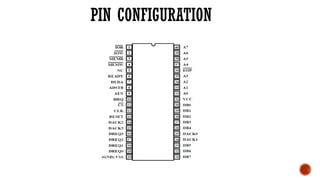
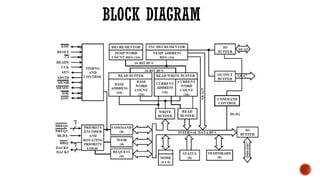
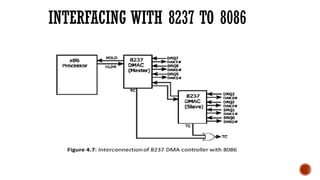
The document discusses the 8237 DMA controller, which facilitates direct memory access (DMA) to transfer data between memory and I/O devices without CPU intervention. It highlights the device's operational features, including four independent channels, modes of operation, and detailed pin configurations. Additionally, it explores its application in enabling data transfers with reduced processor load in computer systems.