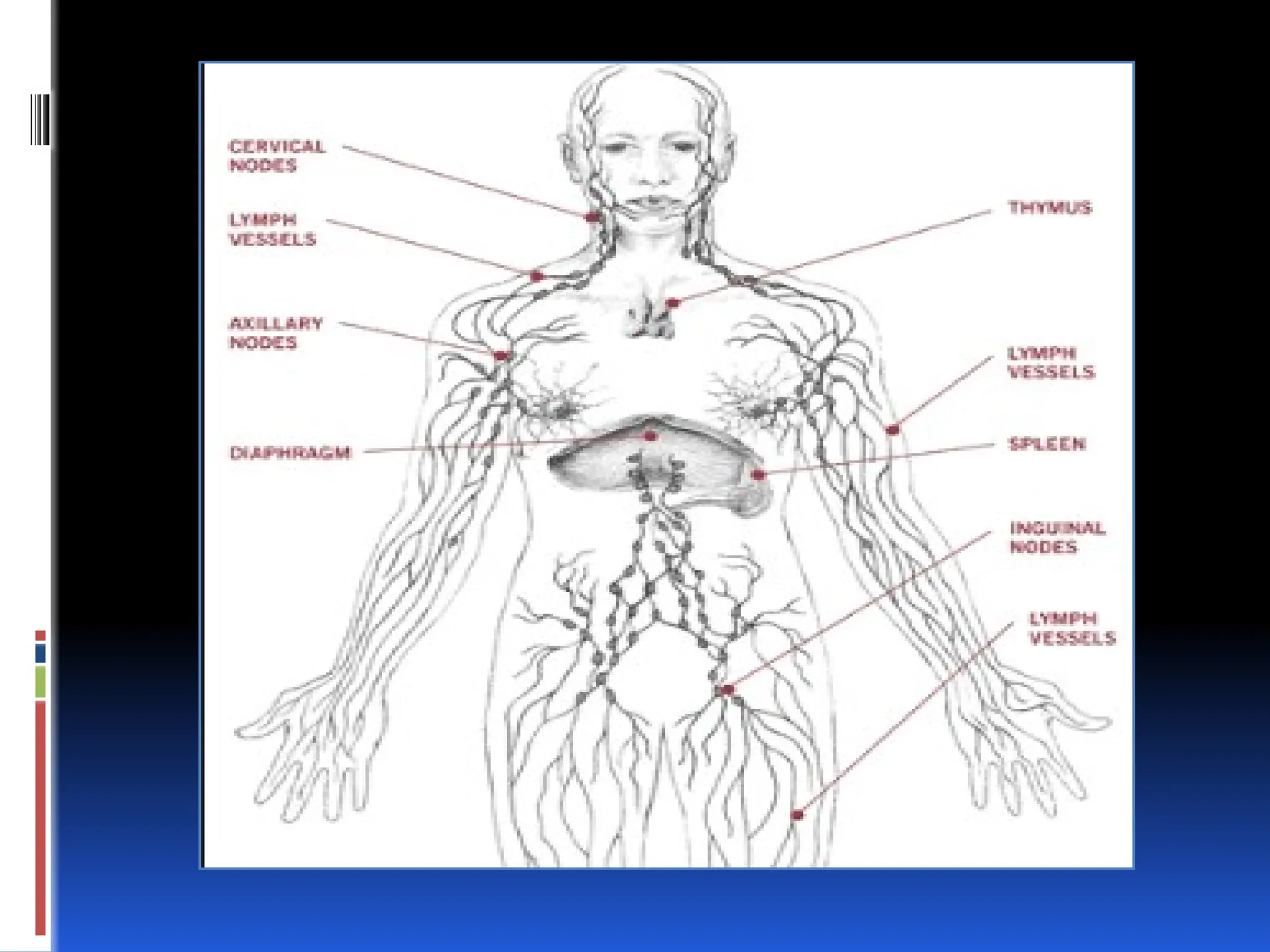
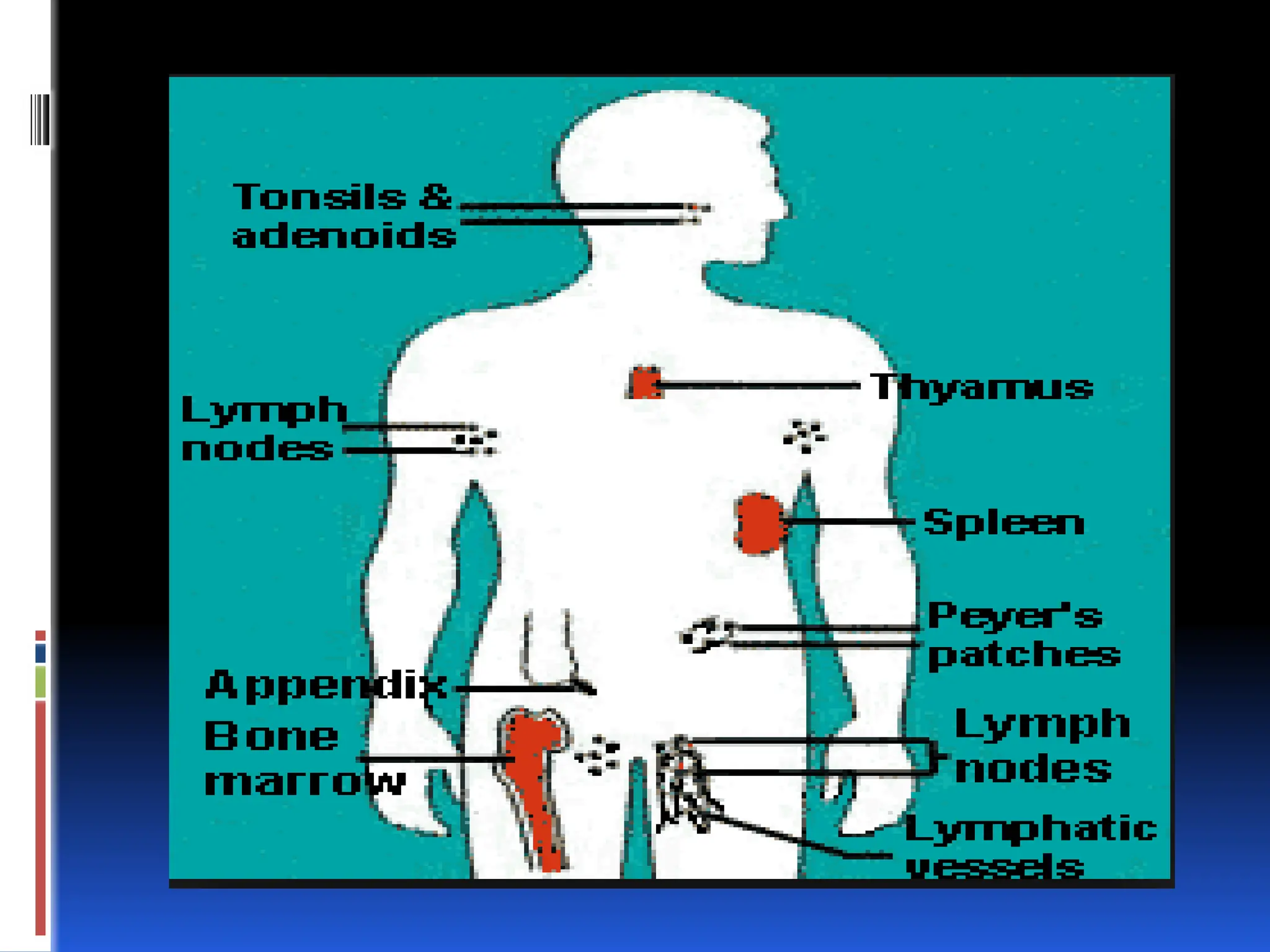
The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and consists of lymphatic vessels and organs that transport lymph, which plays a crucial role in immune function and fluid balance in the body. It is responsible for removing interstitial fluid, absorbing fats from the digestive system, and transporting white blood cells to lymph nodes. Diseases affecting the lymphatic system include lymphedema, swollen lymph nodes, lymphangiomatosis, and lymphangiosarcoma.