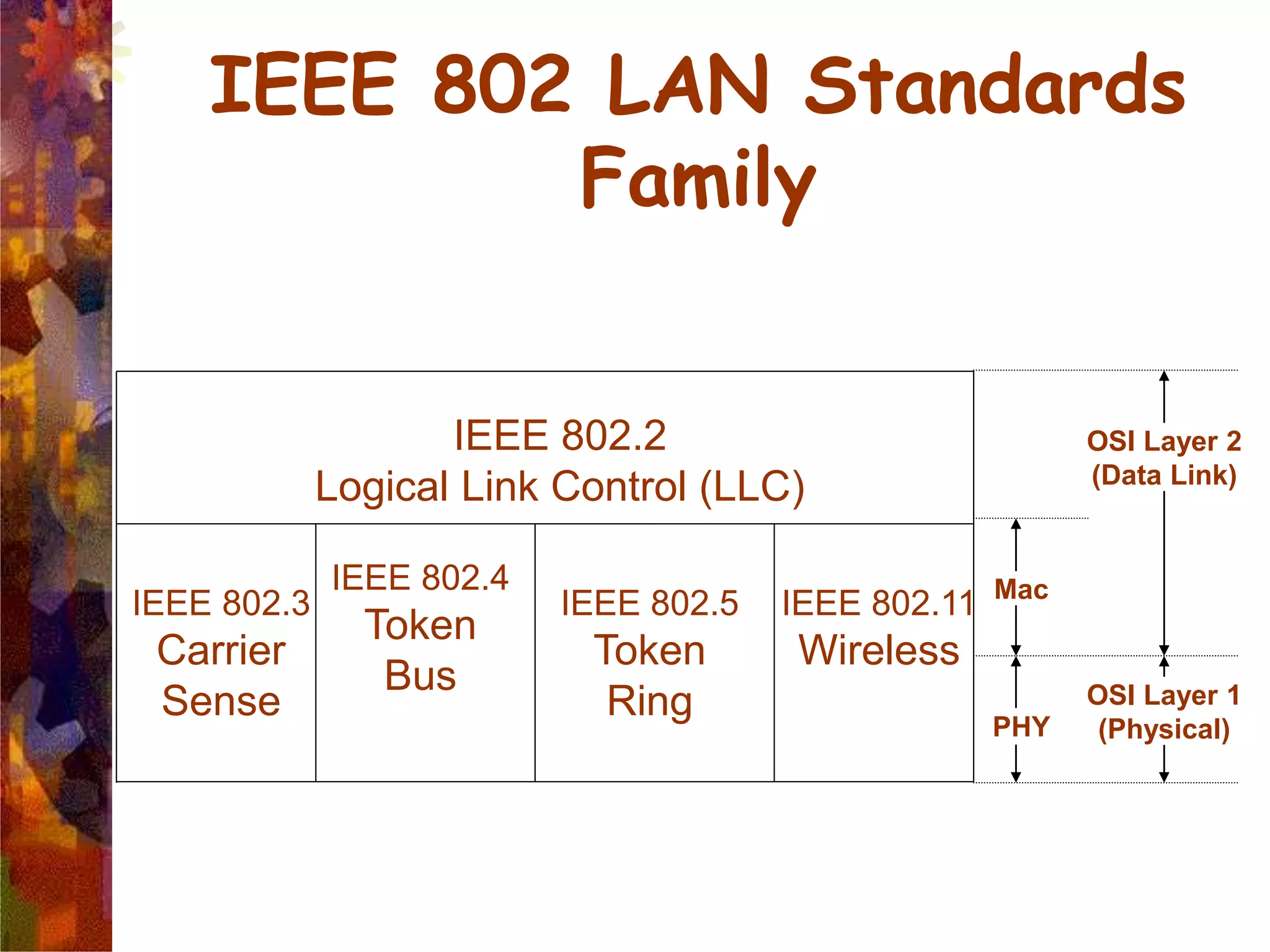
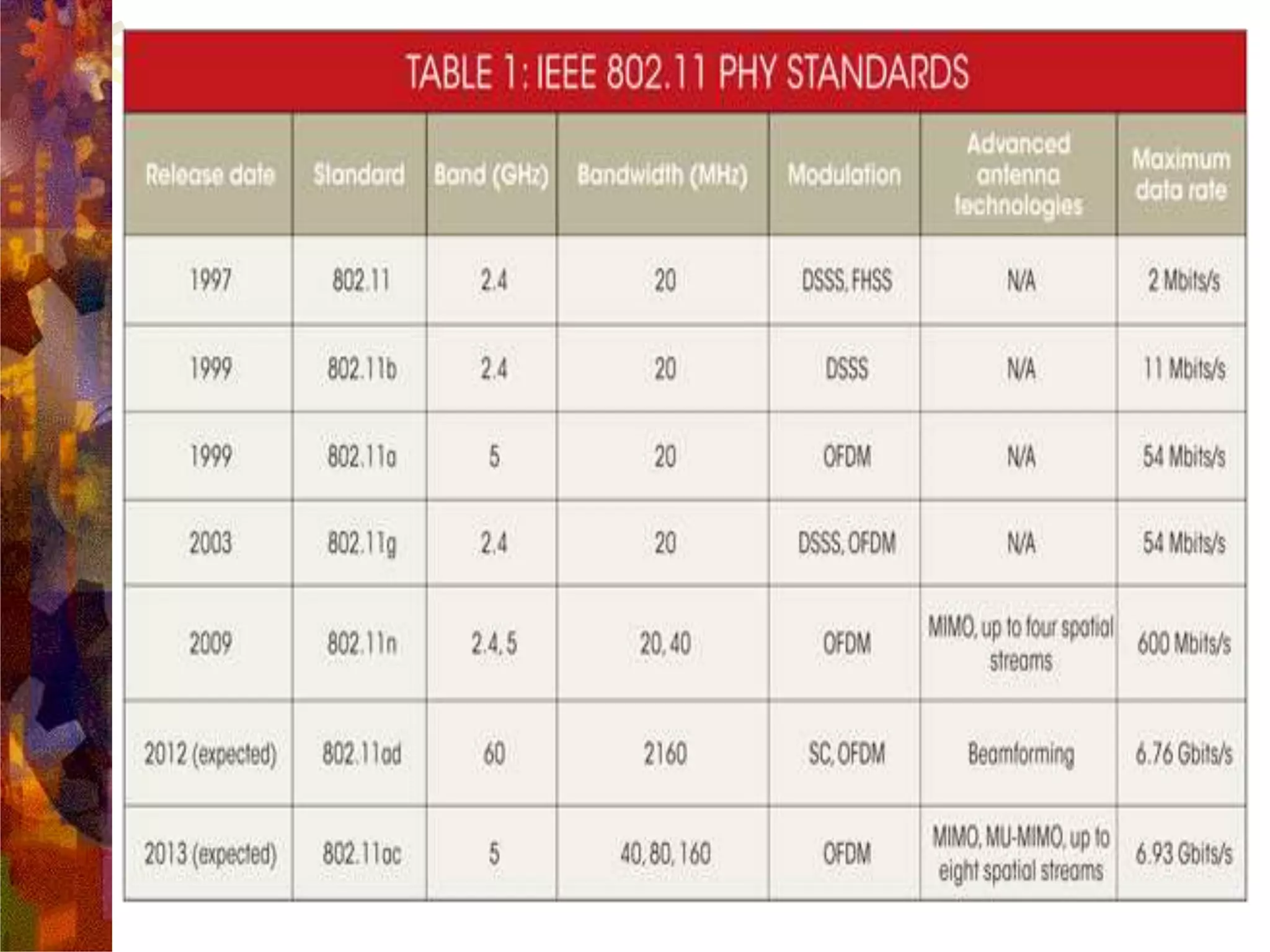
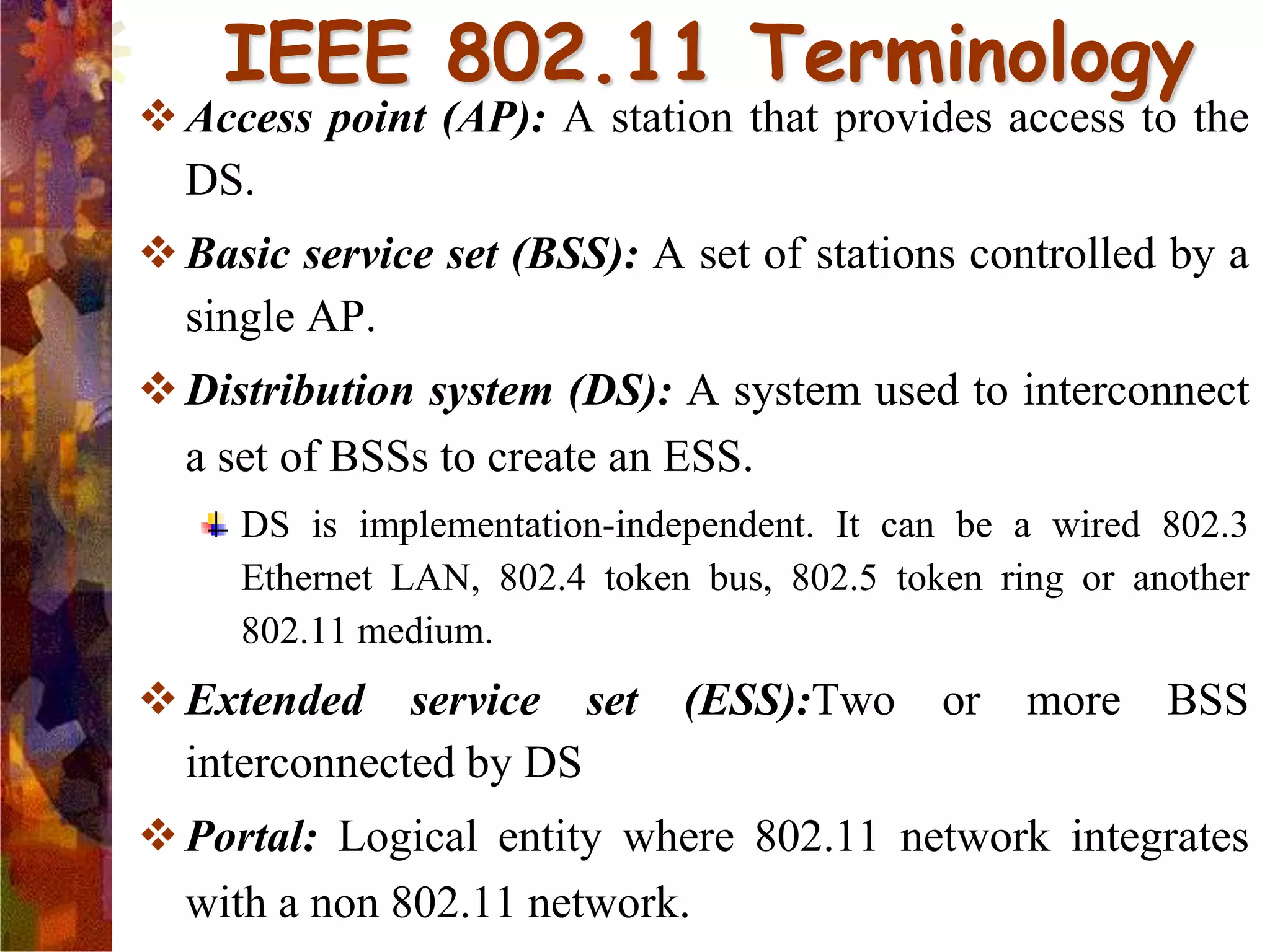
