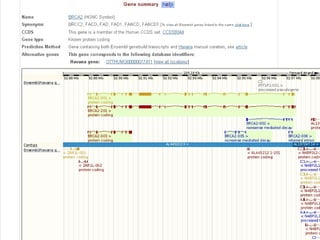
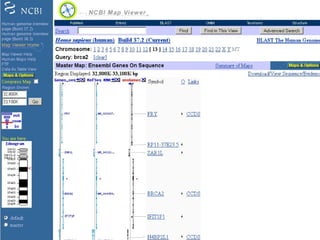
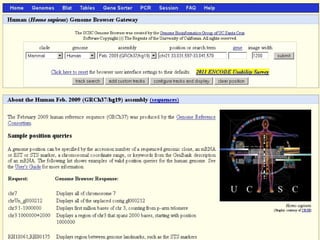
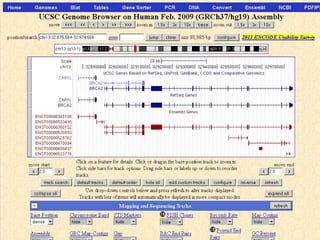
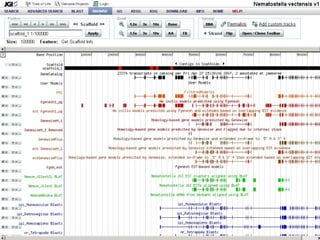
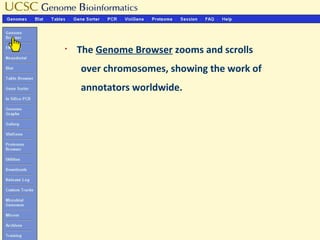
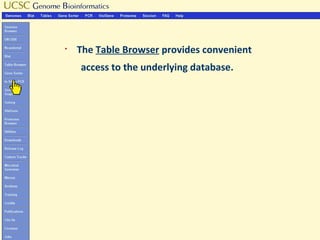
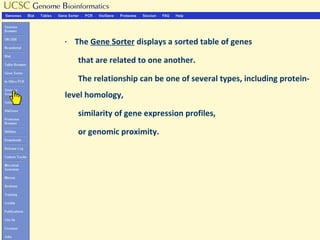
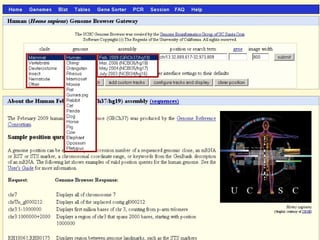
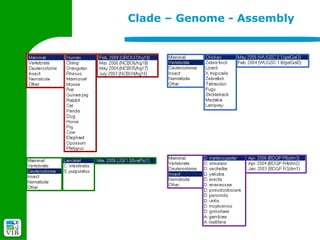
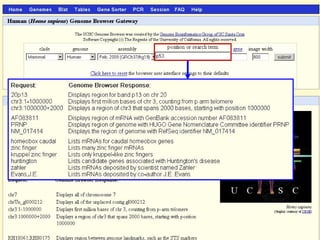
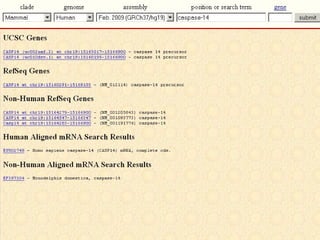
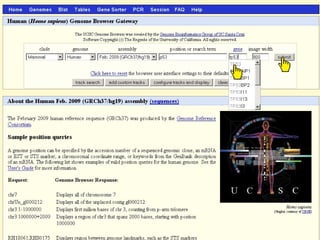
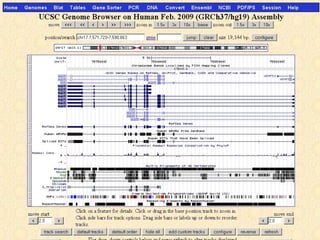
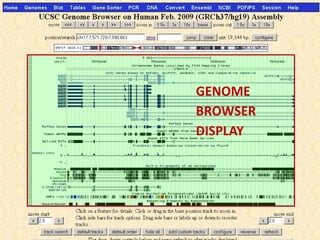
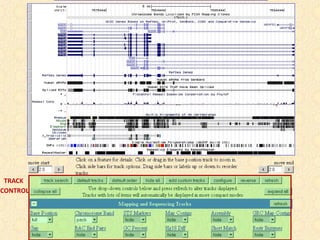
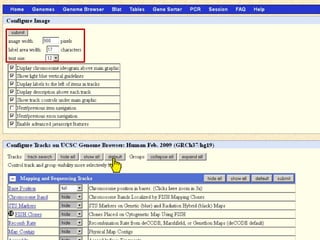
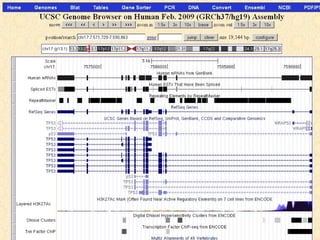
