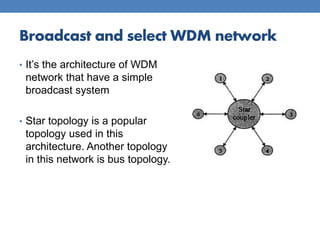
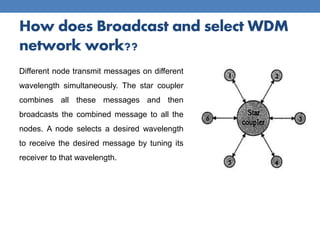
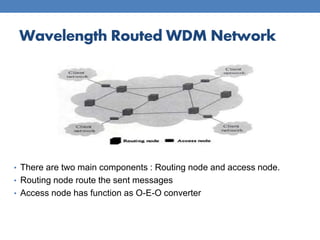
This document provides an overview of basic WDM optical networks. It describes WDM as a multiplexing technique that allows multiple wavelengths to be transmitted over the same fiber. There are two main architectures: broadcast and select, which uses a simple star topology, and wavelength routed, which establishes light paths between nodes using the same wavelength. The document outlines the key components and working principles of each architecture, including their advantages and disadvantages. Wavelength routed networks allow for wavelength reuse but require efficient wavelength assignment to avoid bandwidth loss.