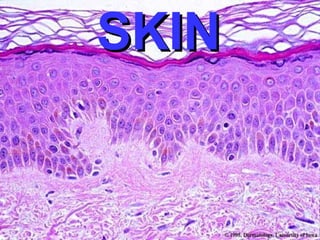
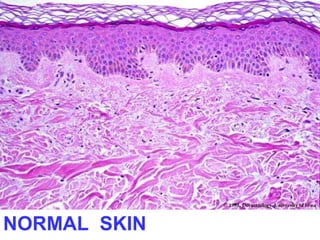
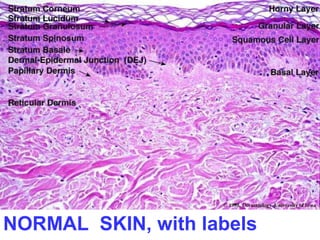
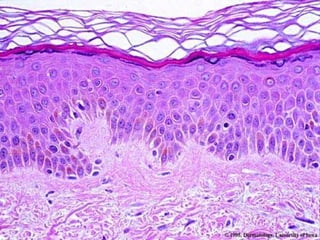
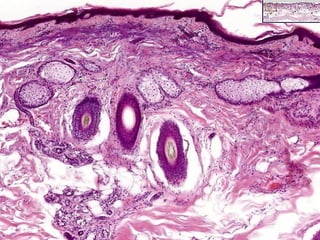
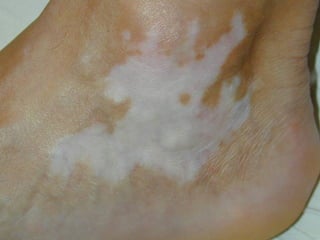
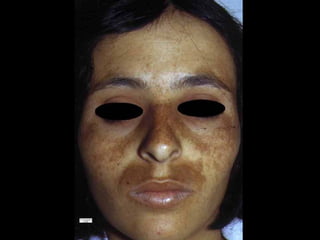
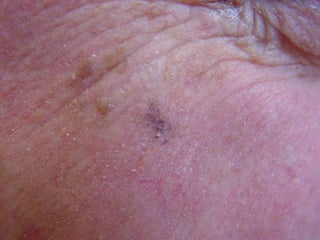
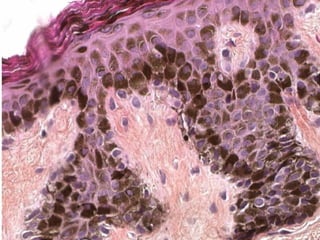
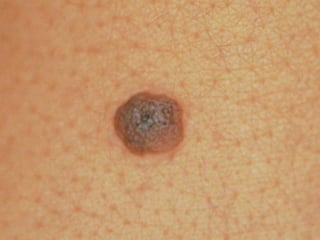
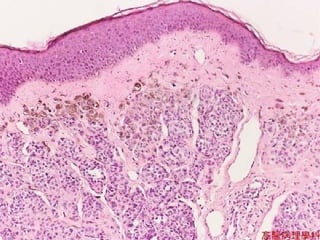
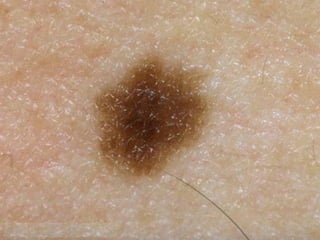
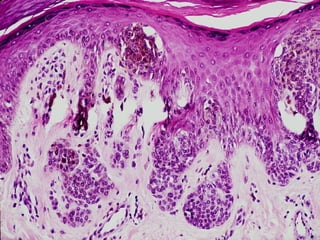
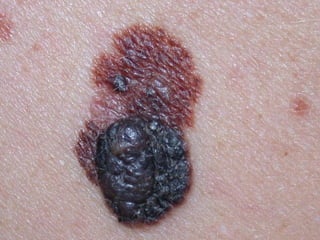
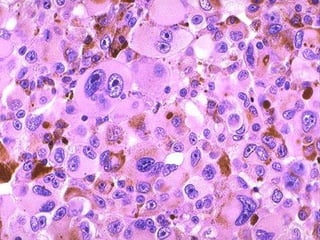
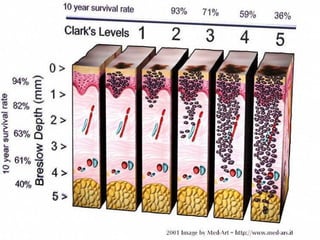
