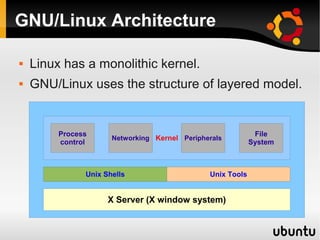
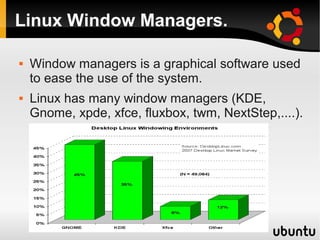
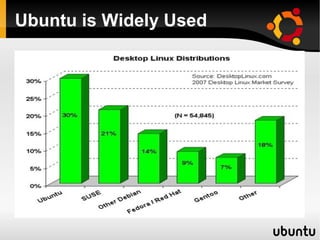
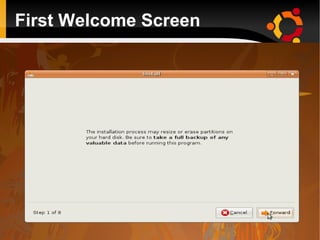
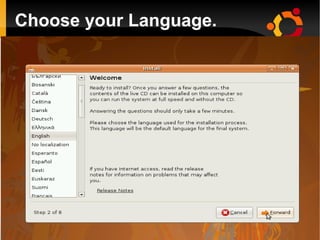
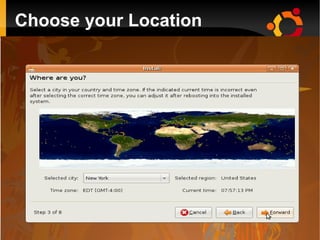
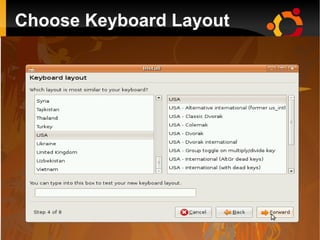
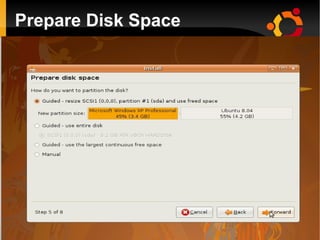
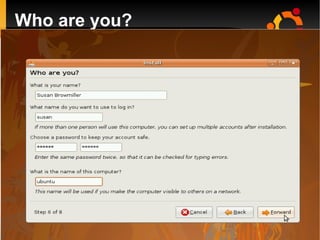
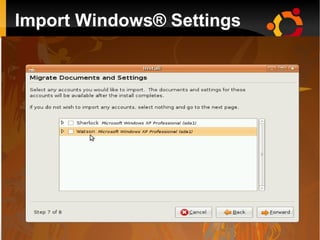
This document provides an introduction to Linux and open source operating systems. It discusses what Linux is, how it was developed as an alternative to Unix, and some popular Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Fedora, and their desktop environments. It also covers installing and using Linux, installing software, programming on Linux, and using the Linux shell.