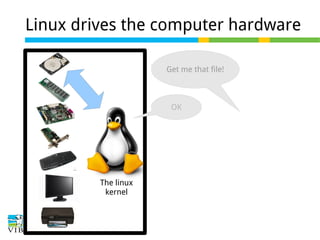
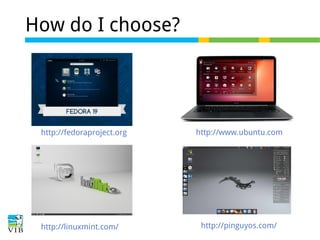
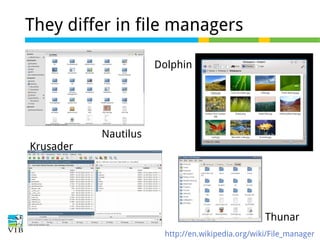
This document serves as a training introduction to Linux for bioinformatics, covering basic concepts, the Linux kernel, and the GNU operating system's role. It discusses the merits of using Linux, such as its open-source nature, stability, and a variety of distributions available for different hardware and user needs. Additionally, it provides guidance on selecting a suitable Linux distribution and offers practical exercises for hands-on experience.