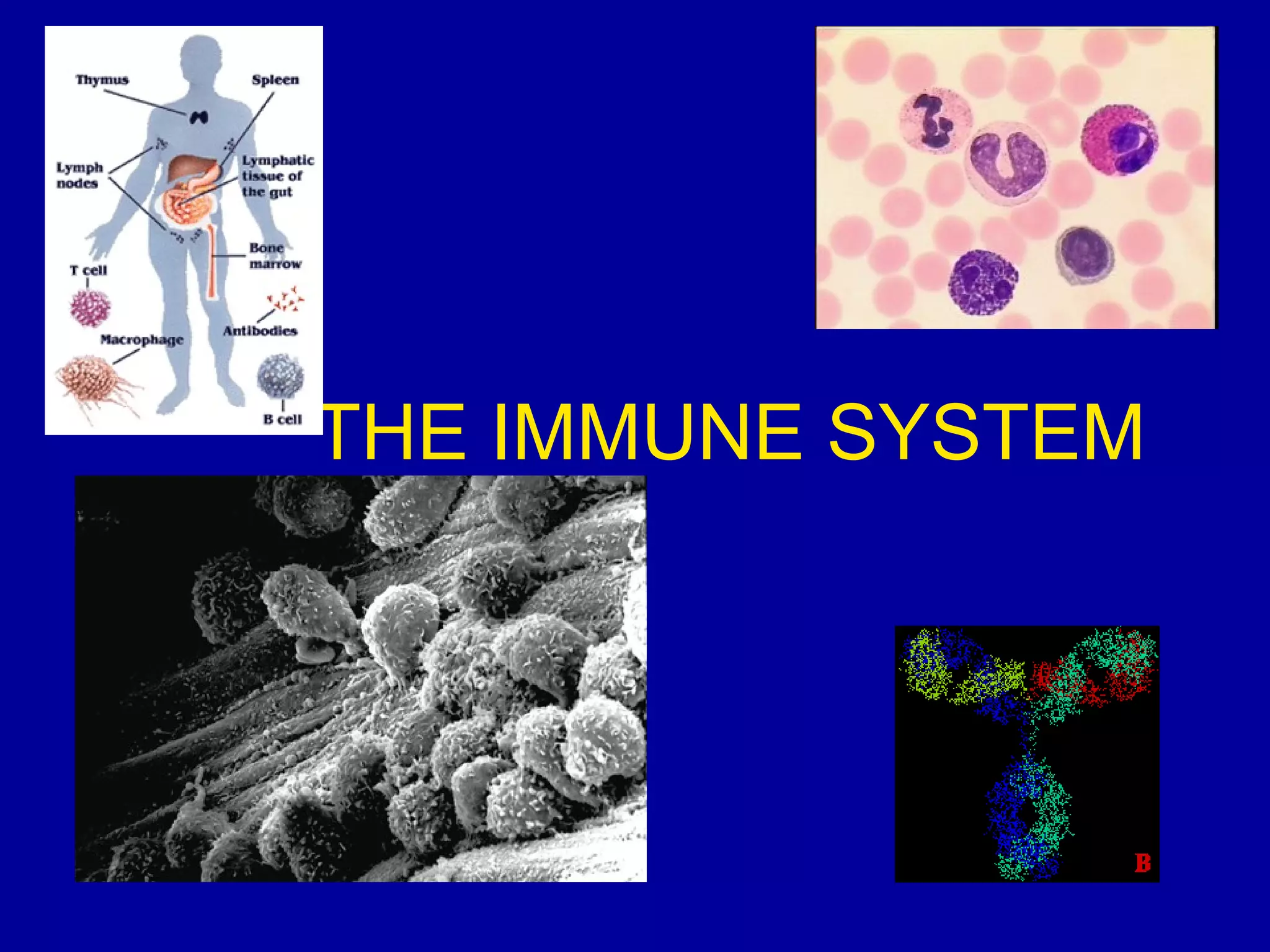
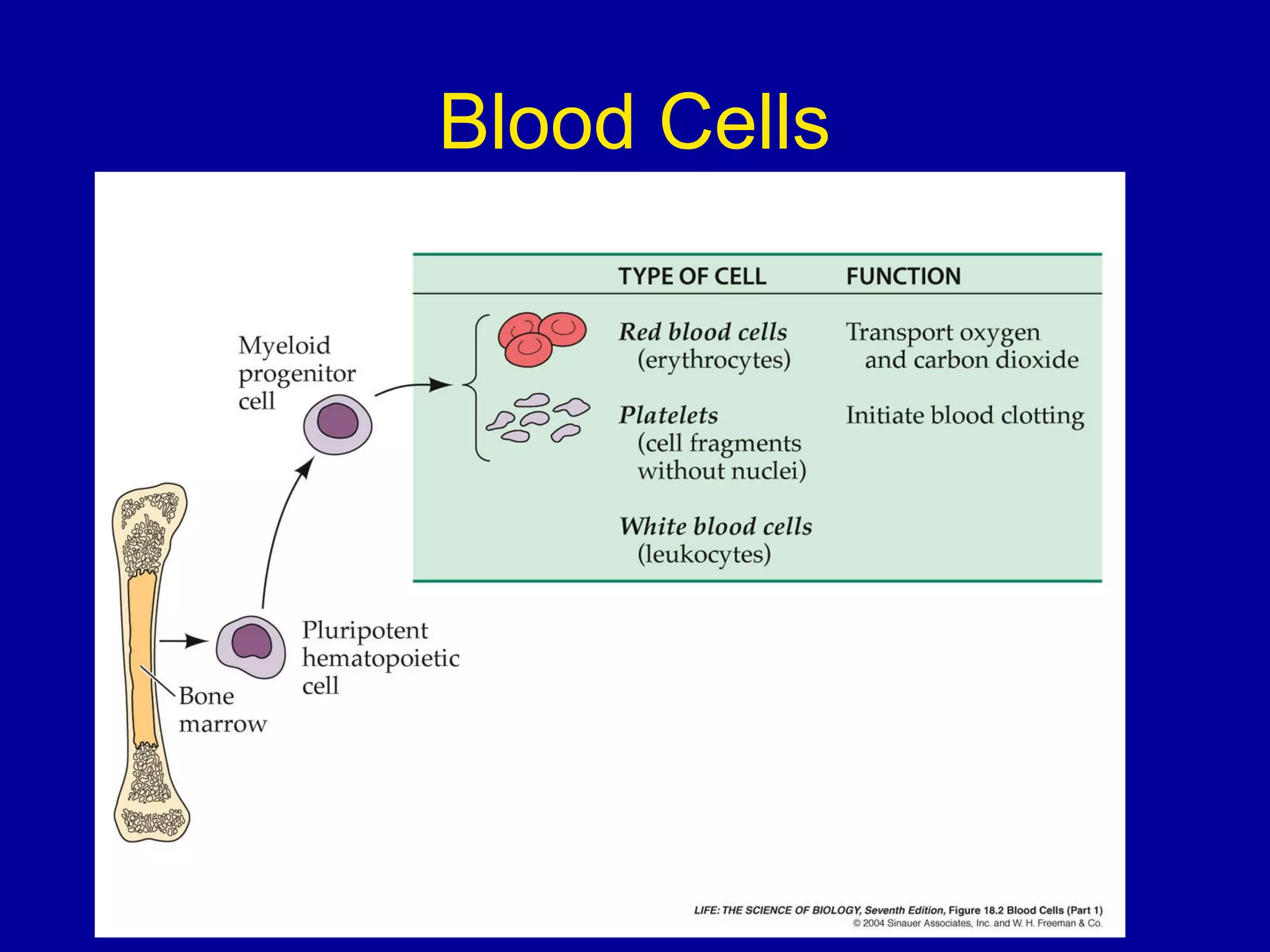
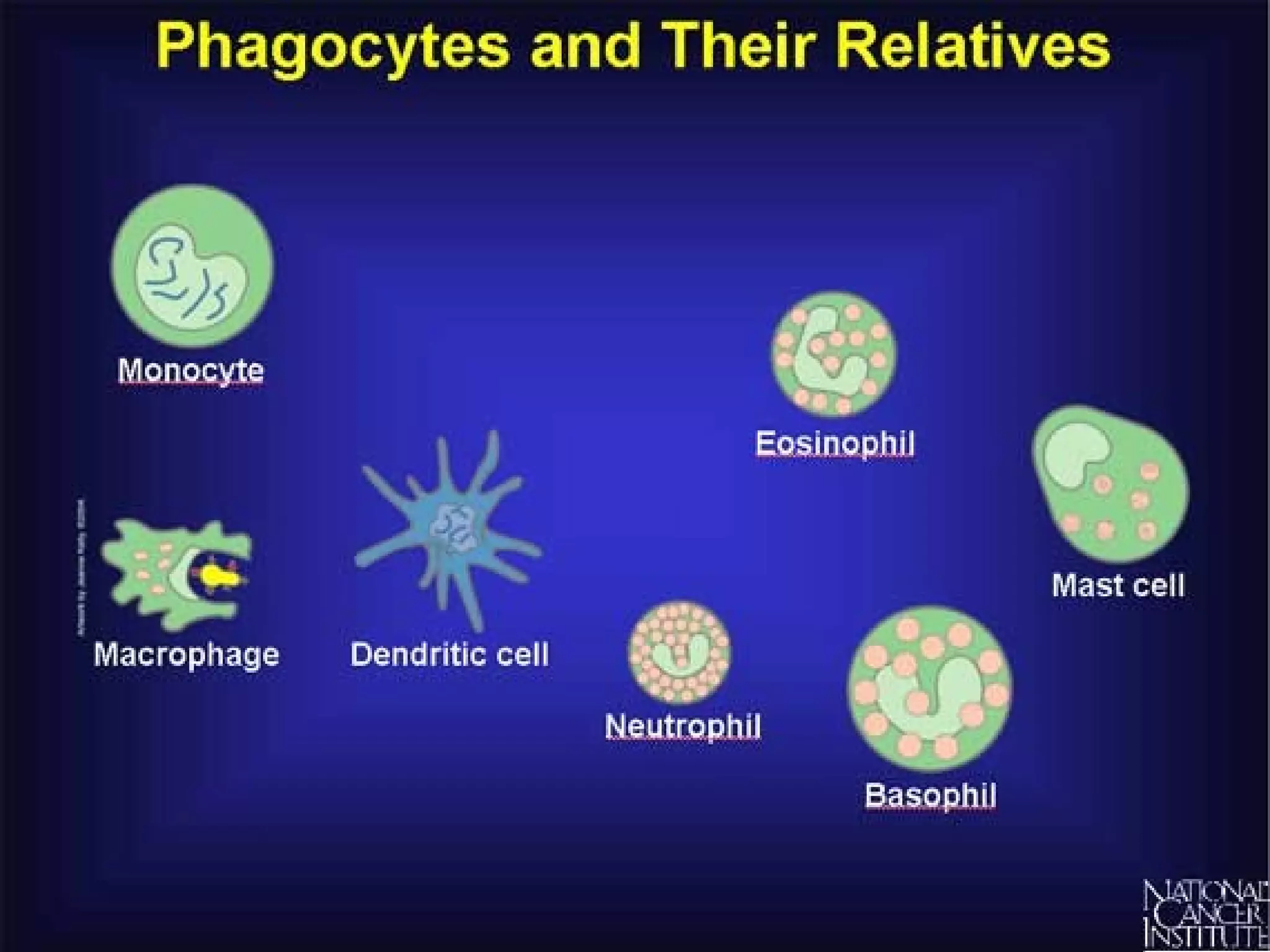
