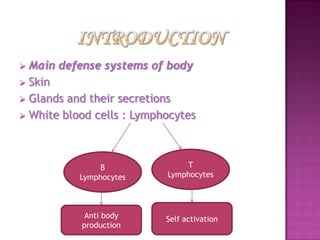
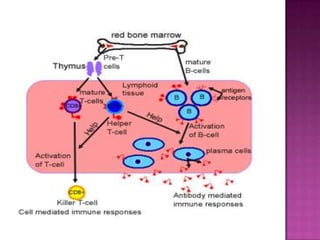
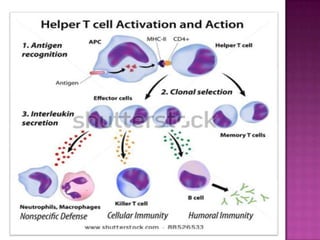
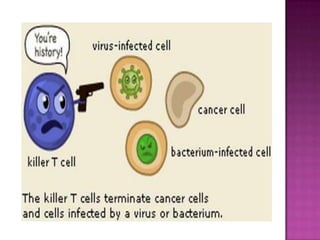
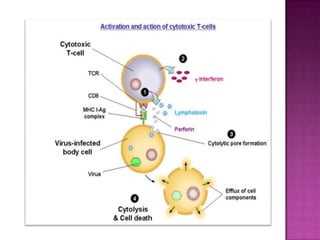
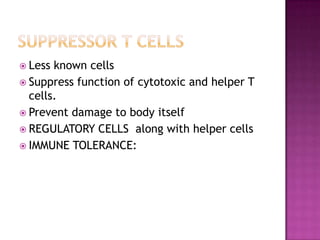
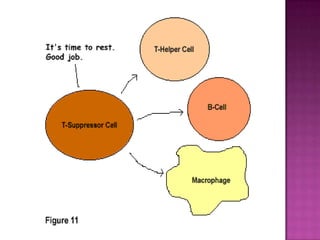
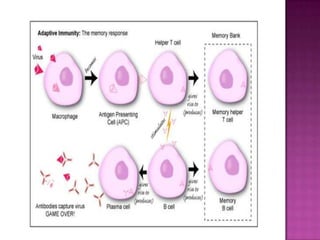
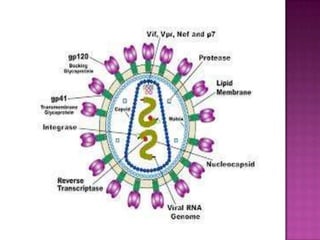
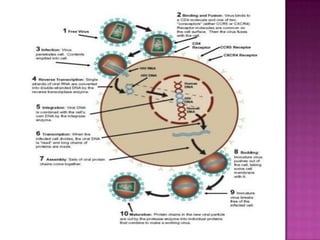
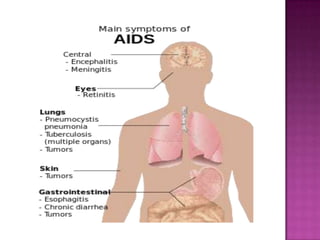
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the human immune system, highlighting the roles of various cells such as T cells, B cells, and their functions in immune responses, including self-activation and antibody production. It also discusses autoimmune disorders, immune deficiencies, and the impact of conditions like HIV/AIDS on the immune system. Additionally, it covers prevention strategies and the implications of lymphocyte count abnormalities.