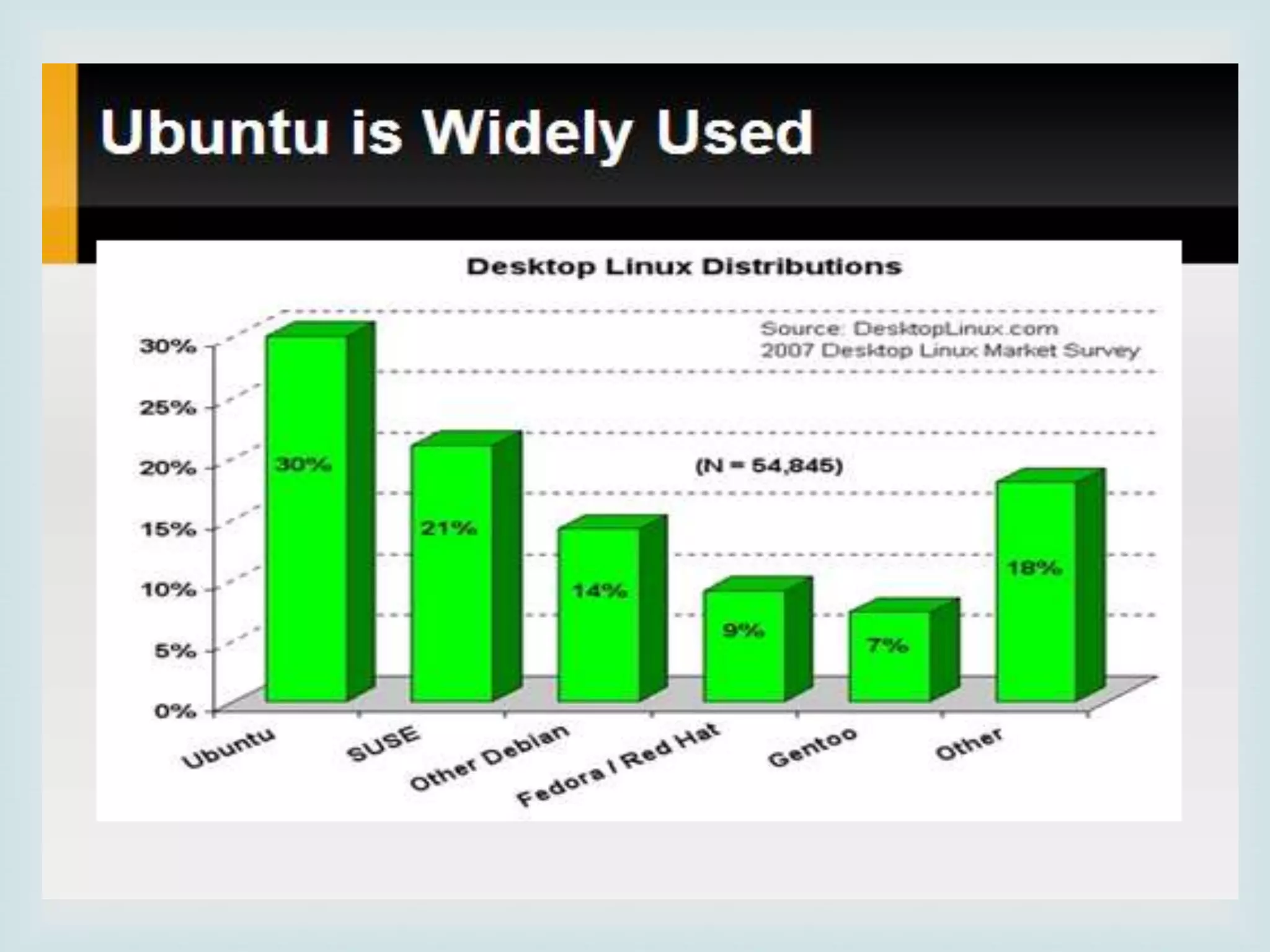
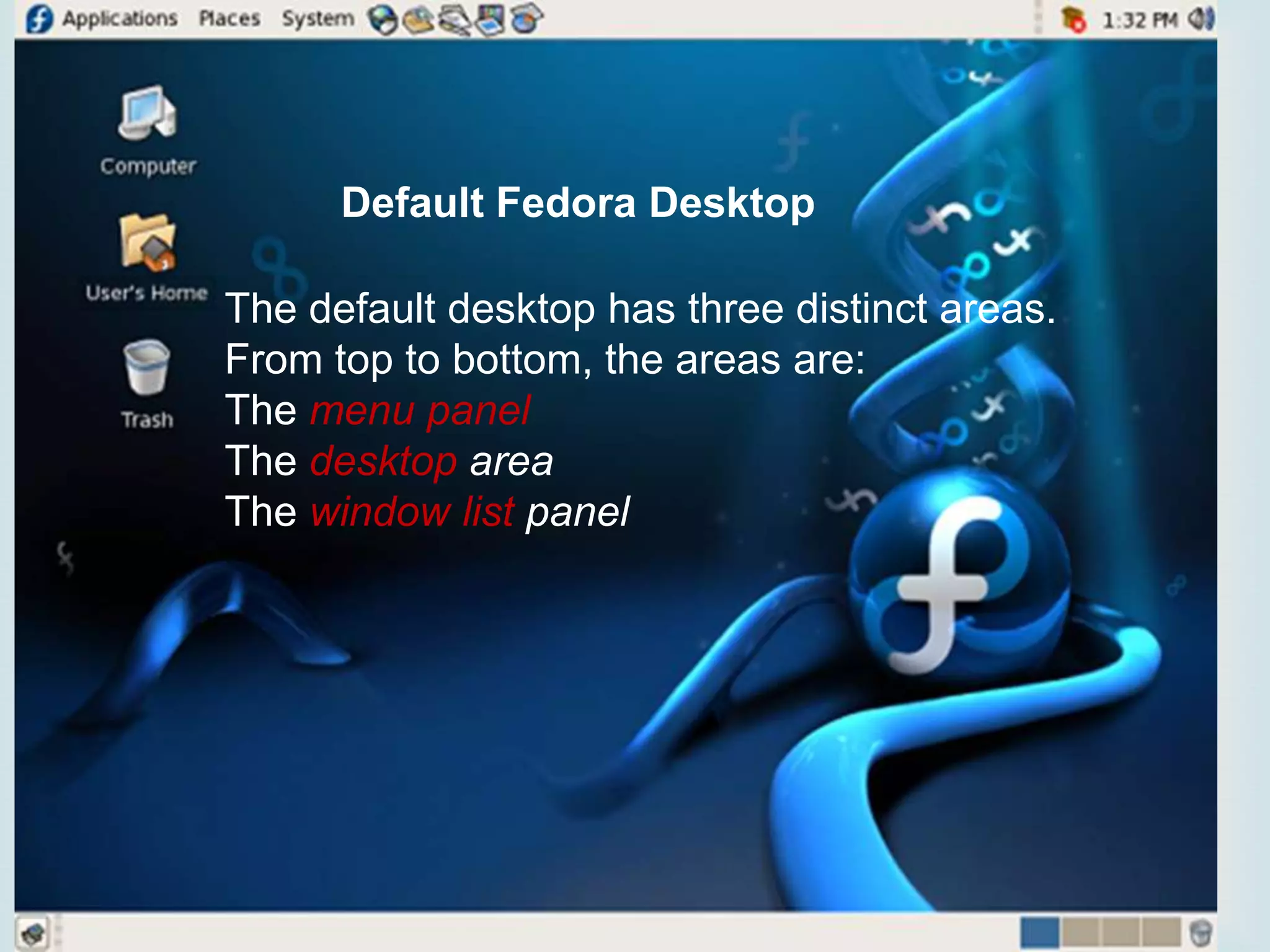
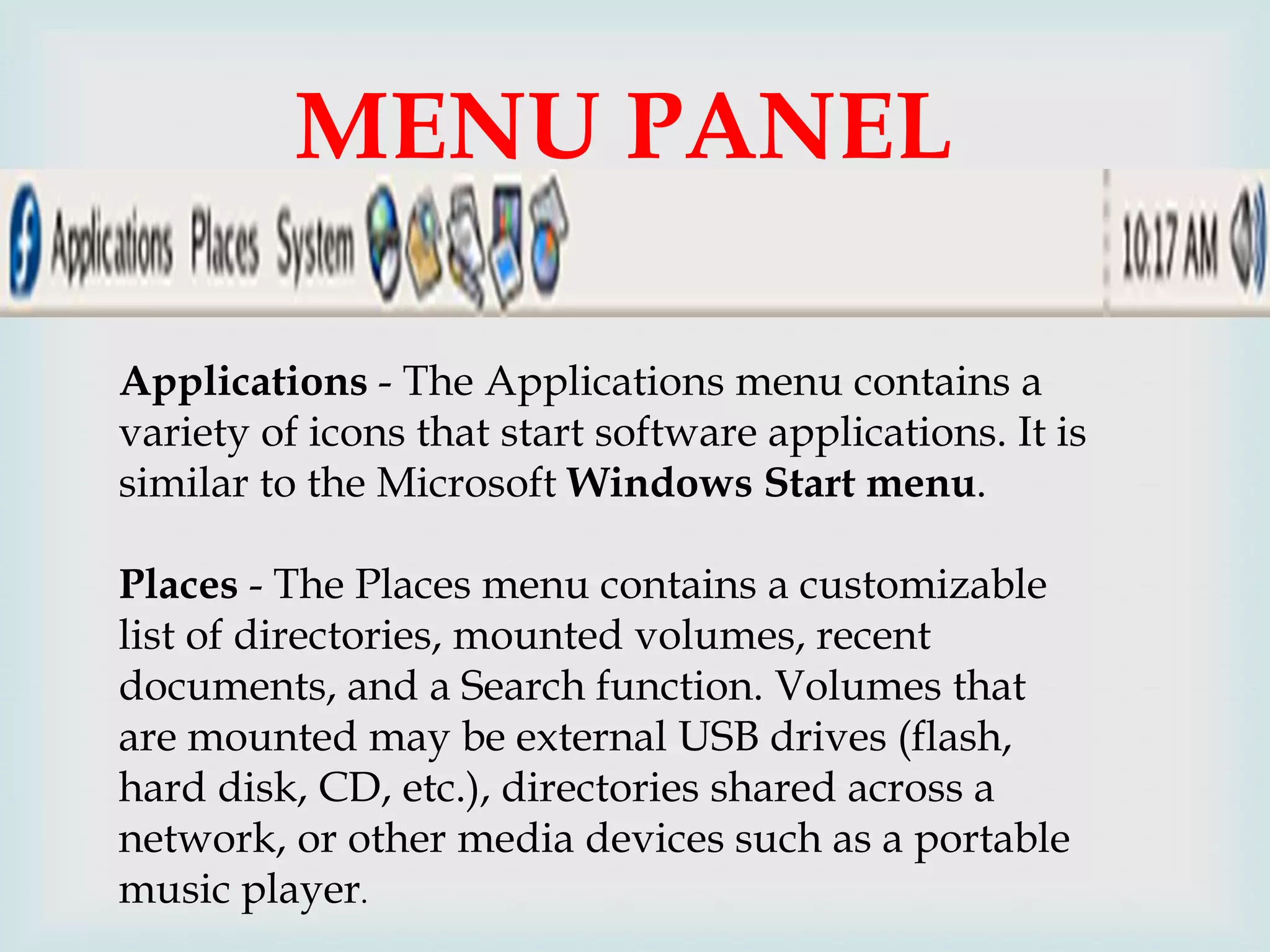