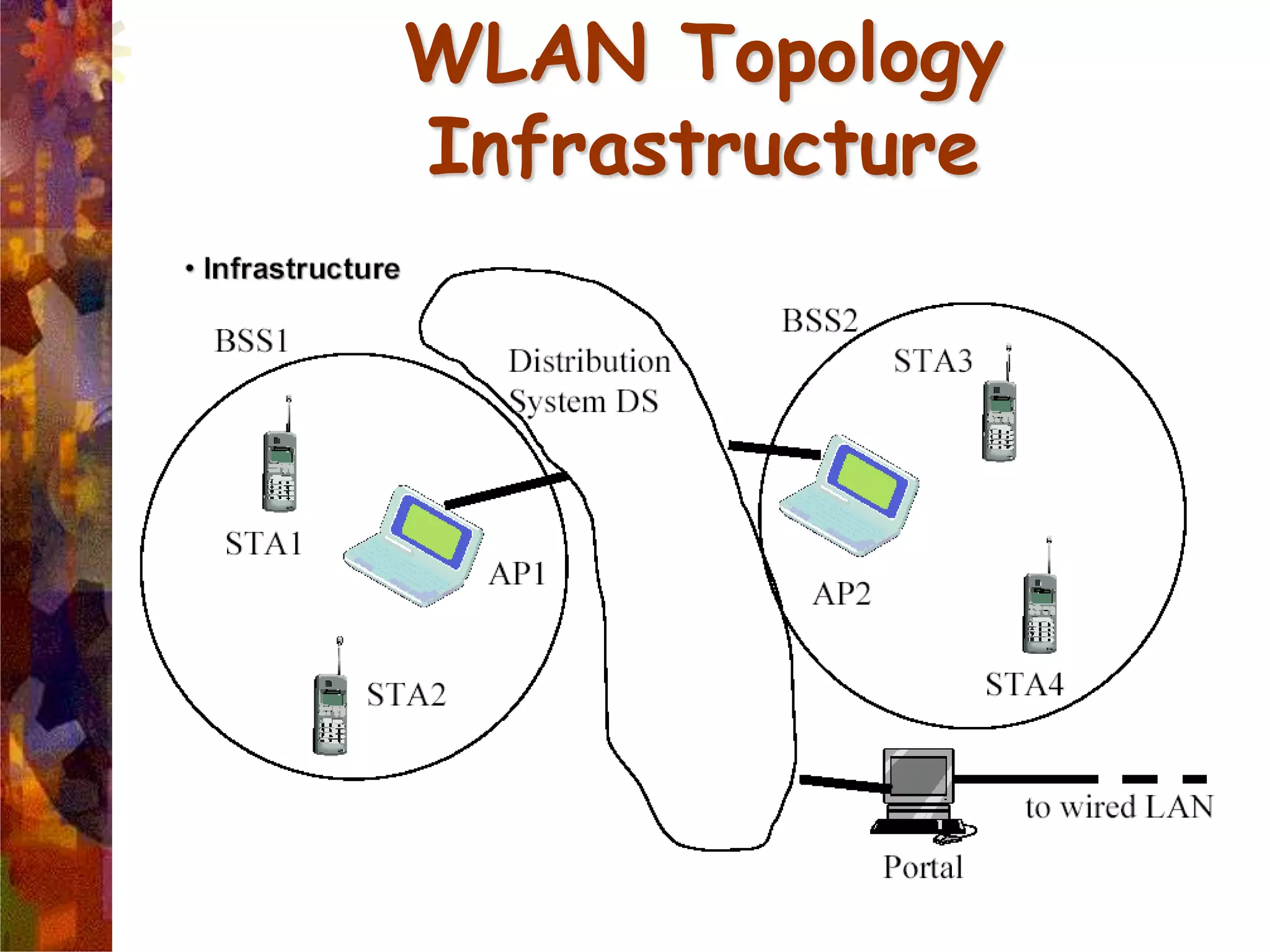
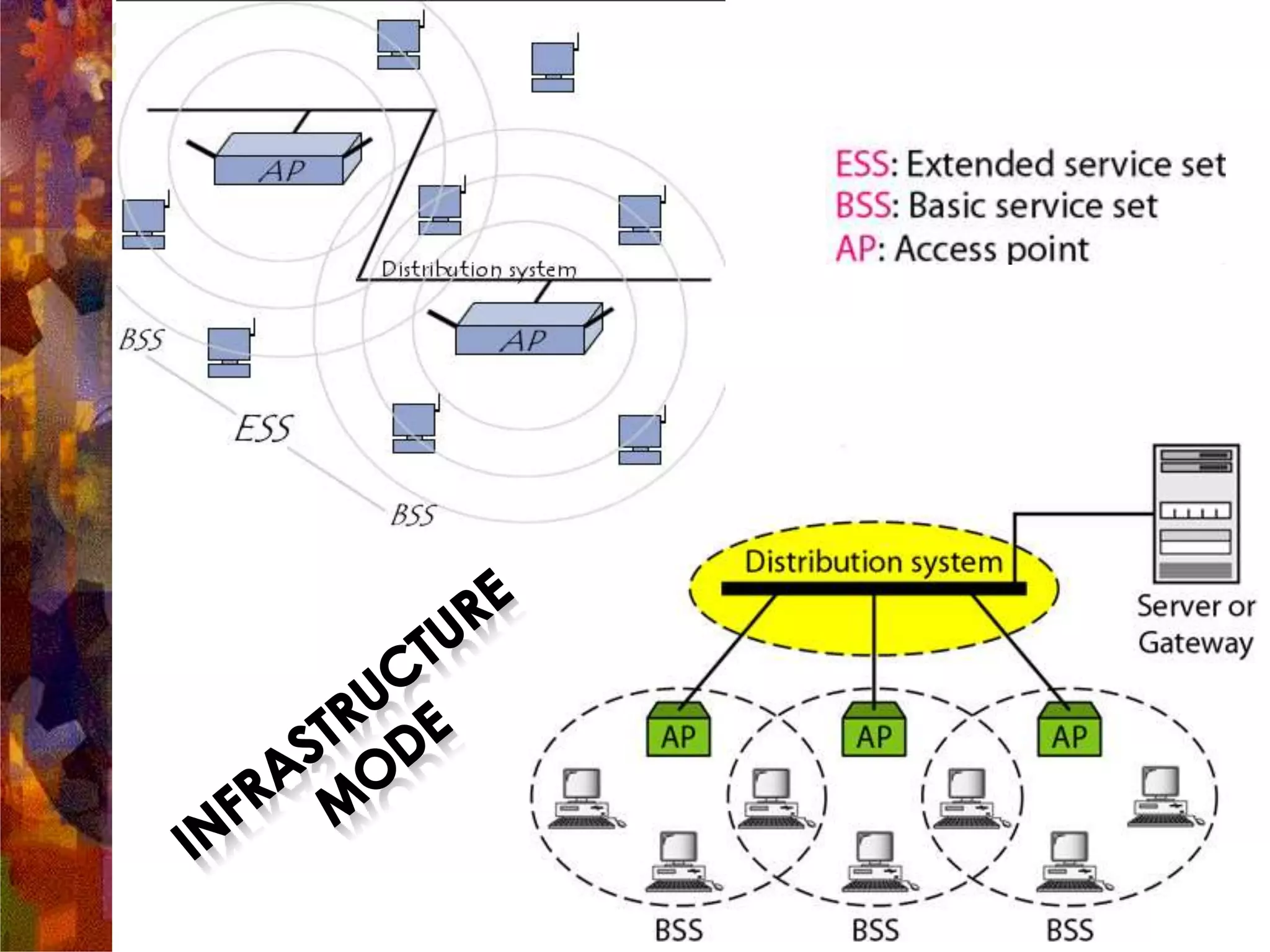
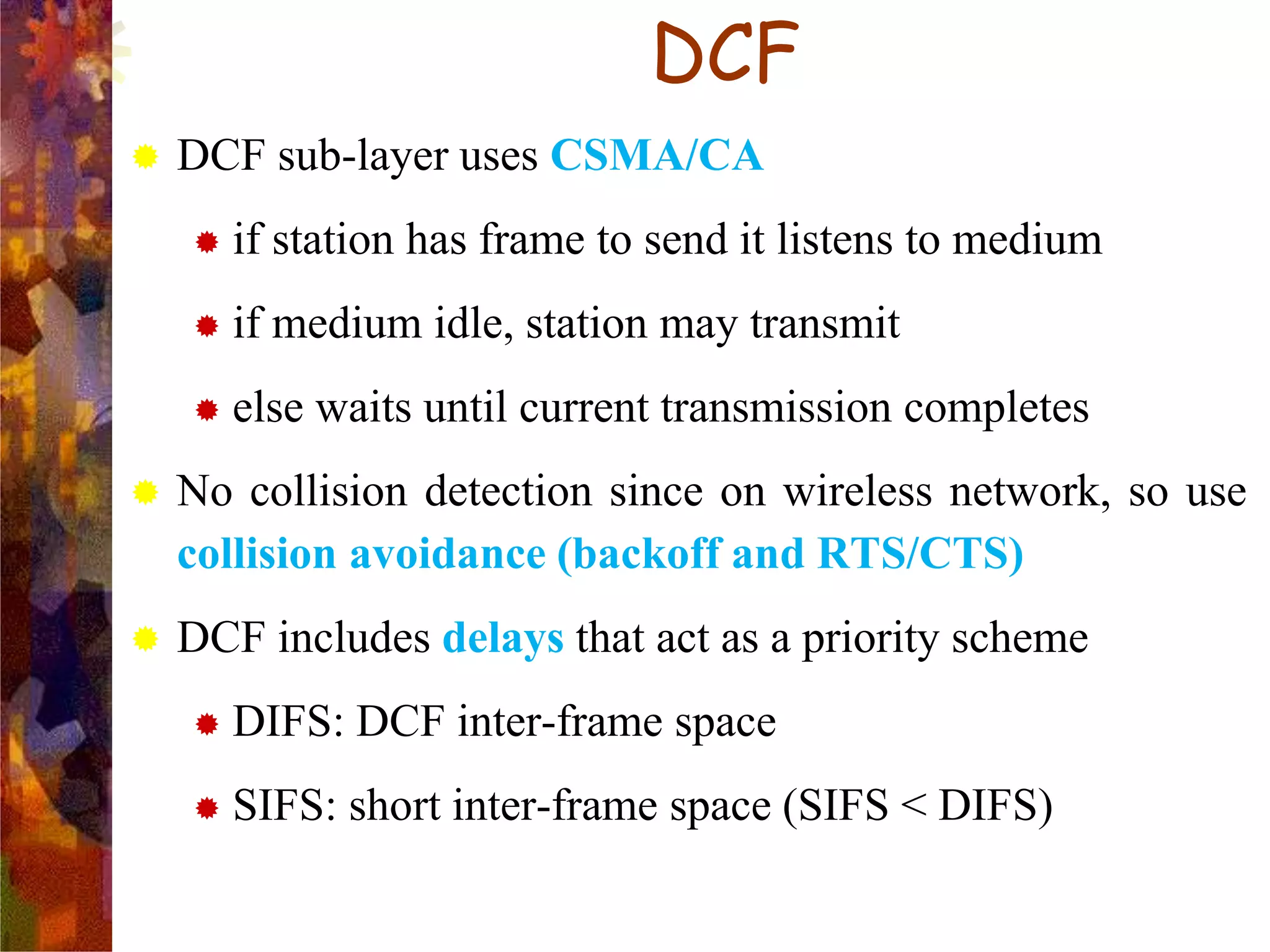
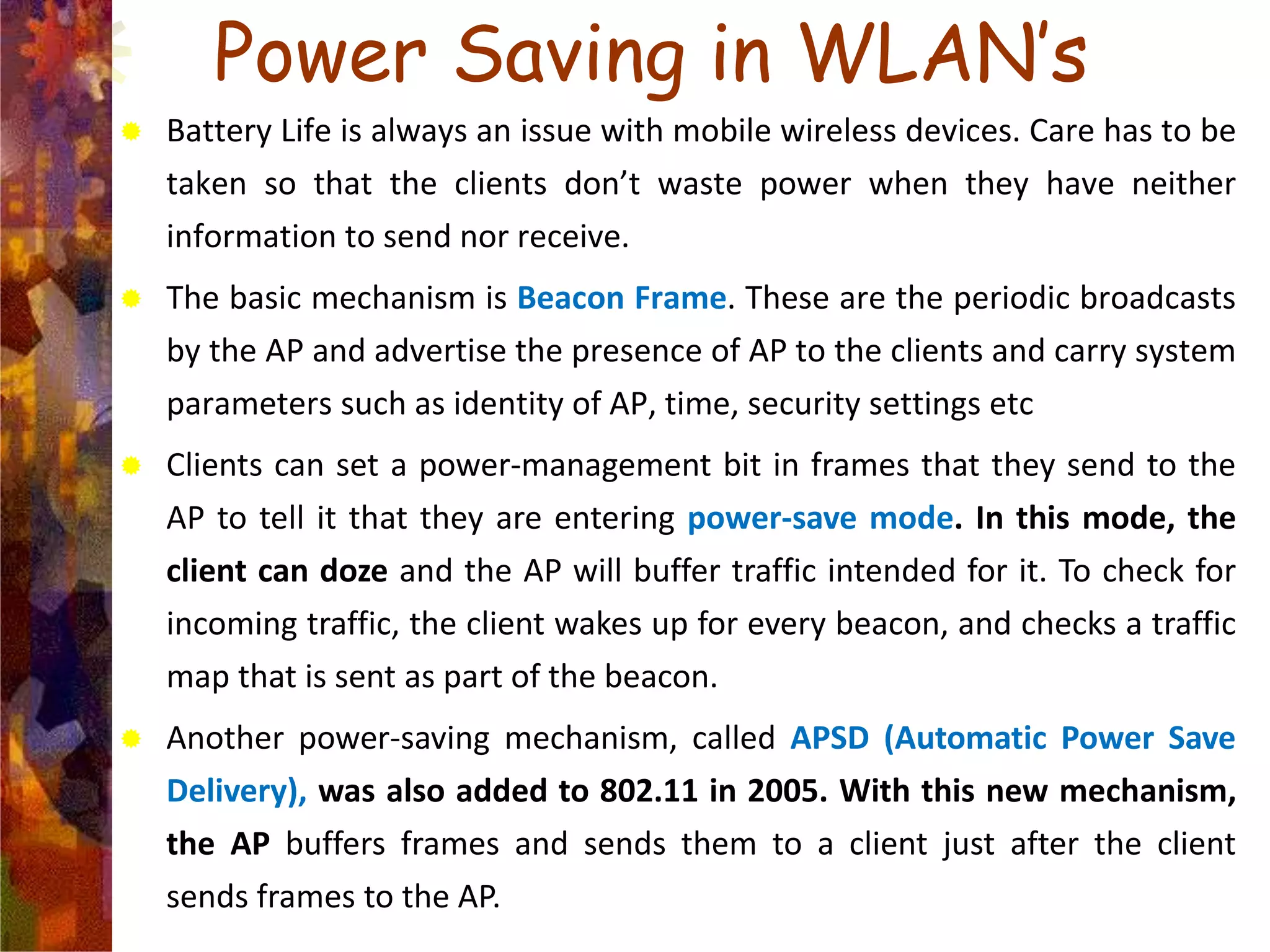
