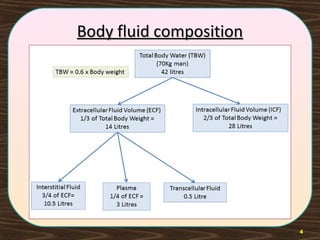
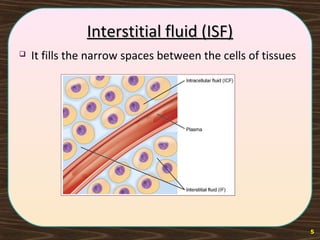
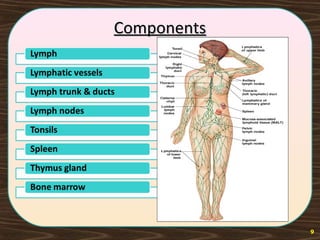
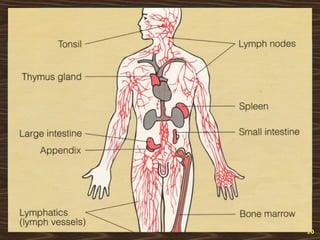
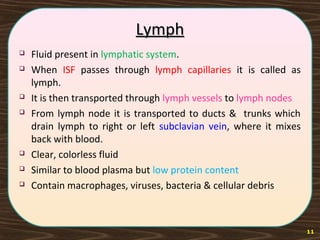
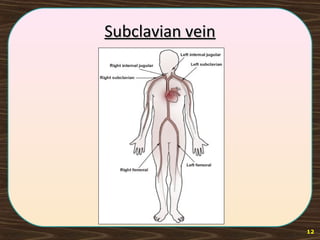
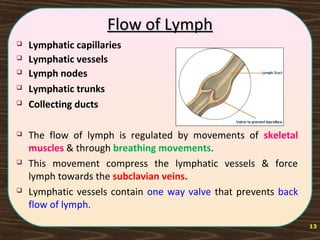
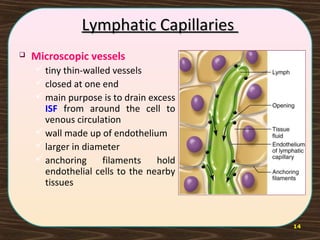
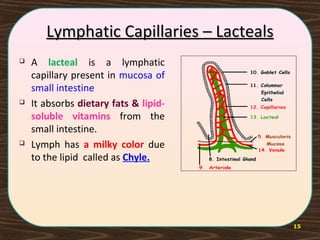
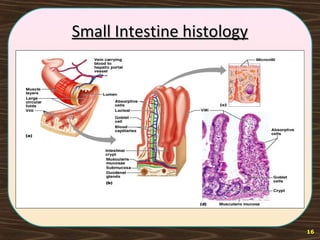
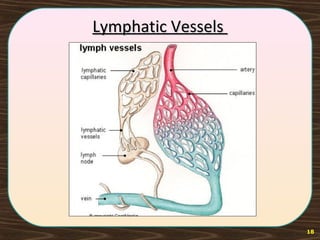
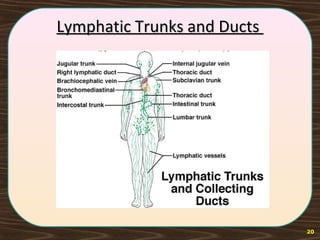
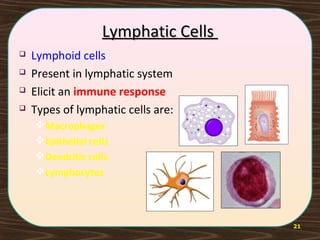
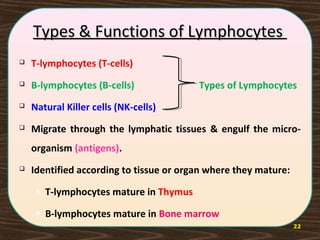
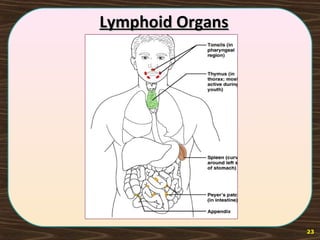
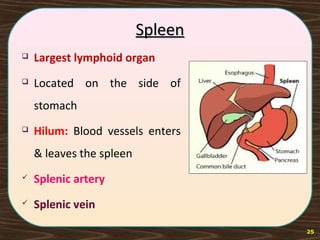
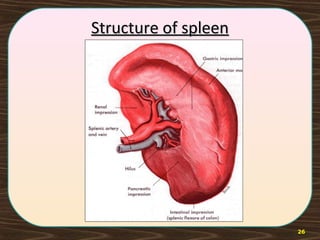
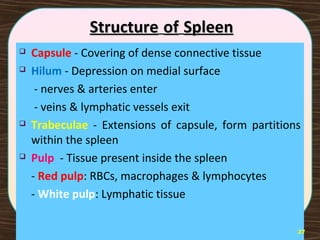
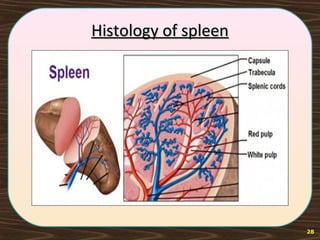
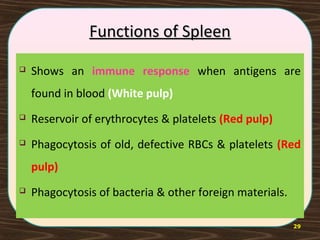
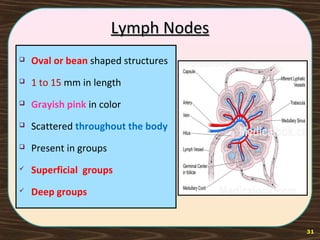
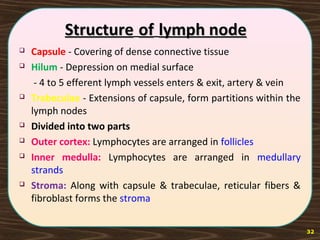
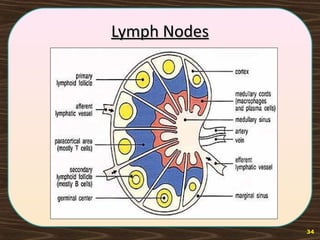
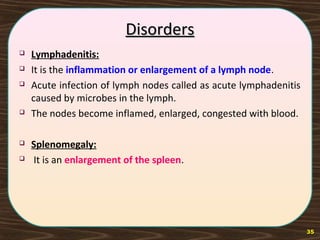
The lymphatic system consists of lymph and lymphatic vessels that transport lymph throughout the body. Lymph is interstitial fluid that has entered lymphatic capillaries and contains lymphocytes, macrophages, viruses, bacteria, and cellular debris. The main components of the lymphatic system are lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic trunks and ducts, and lymphatic tissue. Lymph flows from lymphatic capillaries through vessels, nodes, trunks and ducts and eventually returns to the blood circulation via the subclavian veins. The lymphatic system functions to transport fluids and nutrients, support immune responses, and absorb dietary fats.