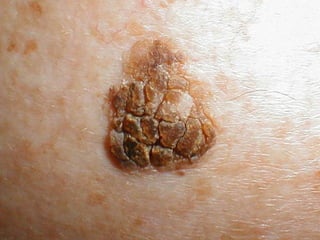
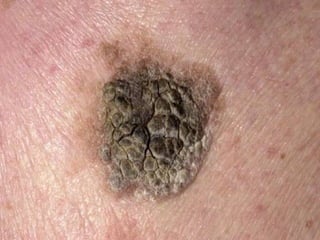
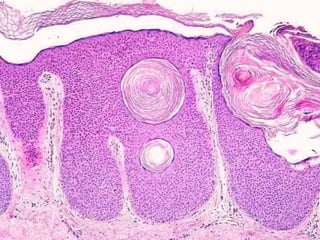
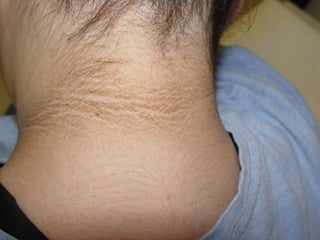
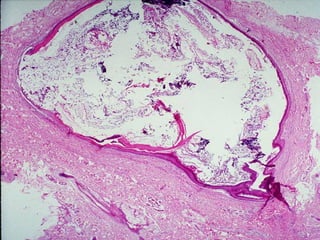
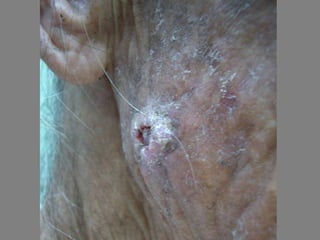
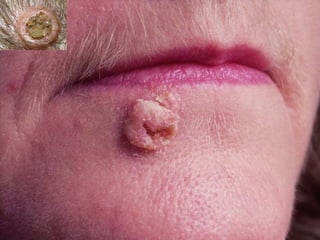
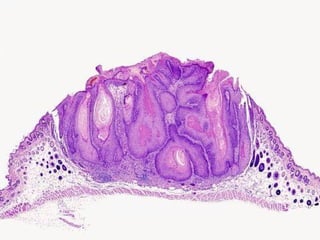
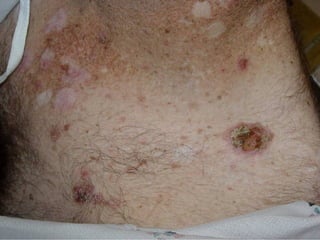
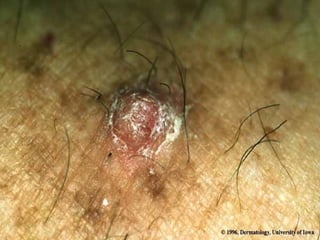
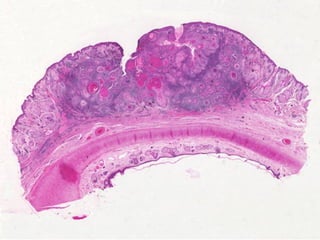
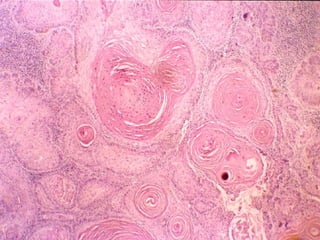
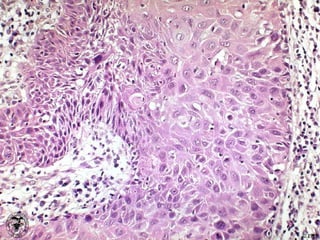
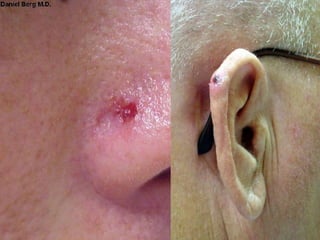
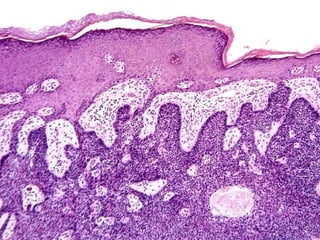
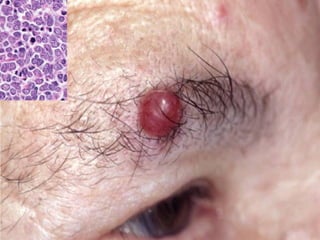
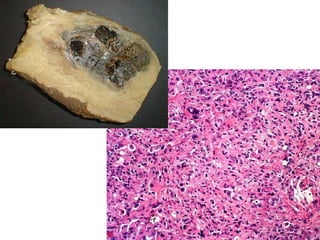
