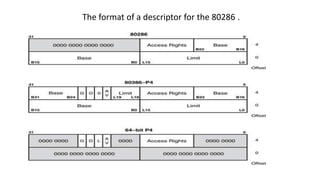
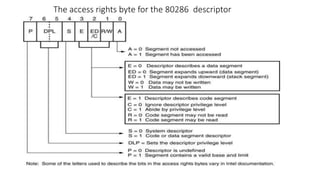
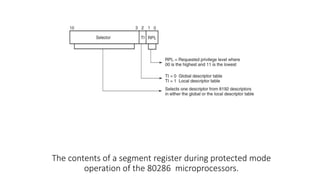
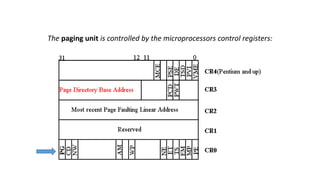
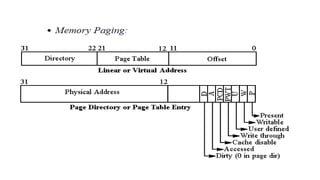
Protected mode memory addressing allows access to memory above 1MB and uses segment descriptors to manage memory segments. The segment register contains a selector that indexes into a descriptor table, which describes a segment's location, length, and access permissions. Descriptors can define segments up to 4GB in size. Paging divides physical memory and disk storage into pages that are mapped to virtual addresses, allowing flexible and protected memory management.