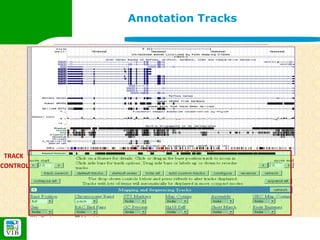
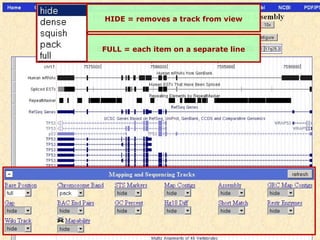
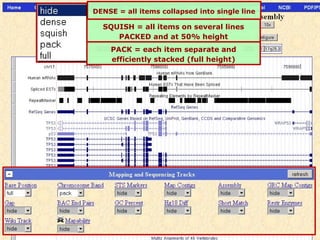
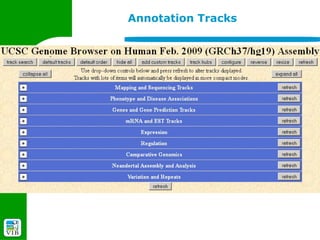
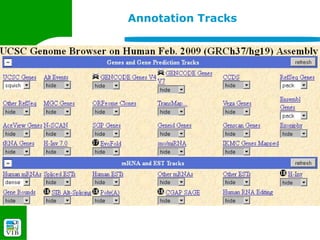
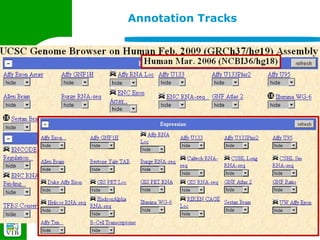
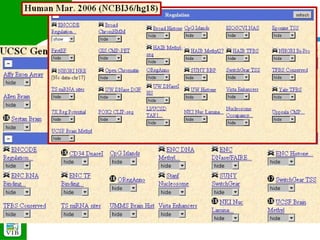
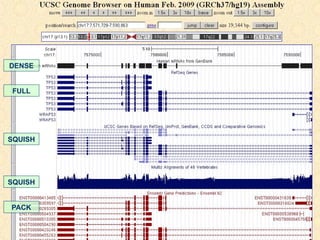
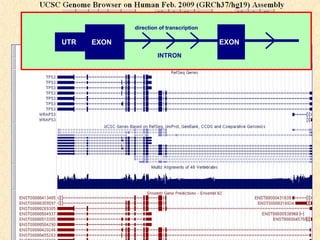
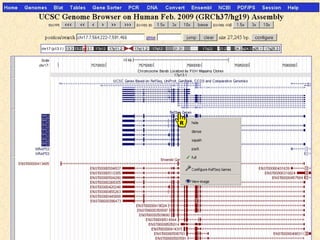
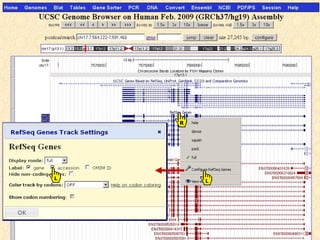
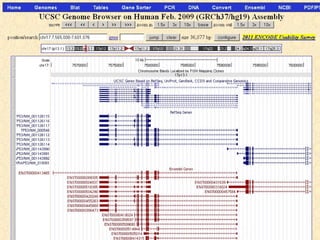
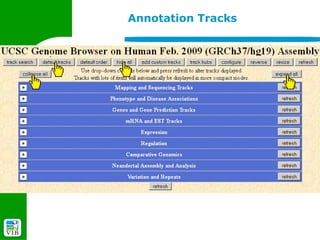
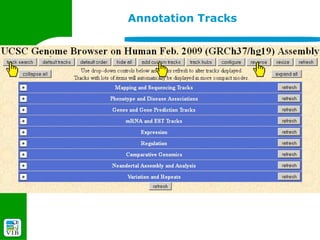
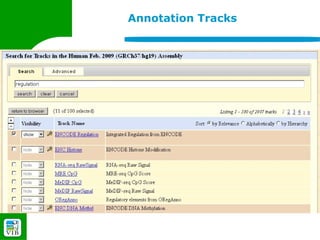
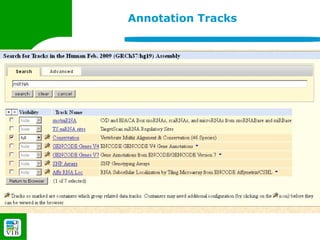
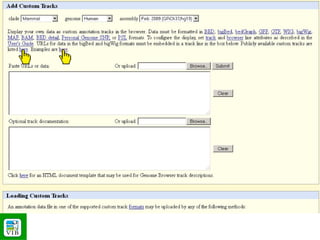