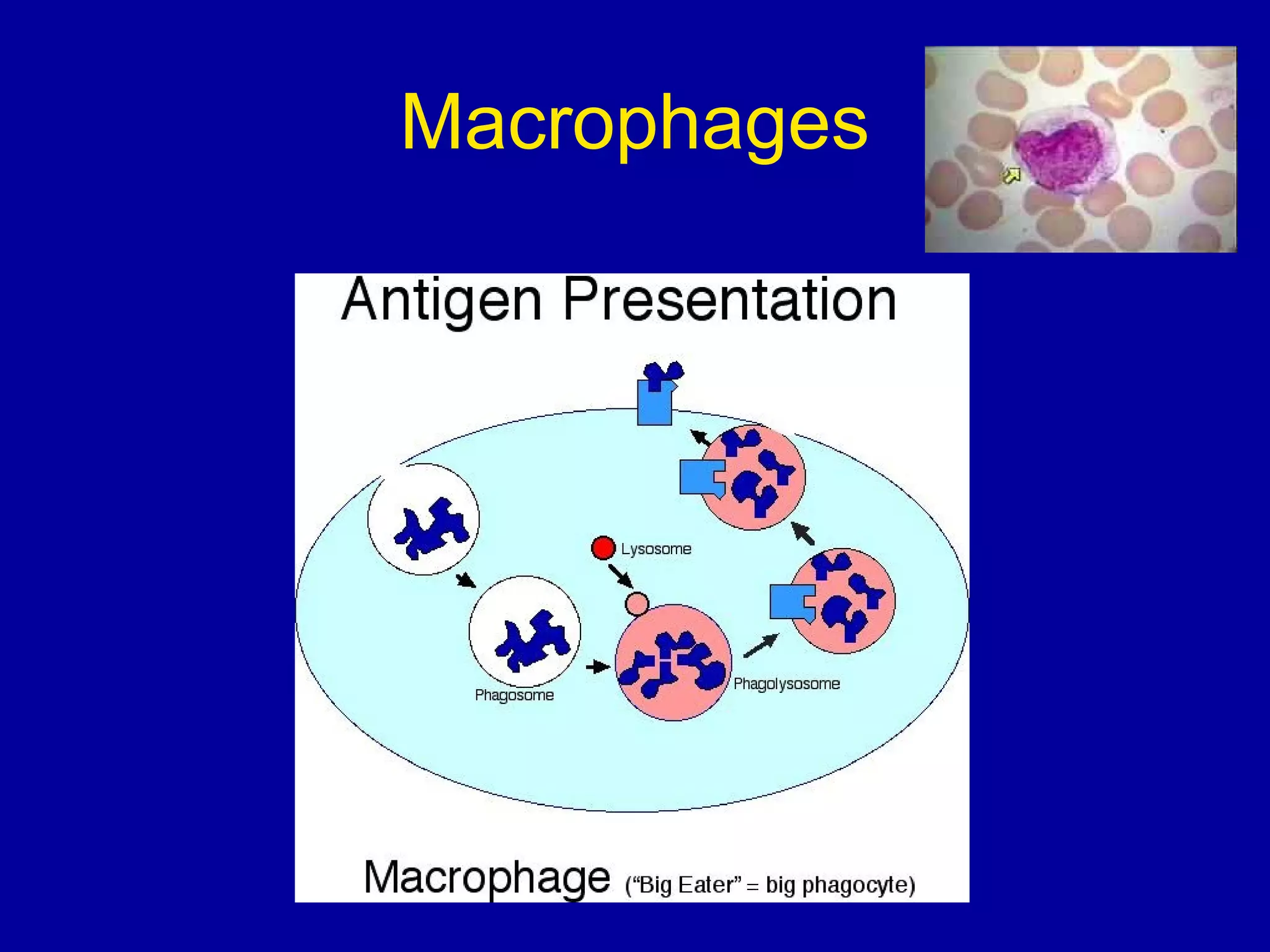
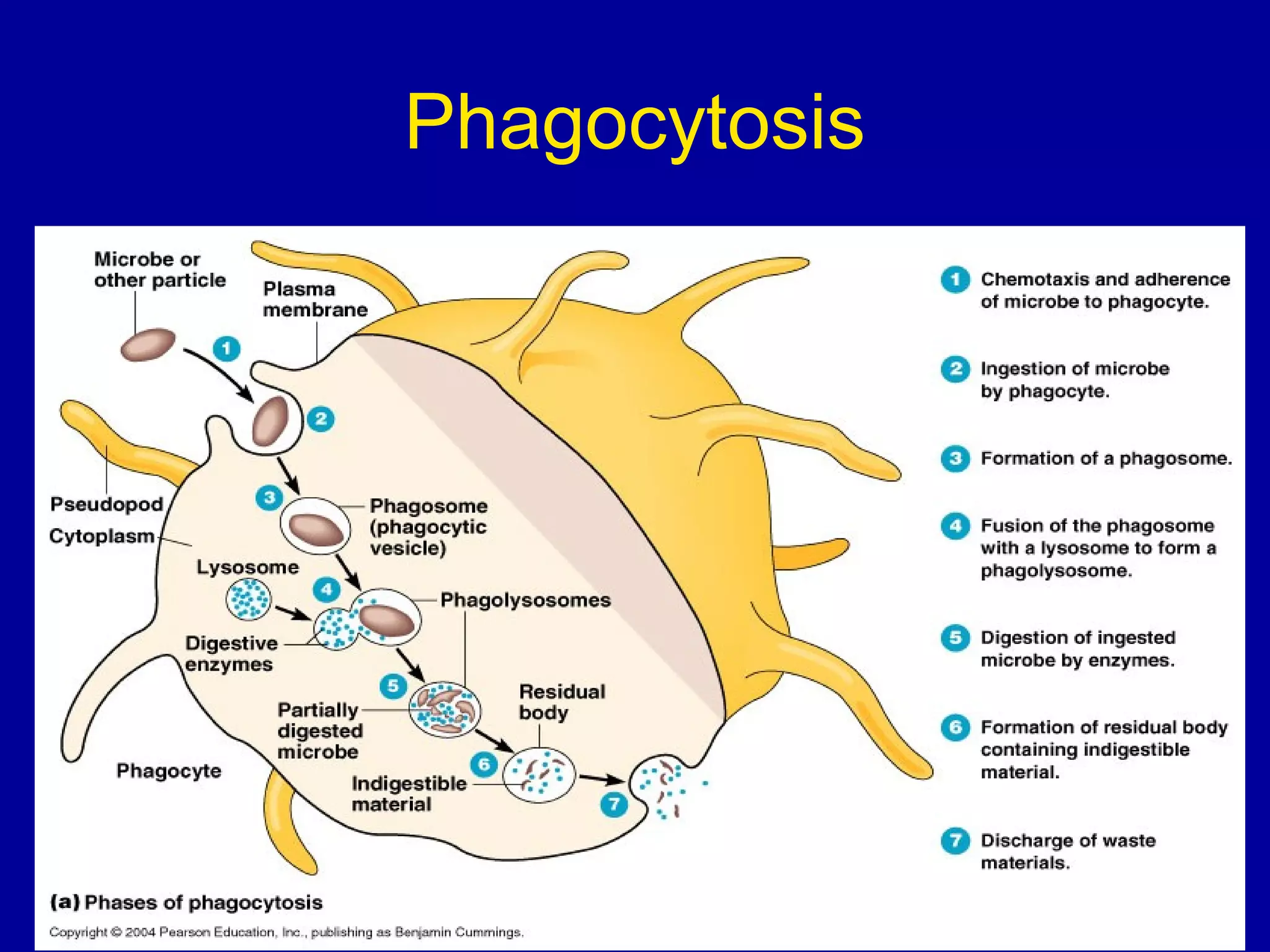
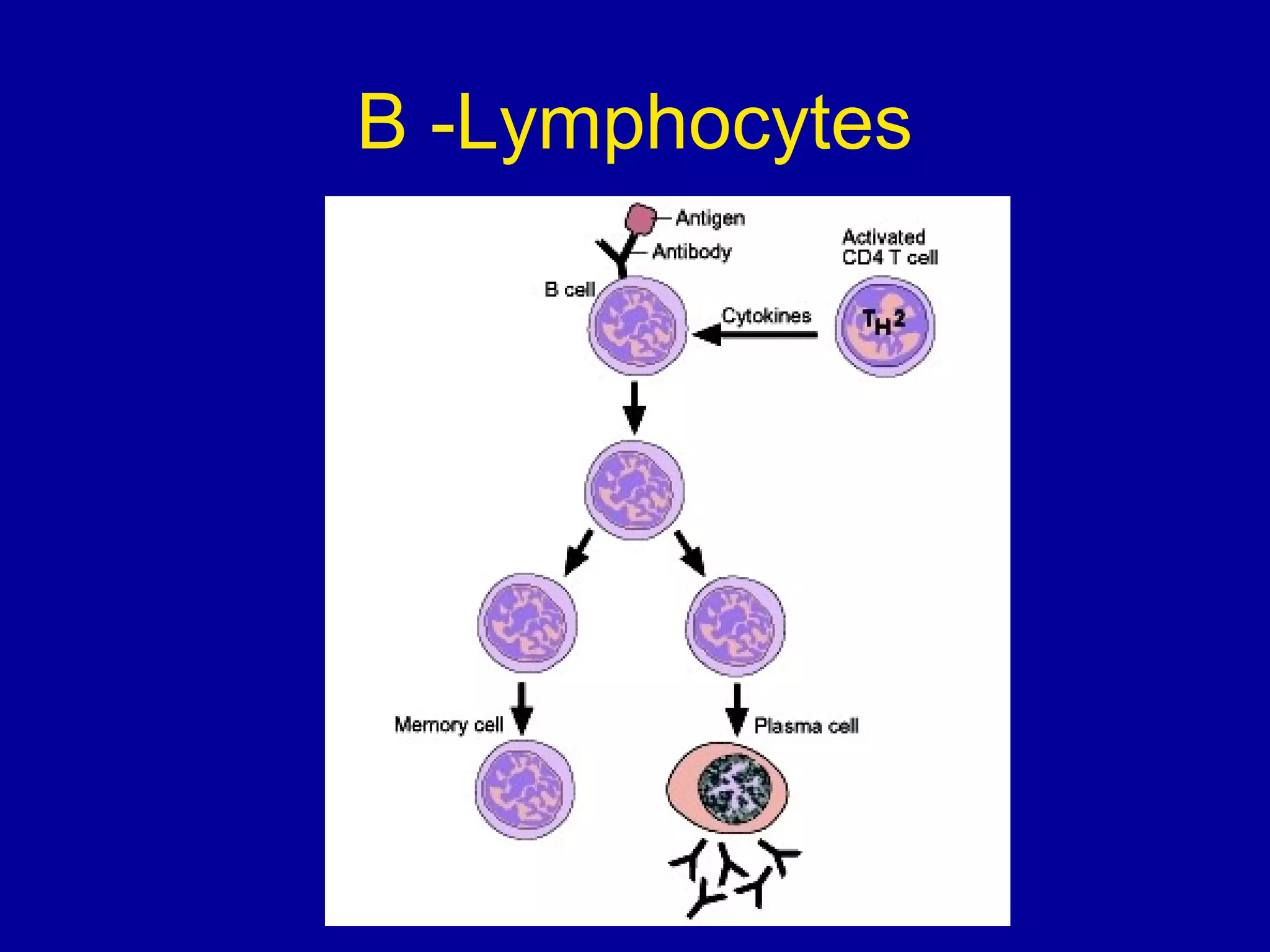
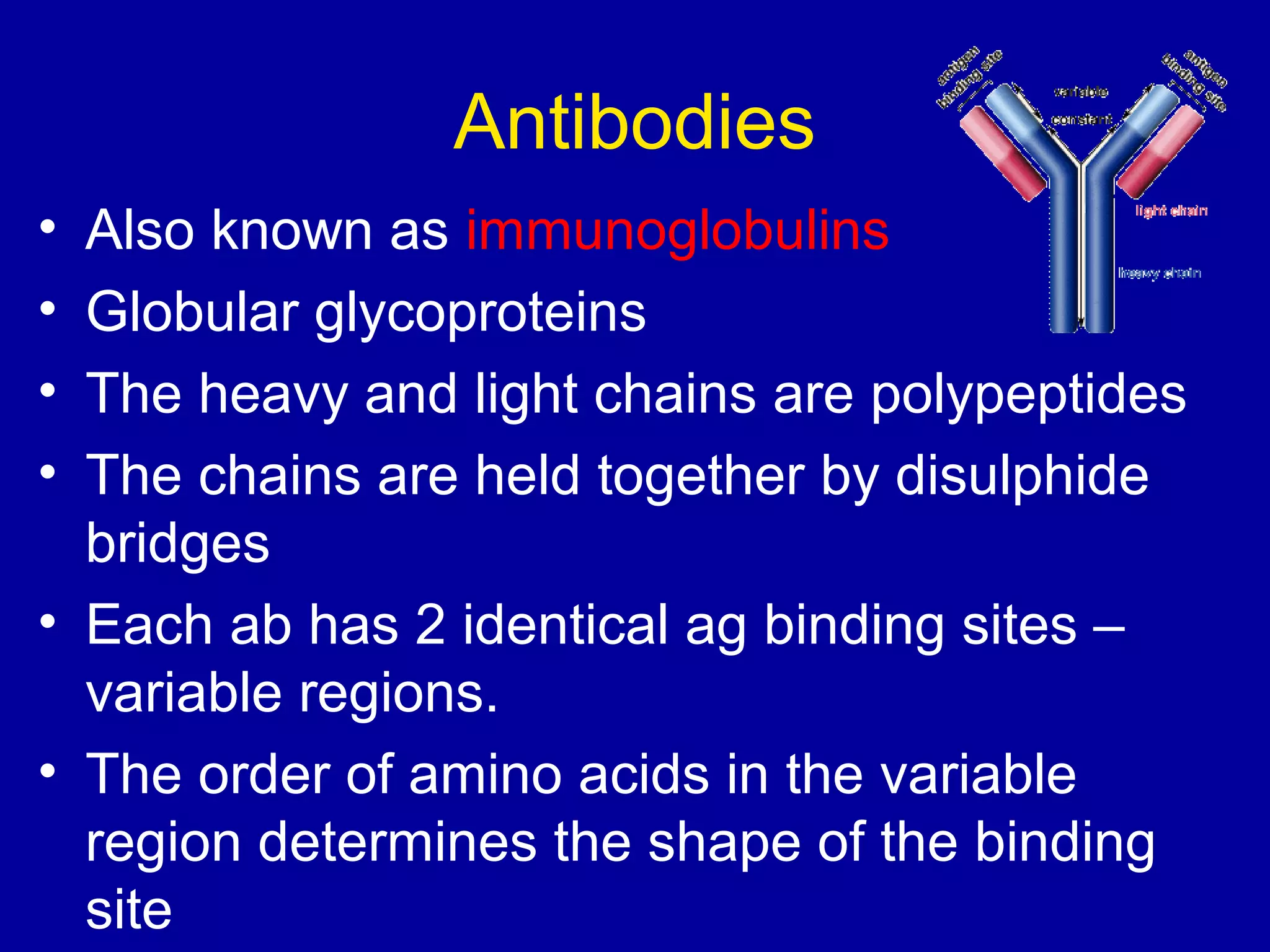
