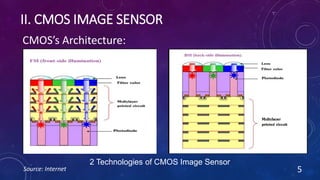
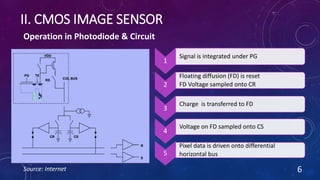
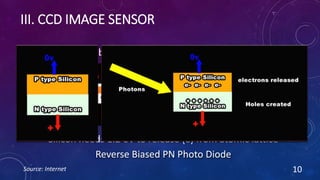
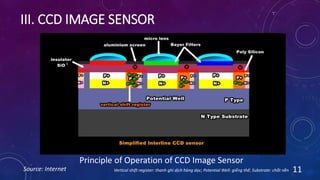
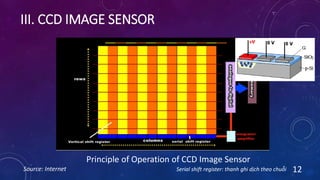
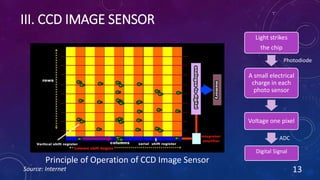
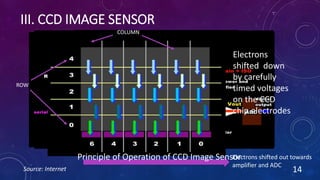
CMOS and CCD are the two most popular types of image sensors. CMOS sensors use less power and operate at faster speeds than CCD sensors, but have higher noise levels. CCD sensors have lower noise but require more power and operate more slowly. Both sensor types convert light into electrical signals that are then processed into digital images. They are widely used in applications like digital cameras, video cameras, CCTV security cameras, and copiers.