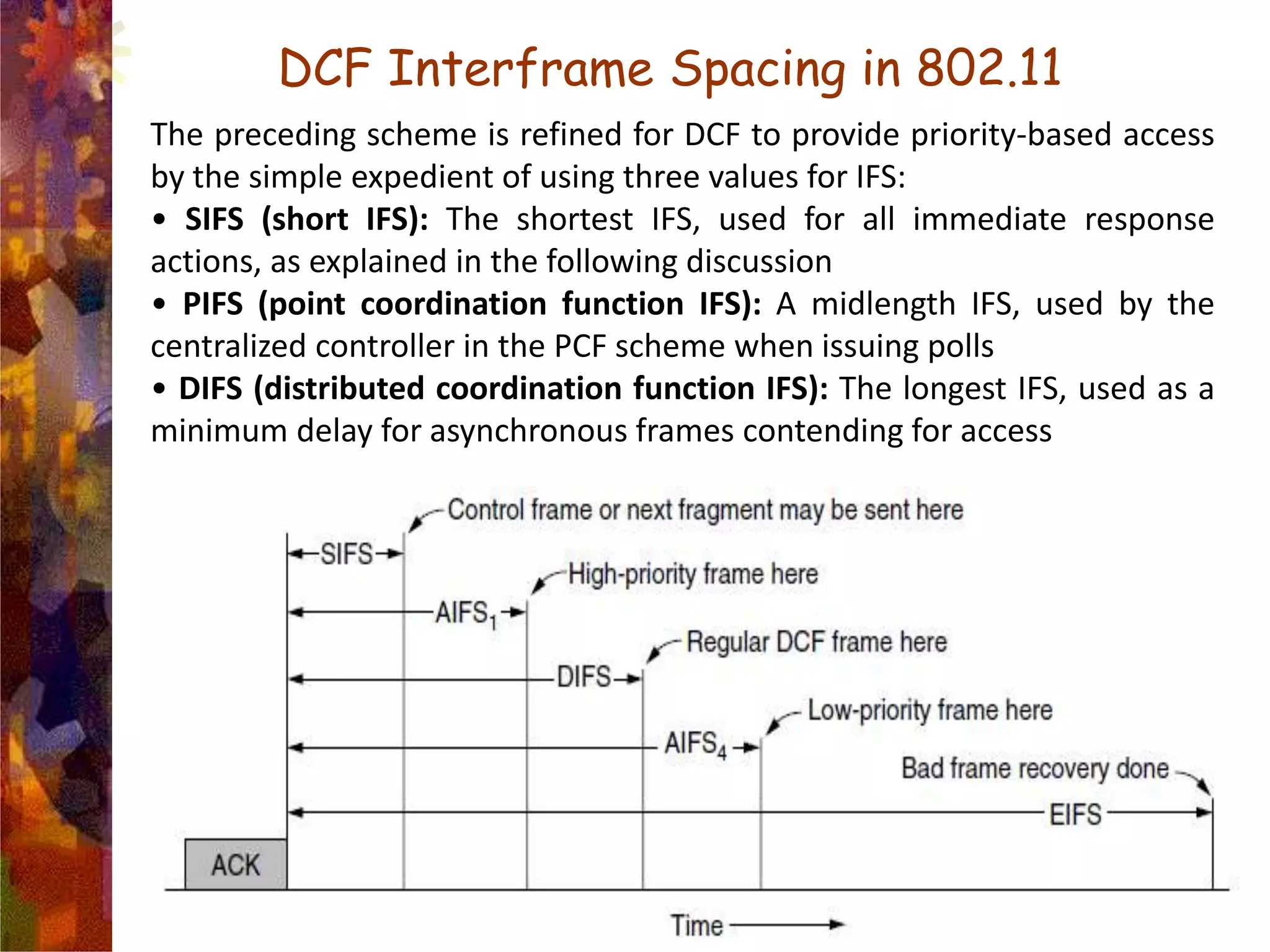
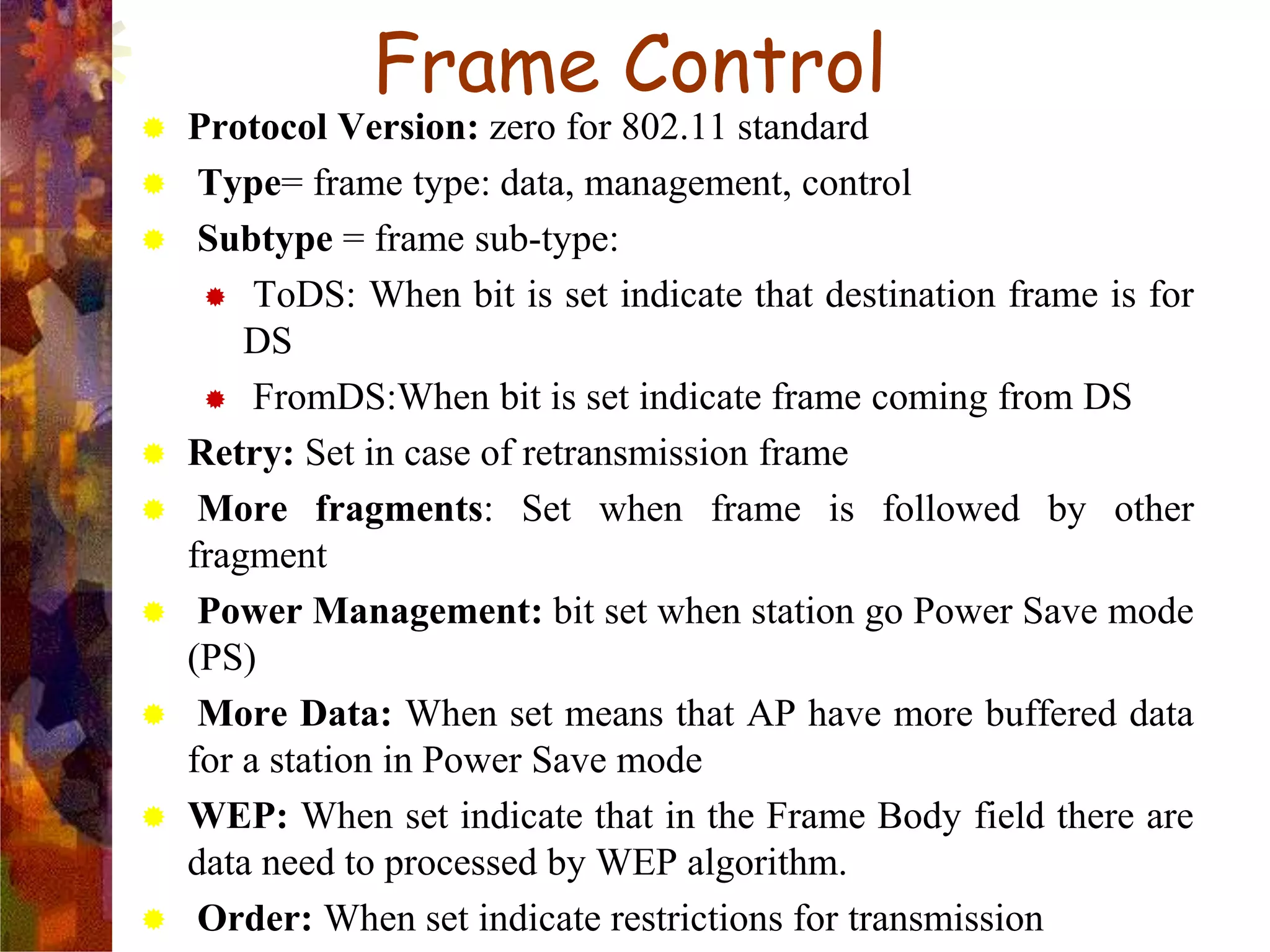
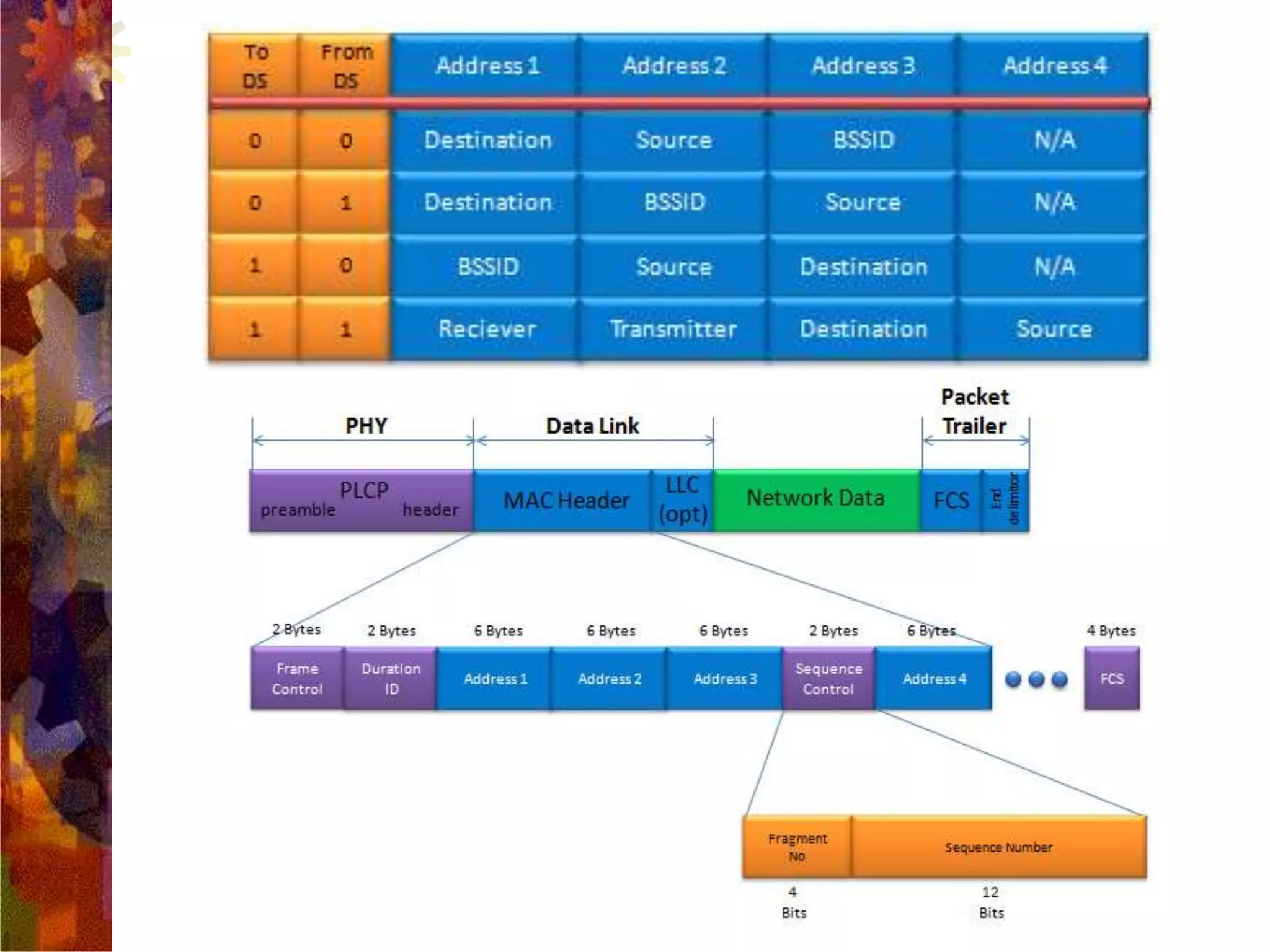