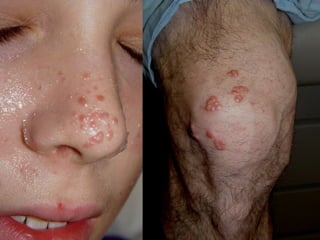
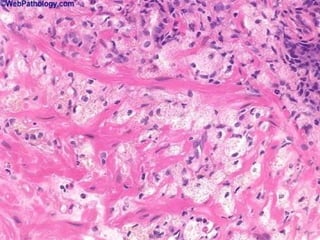
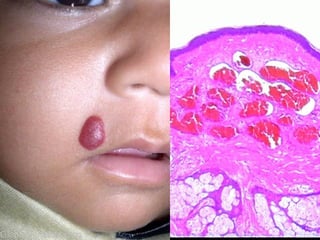
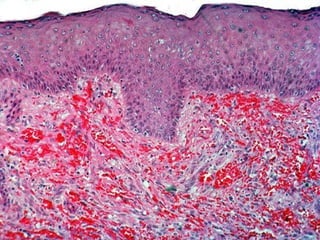
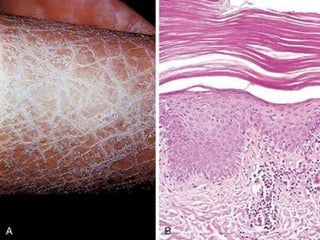
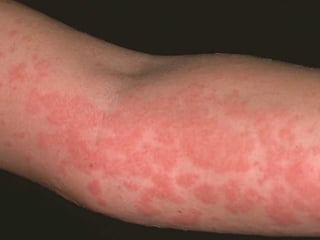
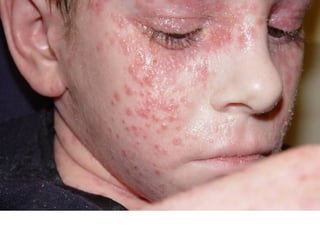
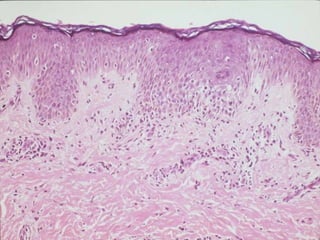
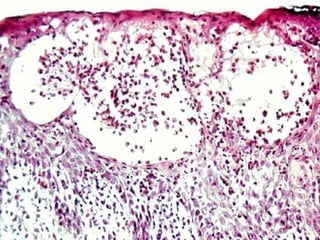
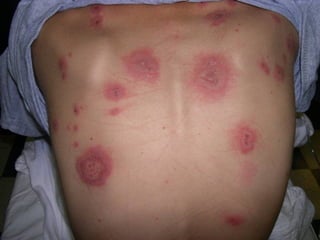
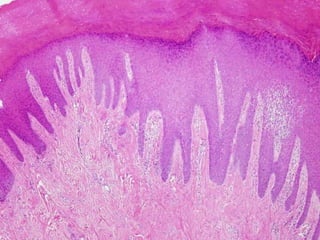
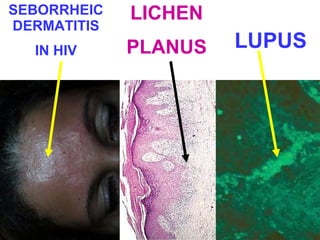
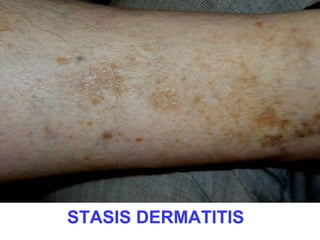
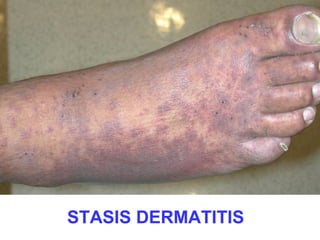
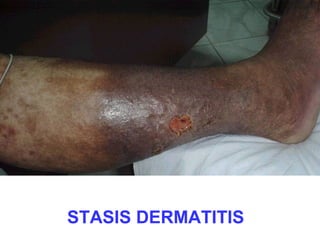
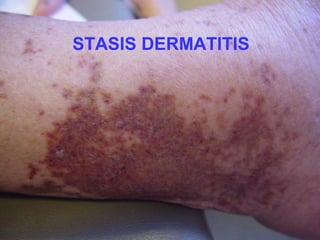
