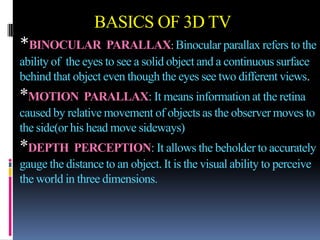
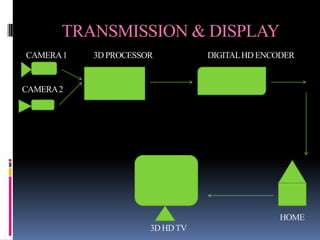
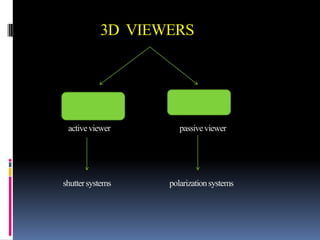
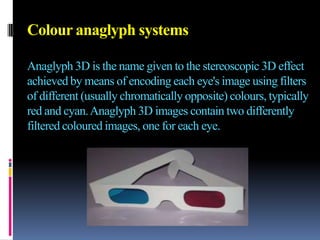
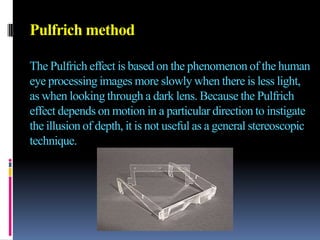
3-D TV uses two cameras to capture slightly different images for the left and right eyes, creating a 3D effect when viewed with special glasses. It transmits the two images via an encoder and displays them on a 3D-enabled TV using technologies like shutter glasses or polarized filters. While 3D TV provides an immersive experience, health concerns remain about prolonged viewing and industry standards have not been fully defined.