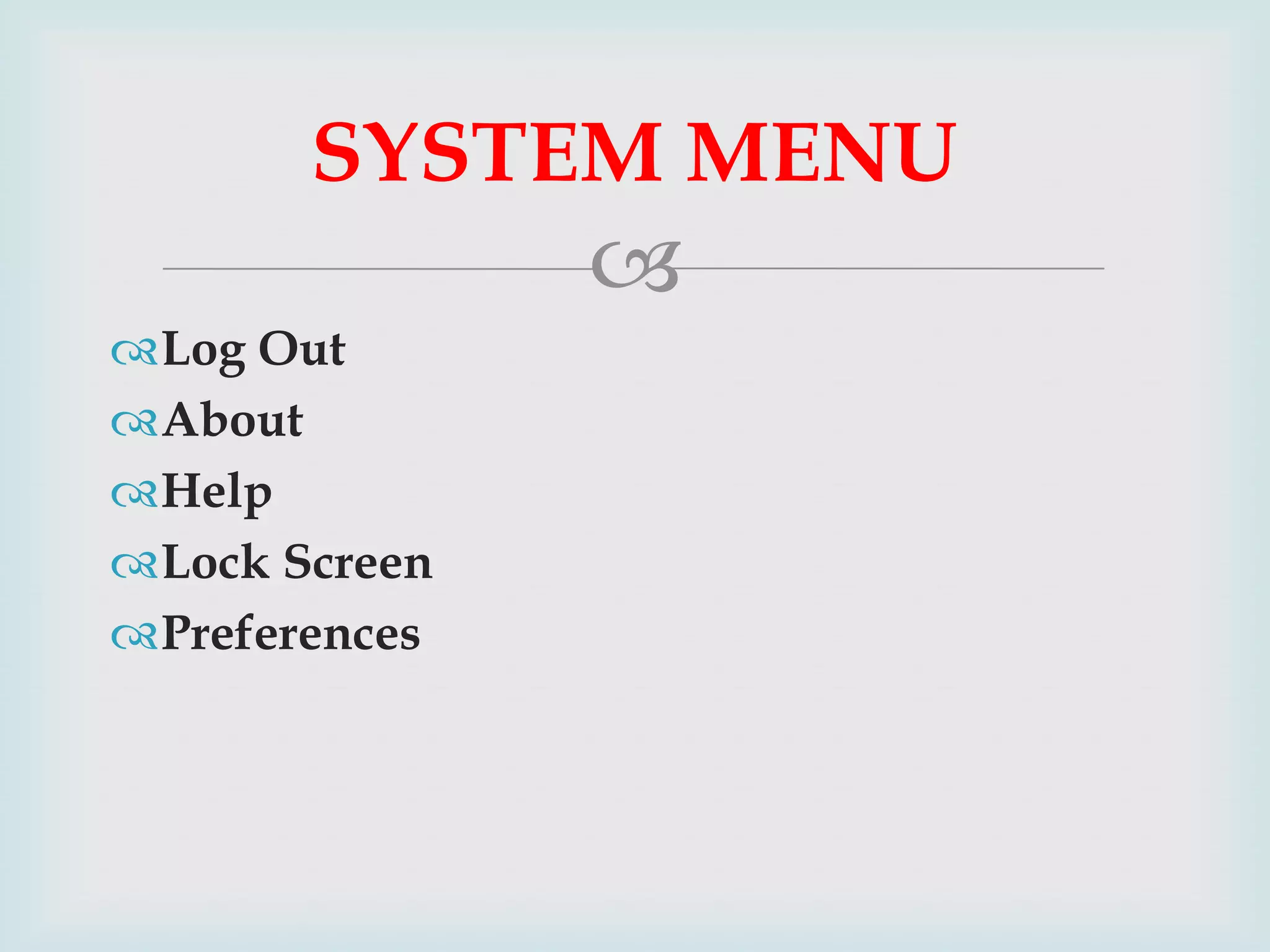
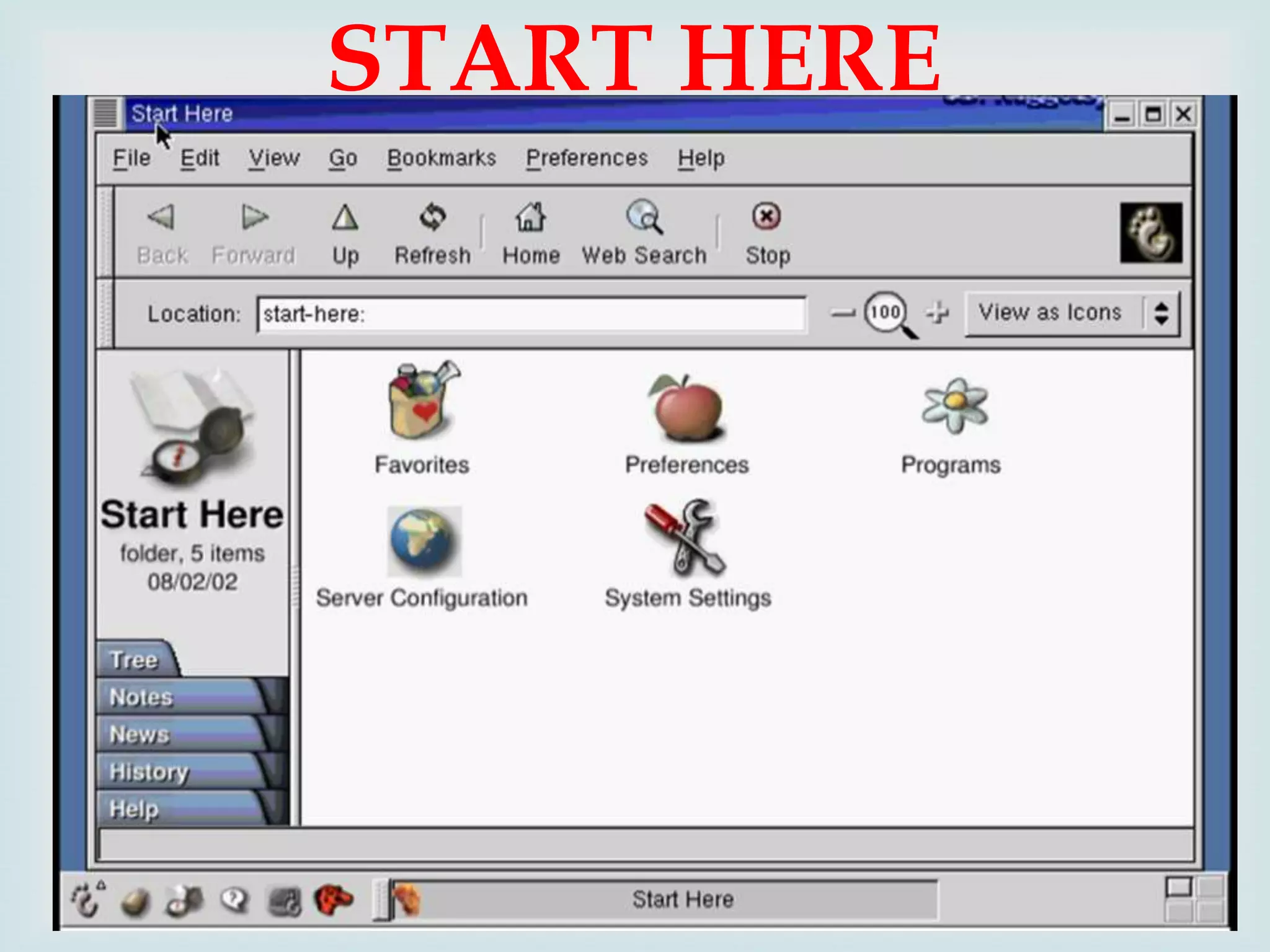