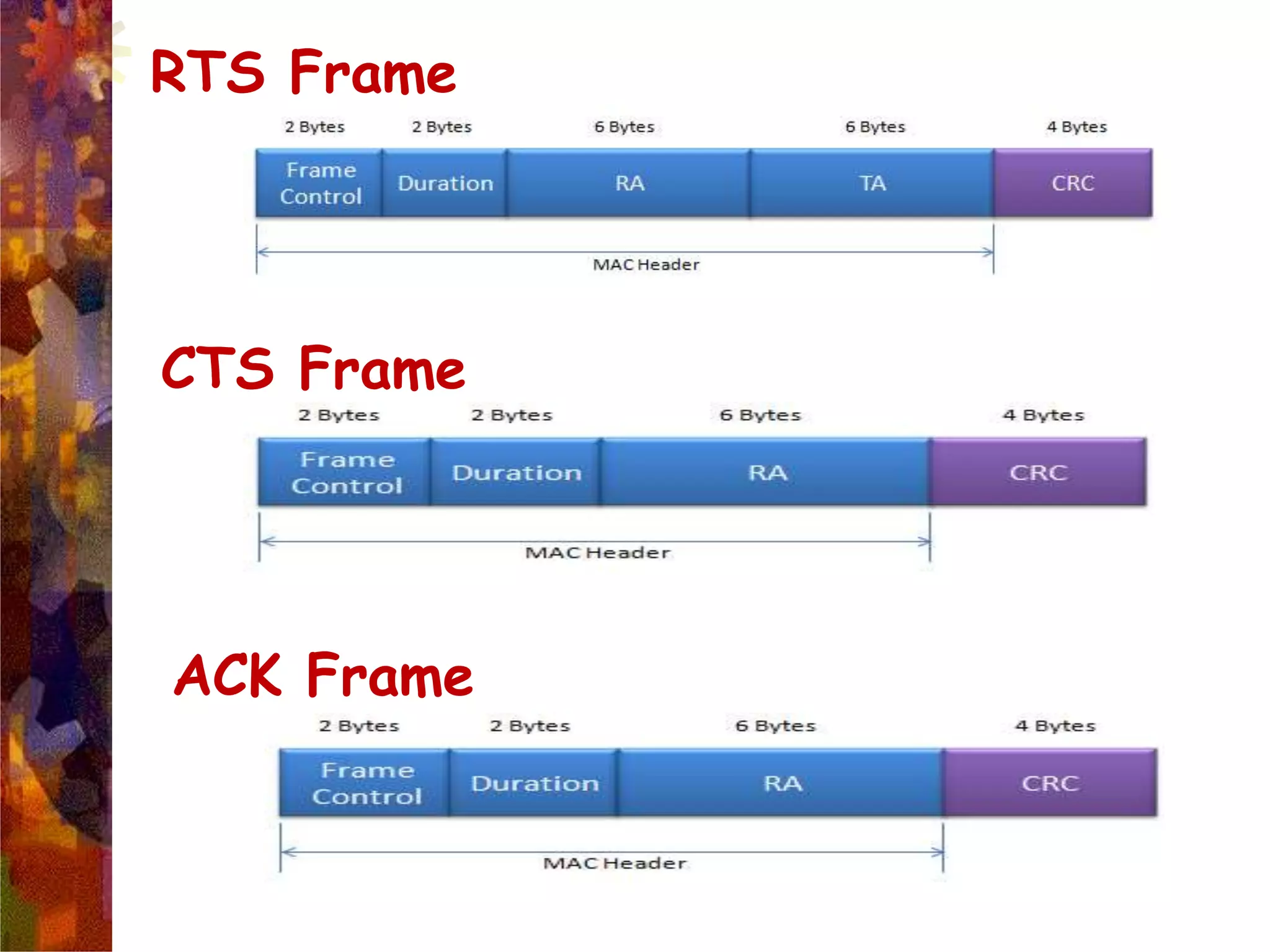
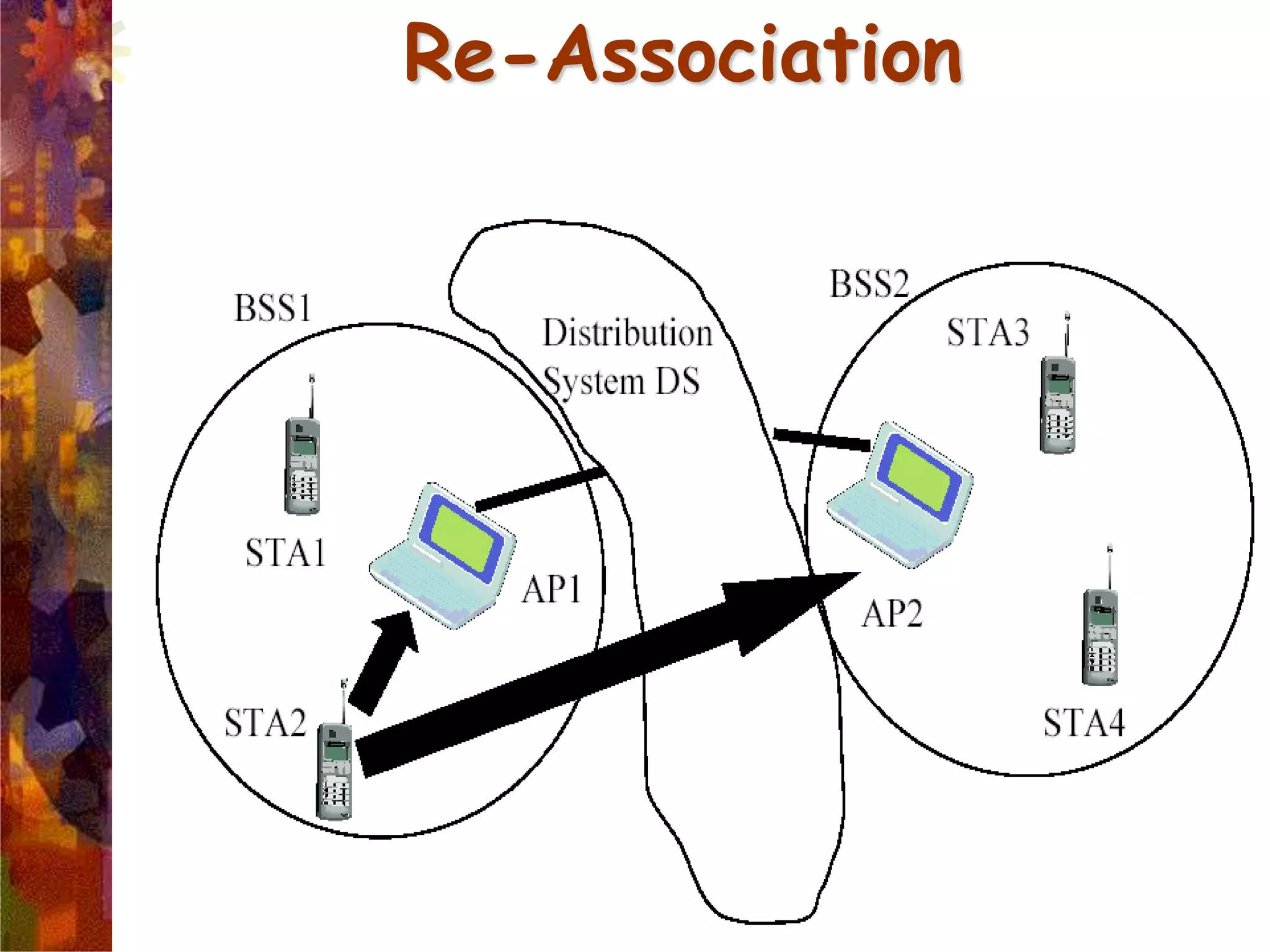
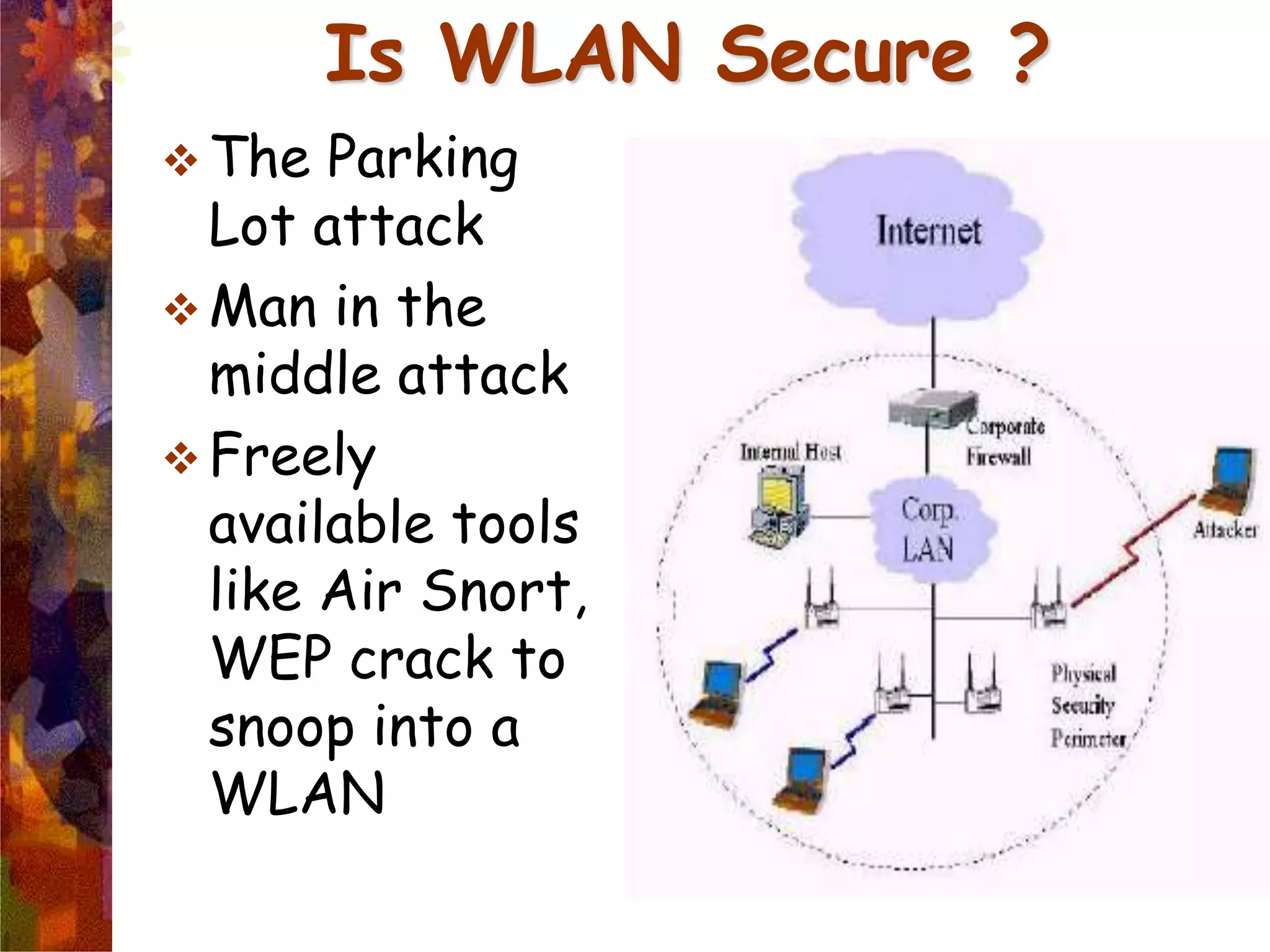
A wireless local area network (WLAN) uses radio frequency technology to transmit and receive data over the air, providing mobility and flexibility as an extension or alternative to wired networks. Key advantages of WLANs include productivity, convenience, lower installation costs and mobility. However, WLANs also have disadvantages such as higher costs for wireless network cards and access points, susceptibility to environmental interference, and lower bandwidth capacity compared to wired networks. Common applications of WLANs include use in corporate, education, medical and temporary settings.