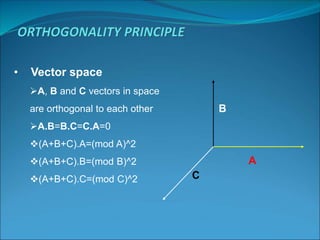
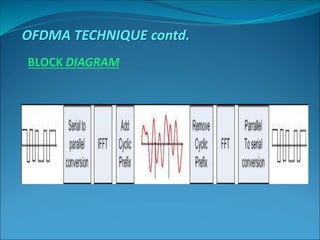
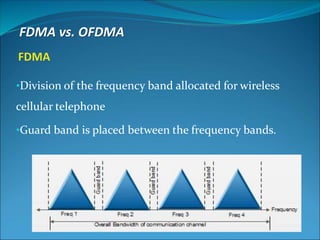
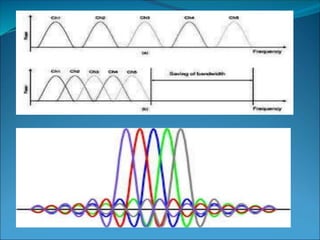
This document discusses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), a multiple access technique used in wireless communication. OFDMA is a specialized version of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) where all subcarriers within a channel are orthogonal to each other, allowing them to overlap without interference. This allows for more efficient spectrum usage than traditional FDMA. OFDMA was introduced in the 1960s-70s and has since been used in technologies like Wi-Fi, WiMAX, LTE, and is being researched for future 5G networks due to its ability to support high-speed data transmission.