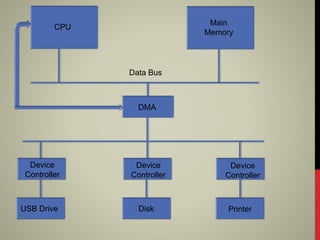
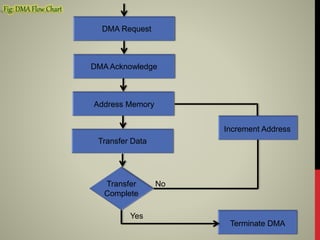
The document discusses the Intel 8257 DMA controller. It allows hardware subsystems to access main memory independently of the CPU, improving data transfer speeds. The 8257 has 4 channels that can service requests from I/O devices simultaneously. It interfaces between devices and the system bus, controlling direct memory access operations and arbitrating bus access. When an I/O device needs to transfer data, it sends a request to the 8257, which then coordinates the transfer directly between memory and the device without involving the CPU. This allows the CPU to continue processing without waiting for I/O, improving overall system efficiency and performance.