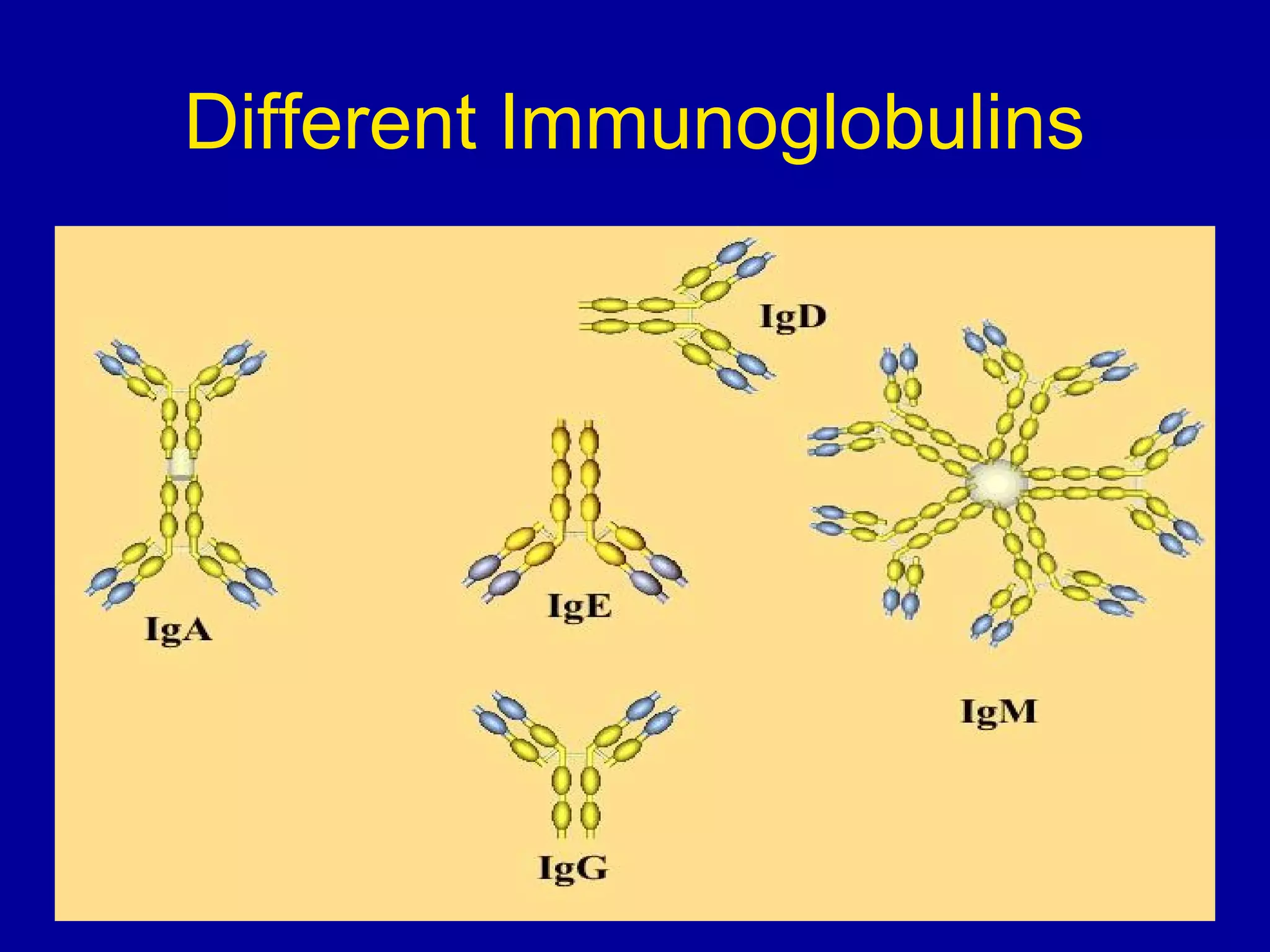
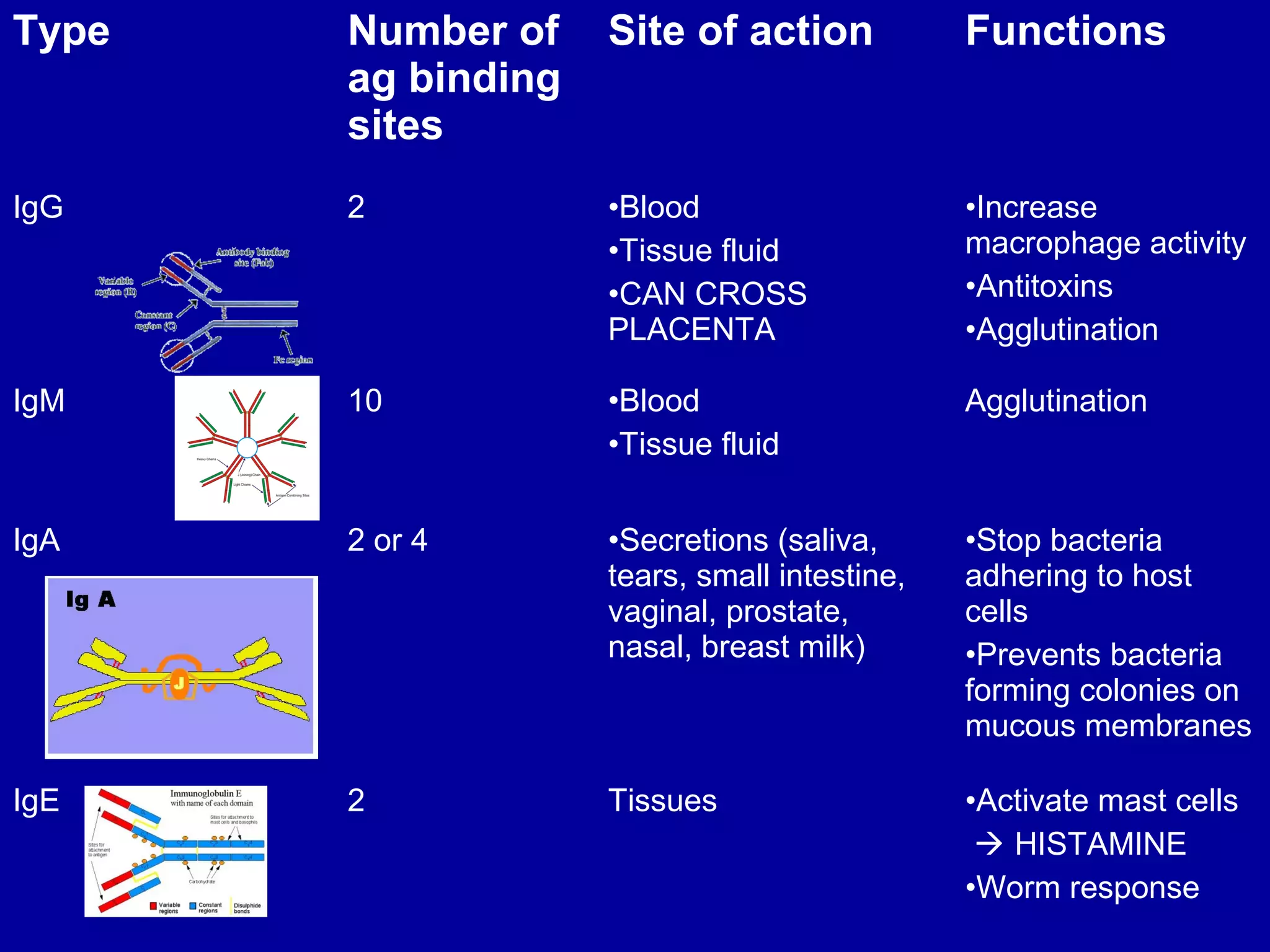
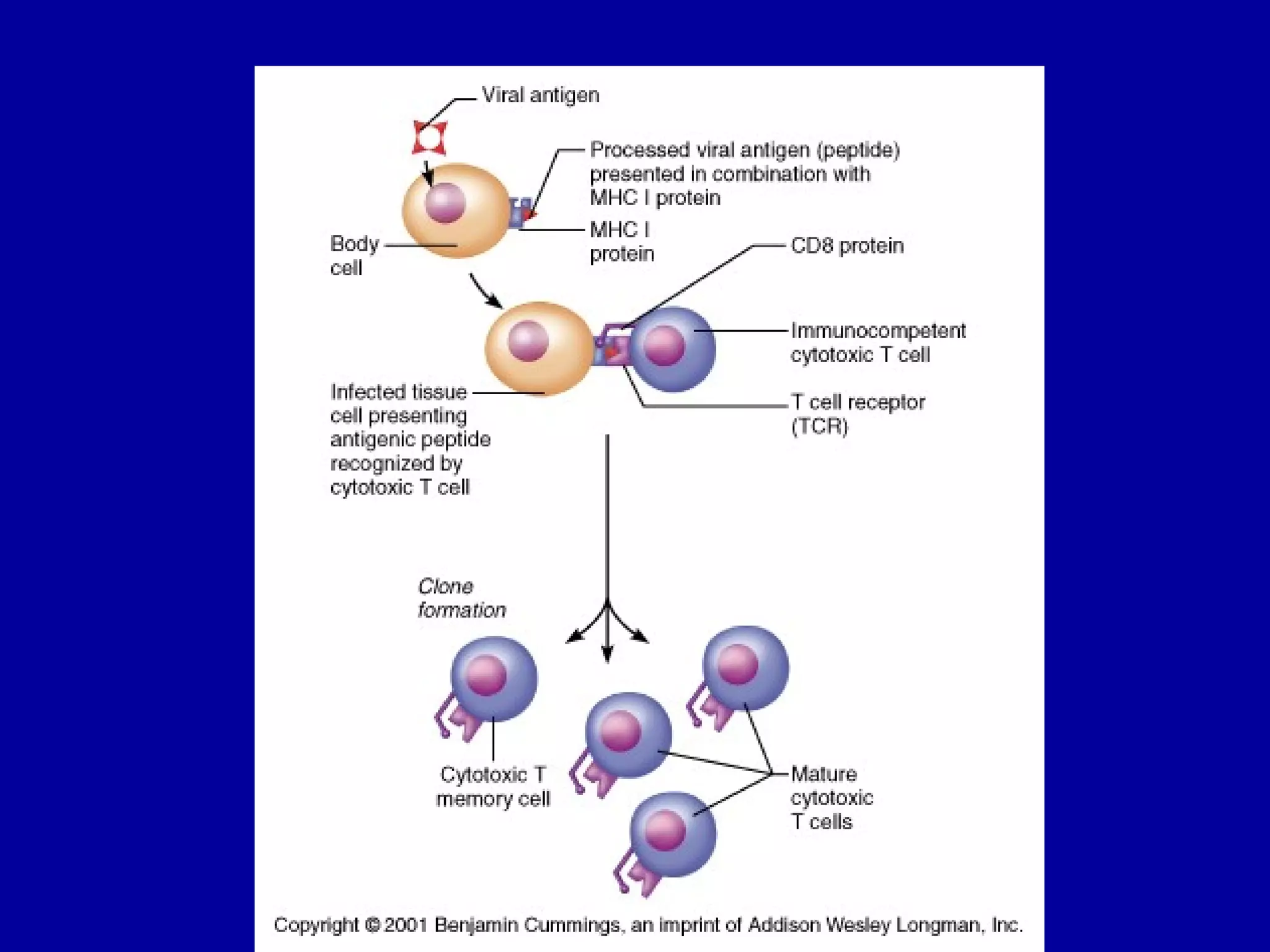
