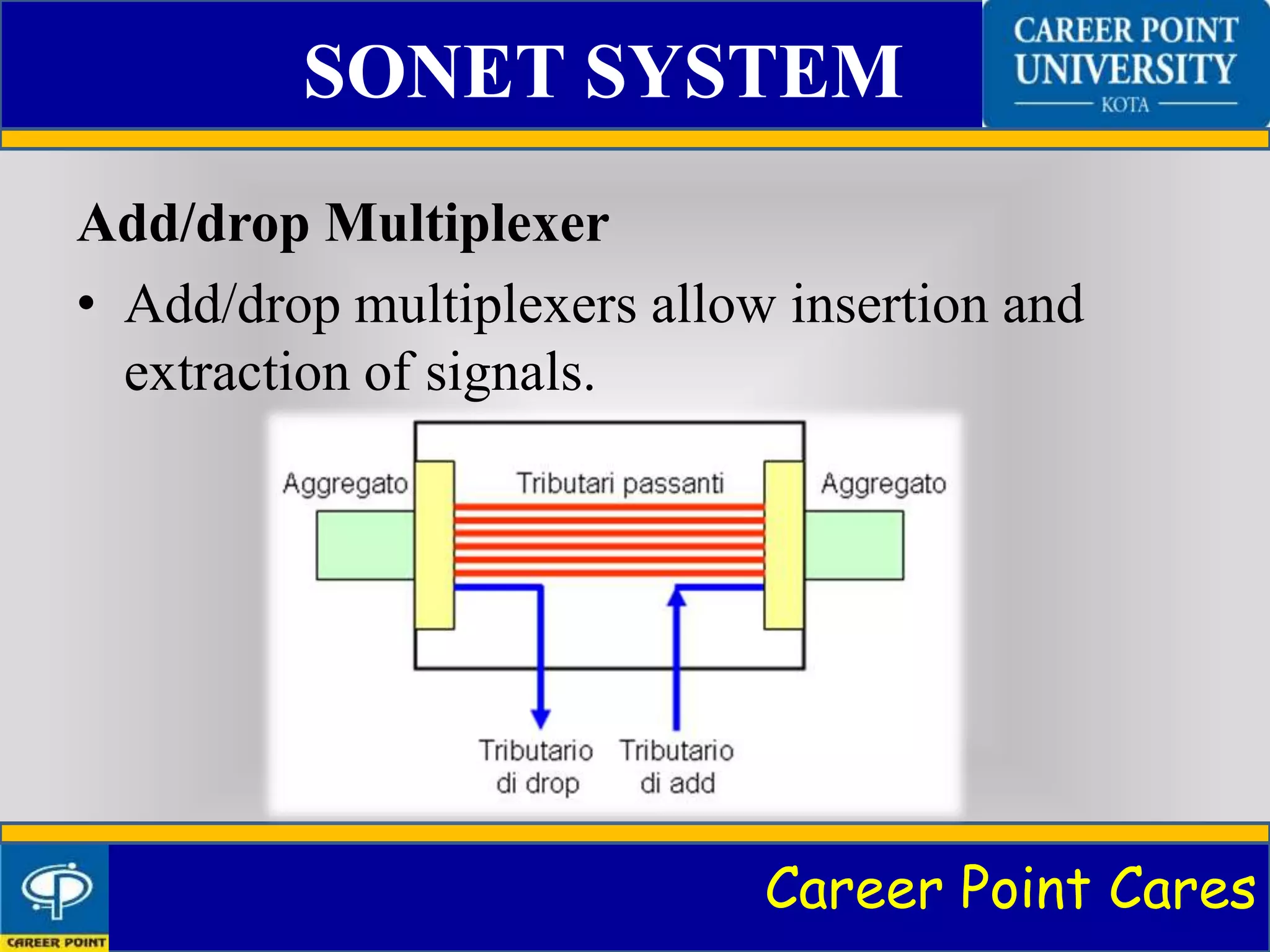
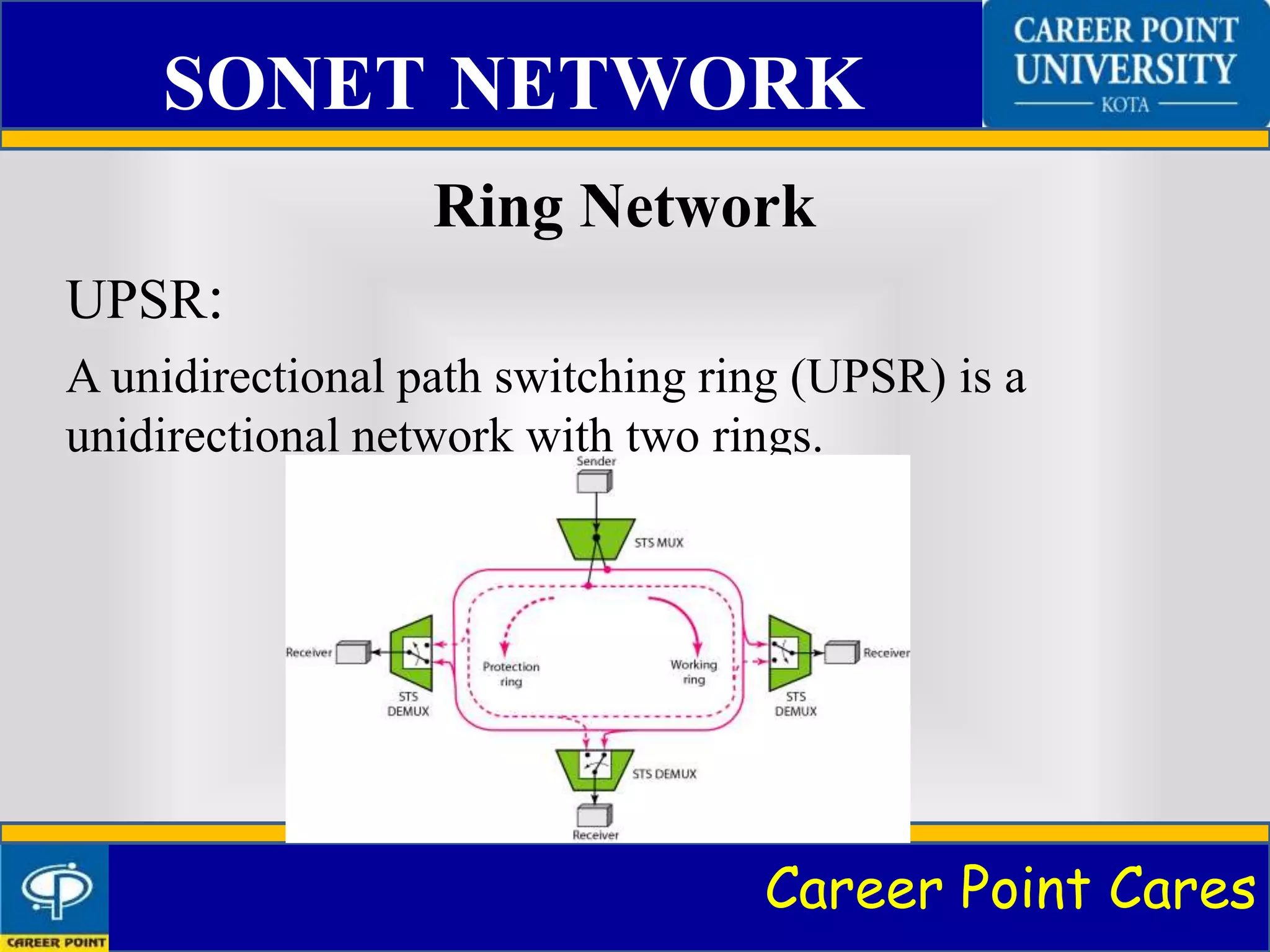
SONET and SDH are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fibre using lasers. SONET is used in North America while SDH is used globally. The document discusses the architecture of SONET systems including signals, devices, and connections. It also covers the SONET frame format, layers, and how SONET networks can be configured in linear, ring, or mesh topologies to provide bandwidth and protection.