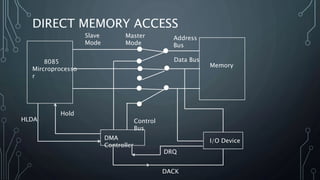
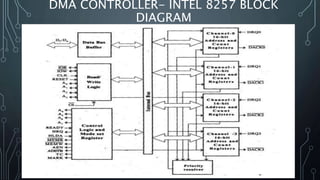
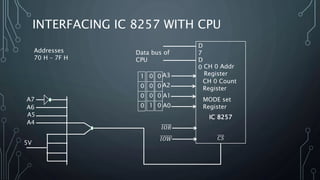
The document discusses Direct Memory Access (DMA) and the Intel 8257 DMA controller chip. DMA allows direct transfer of data between memory and I/O devices without CPU involvement, improving transfer speeds. The 8257 controls 4 DMA channels. Each channel has address/count registers that are initially loaded by the CPU and incremented during transfer. The 8257 operates in both master and slave modes to perform DMA operations independently of the CPU.