This document provides an overview of the Linux file system including:
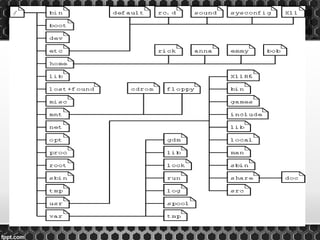
1. It defines the main directories and contents according to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) with the root directory being "/" and possible multiple partitions and filesystems.
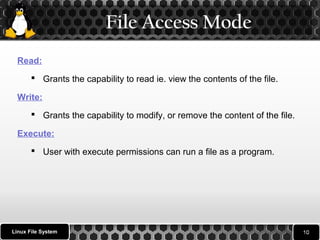
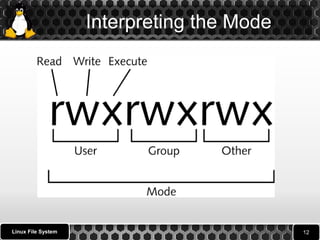
2. It describes the different types of files like ordinary files, directories, and special files as well as file permissions for reading, writing, and executing files and directories.
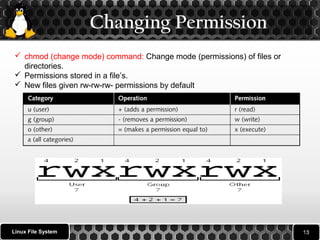
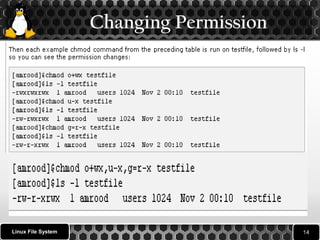
3. It explains how to change file permissions using the chmod command and navigate the file system using commands like pwd, cd, and ls including examples of using options, wildcards and navigation.










![Using the pwd Command
pwd stands for Print Working Directory.
pwd is a Linux / Unix command which prints the current working
directory.
pwd prints the full pathname of the current working directory.
Syntax
Linux File System
pwd [OPTION]...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxpptpresentationfinal-140918091636-phpapp01/85/Linux-file-system-nevigation-17-320.jpg)


![Using the cd Command
The Linux cd command stands for change directory.
It is the primary command for moving between directories on a
Unix/Linux filesystem.
Syntex:
Linux File System
cd [directory]
Here directory is the name of the directory where you wish to go.
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxpptpresentationfinal-140918091636-phpapp01/85/Linux-file-system-nevigation-20-320.jpg)



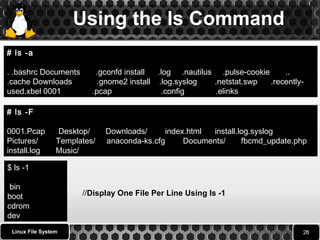
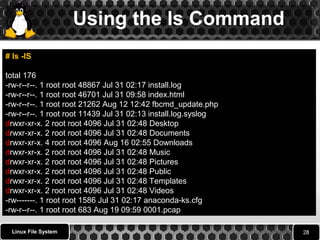
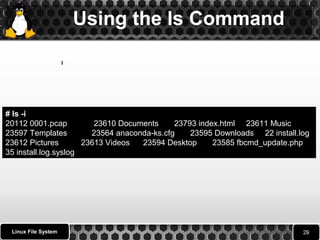
![Using the ls Command
ls is a Linux shell command that lists directory contents and
Files.
ls syntax
$ ls [options] [file|dir]
# ls
0001.Pcap Desktop Downloads index.html install.log.syslog Pictures
Templates anaconda-ks.cfg Documents fbcmd_update.php install.log
Music Public Videos
Linux File System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxpptpresentationfinal-140918091636-phpapp01/85/Linux-file-system-nevigation-24-320.jpg)