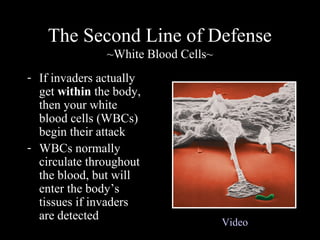
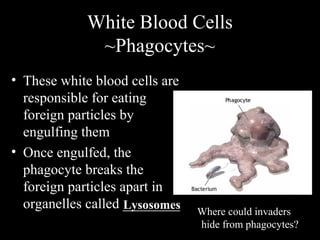
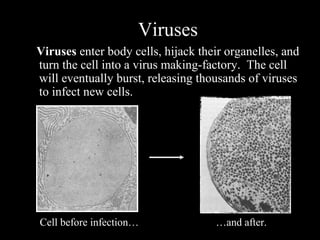
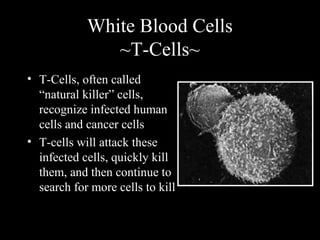
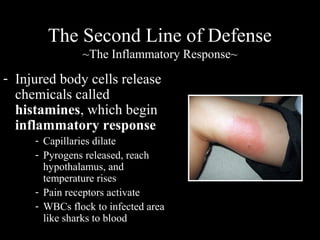
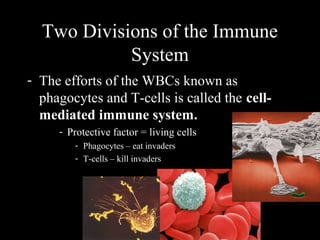
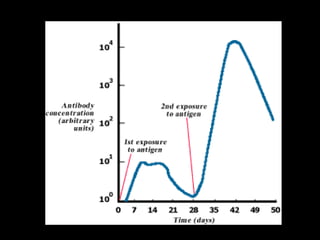
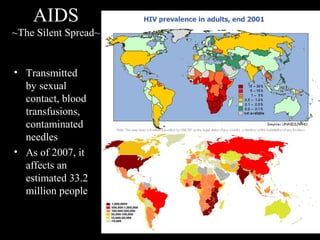
The human immune system has three lines of defense against pathogens. The first line includes physical barriers like skin and mucus membranes, and chemicals in saliva and stomach acid. The second line consists of white blood cells that attack pathogens inside the body. This includes phagocytes that engulf bacteria and T-cells that destroy virus-infected cells. The third line of defense involves antibodies that target specific pathogens. Antibodies provide long-lasting active immunity against diseases, while vaccines produce immunity by exposing the immune system to weakened or dead pathogens. The immune system also has memory, allowing it to respond faster upon re-exposure to a pathogen.