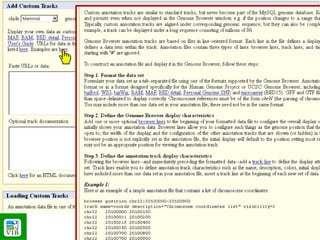
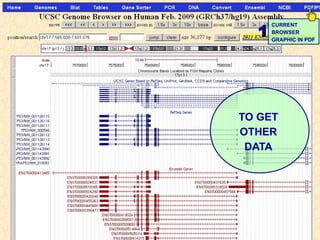
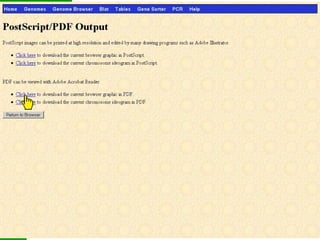
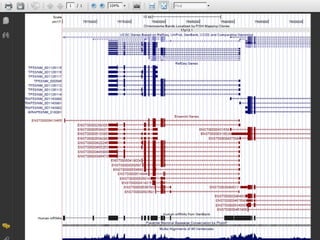
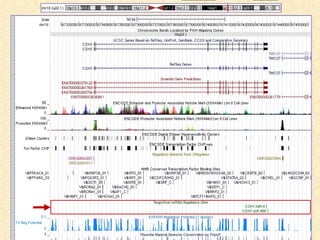
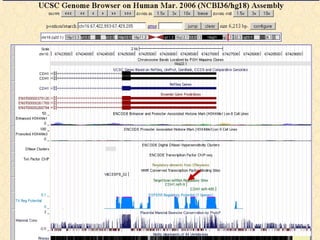
The document provides an overview of the UCSC Genome Browser, detailing its features for browsing genes, searching genomic information, and viewing genome organization. It highlights collaborations with other genome browsers such as Ensembl and NCBI, and introduces tools available for genomic analysis, including BLAT, in-silico PCR, and various visualization options. Additionally, it outlines navigation methods and exercises for users to explore specific genes and their associated data.