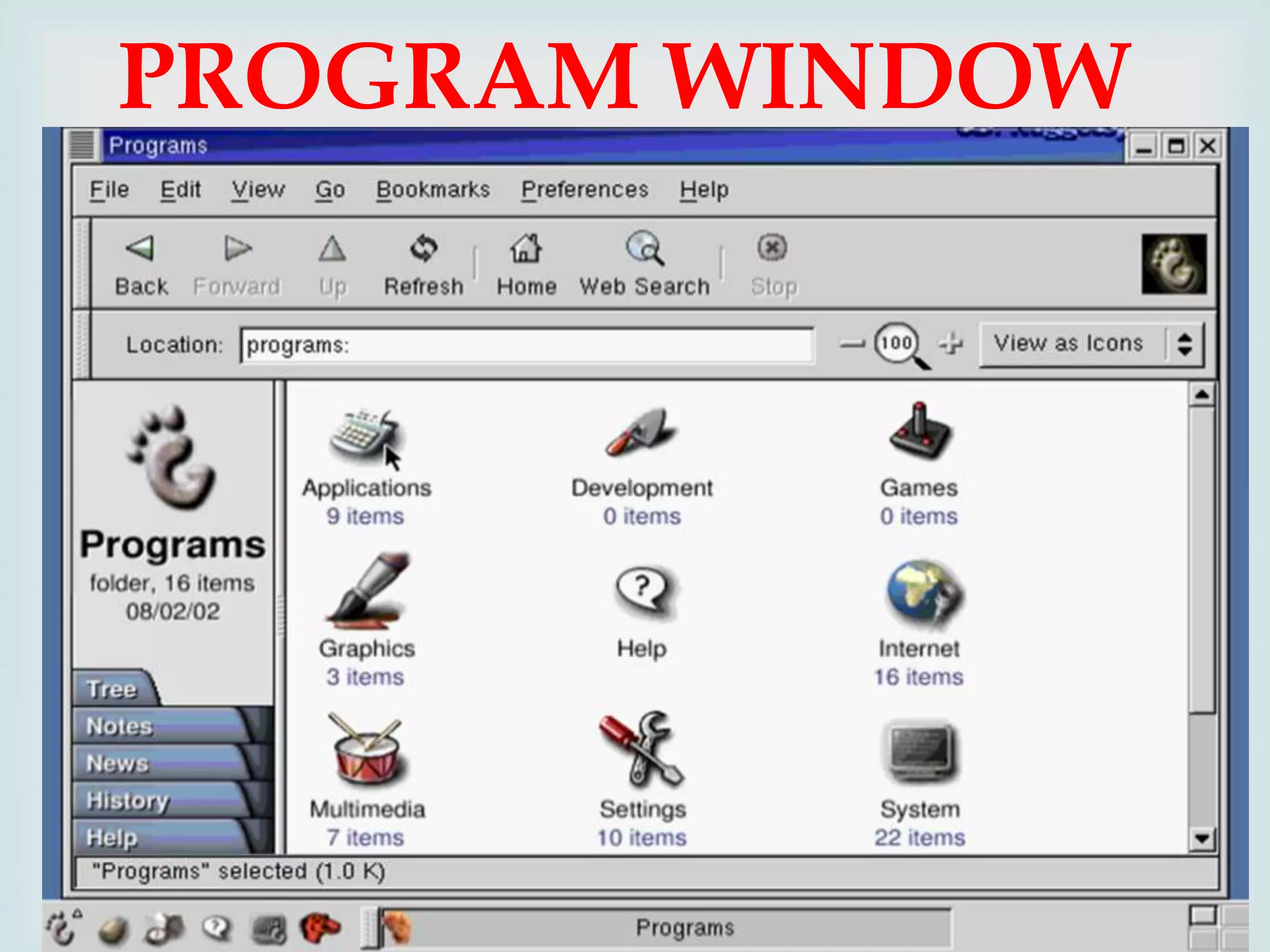
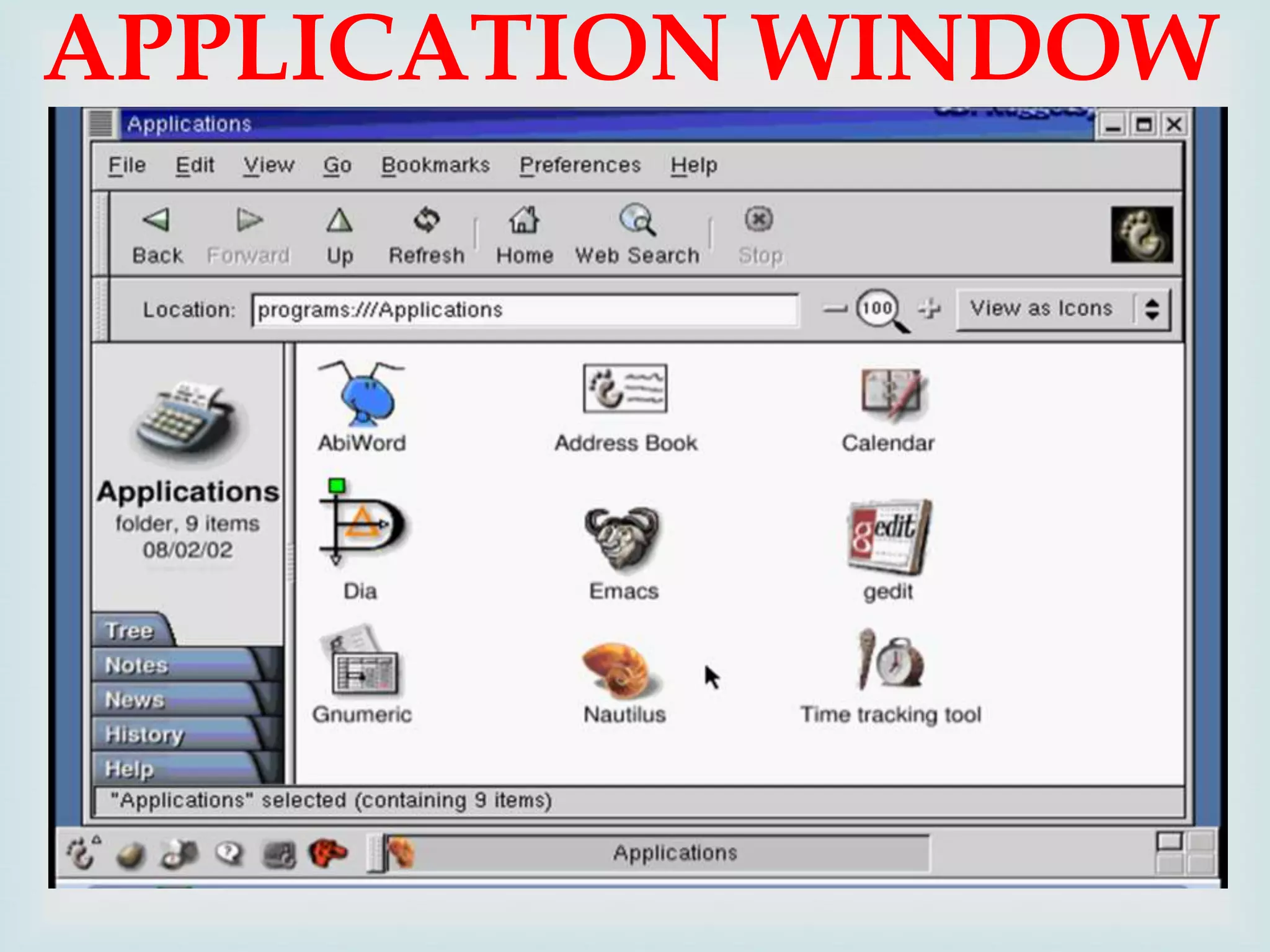
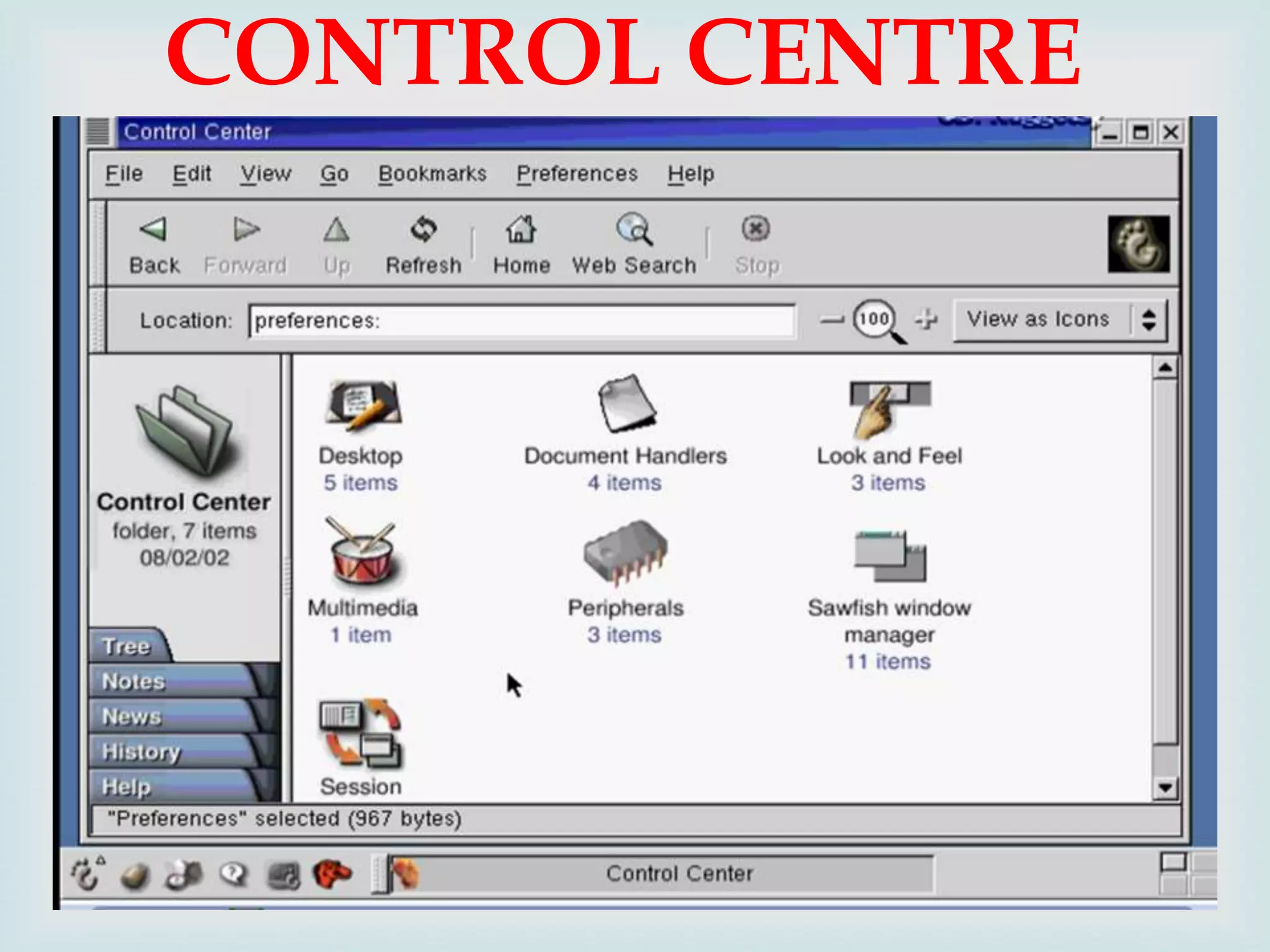
