarization, eclipse, interference filter technology, Pulfrich, spectral separation, and lenticular/barrier screens. It also covers technologies like LCD shutter glasses, polarized glasses, and autostereoscopic displays that do not require glasses.