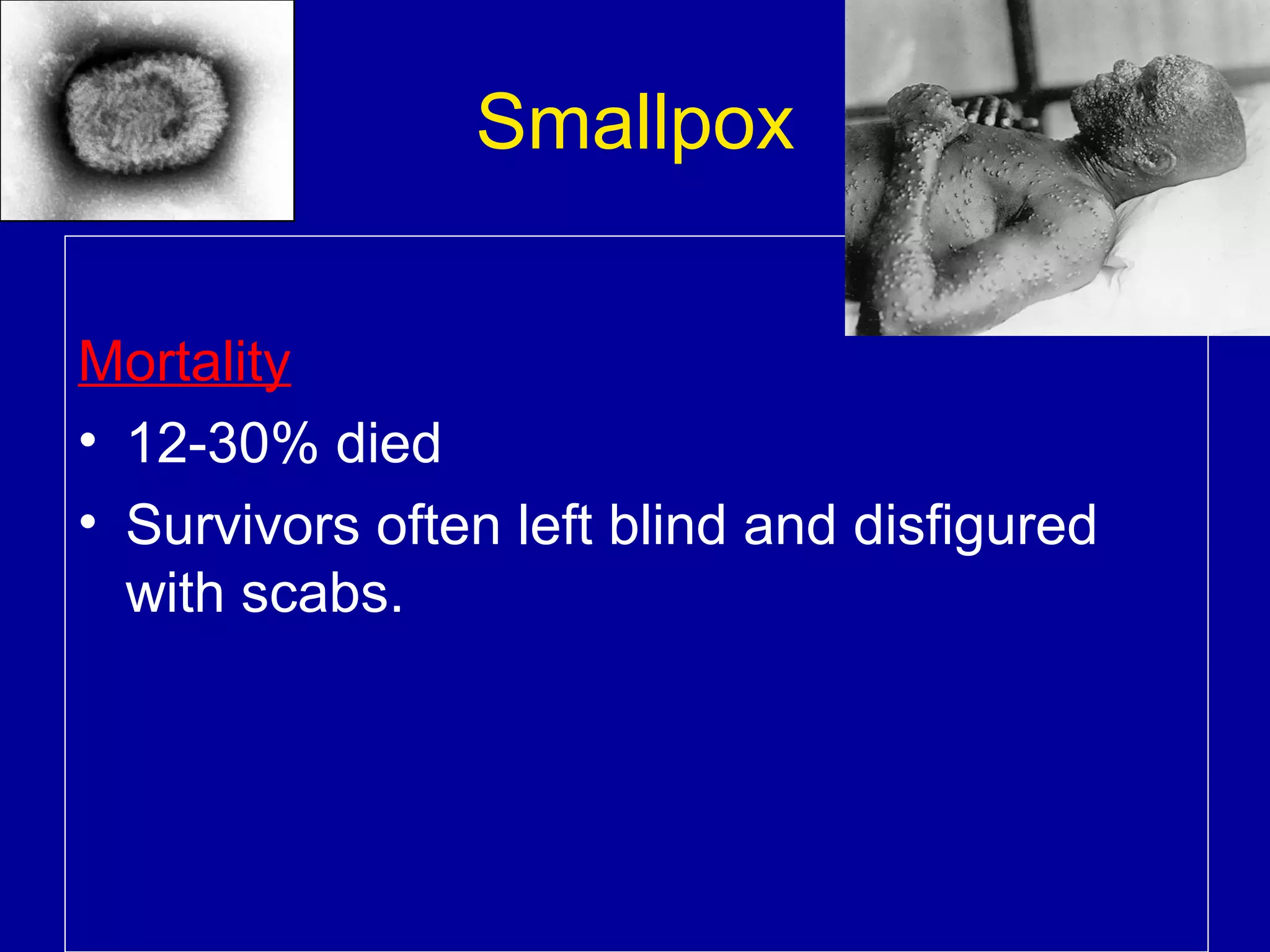
The immune system consists of white blood cells that defend the body against pathogens. Phagocytes such as neutrophils and macrophages ingest and digest pathogens. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies that target pathogens for destruction. T cells help activate other immune cells and kill infected cells. Vaccines expose the immune system to antigens in a controlled way to produce immunity against diseases. While vaccines have eradicated smallpox, limitations remain for other diseases due to antigenic variation and concealment within host cells. Allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly reacts to harmless substances.