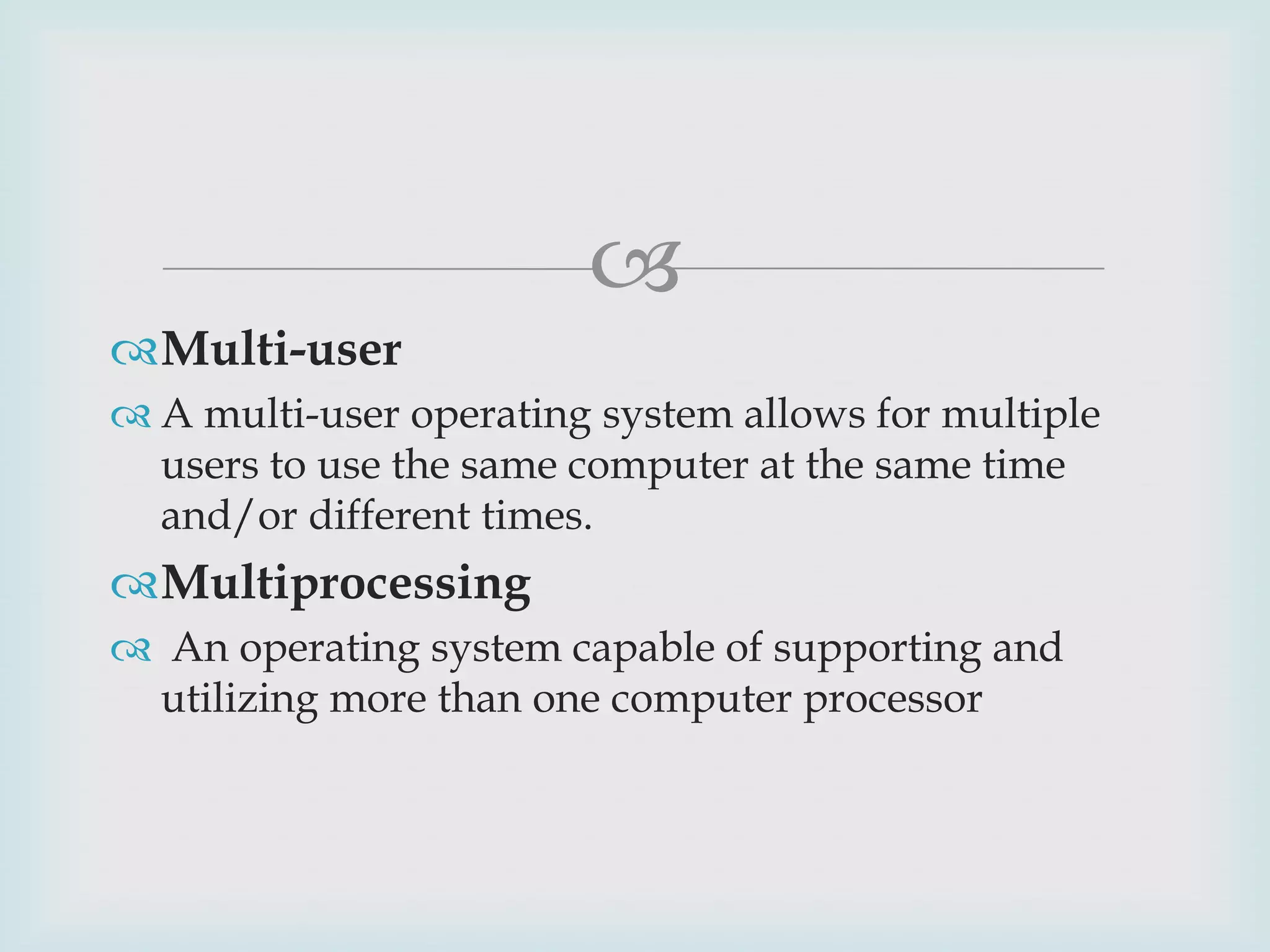
The document provides an overview of Linux, including its history and features. It discusses how Linux originated from the GNU project and was started by Linus Torvalds. Linux is an open source operating system that can run on various platforms. It provides features like multi-user access, multitasking, and security benefits compared to other operating systems. The document also describes the typical Linux desktop environment and popular software applications available for Linux.