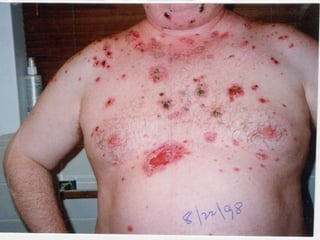
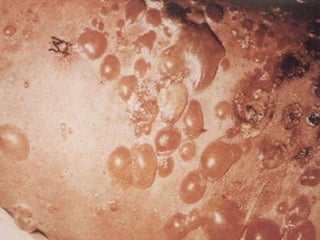
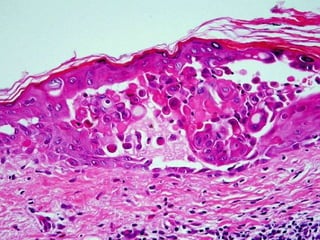
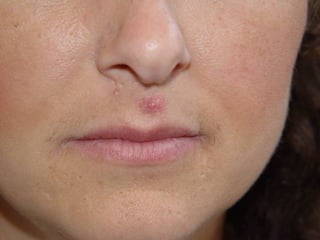
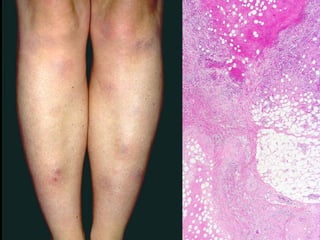
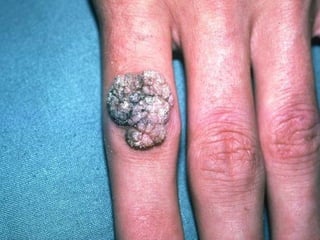
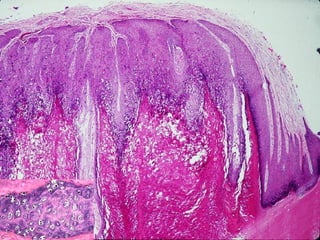
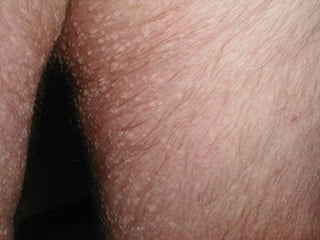
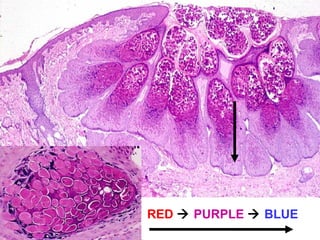
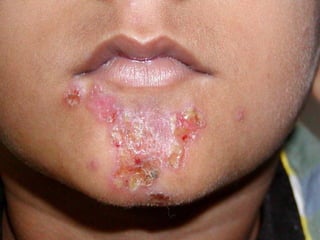
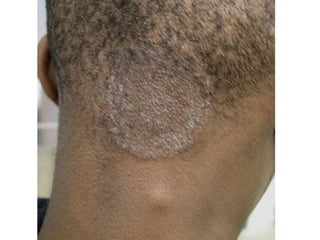
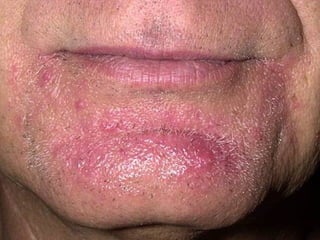
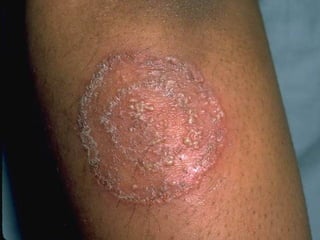
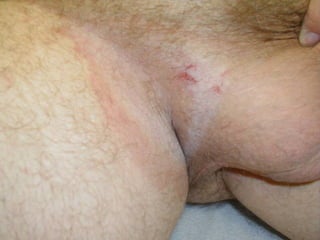
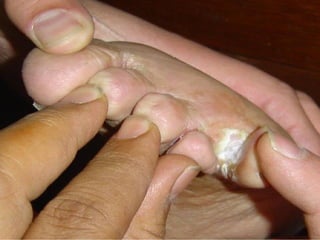
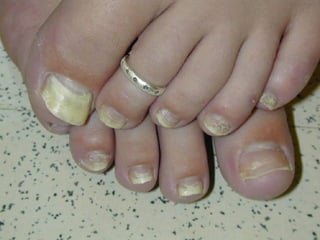
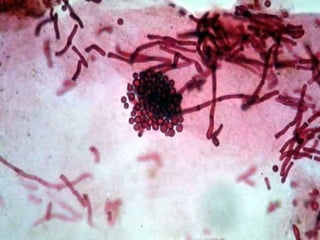
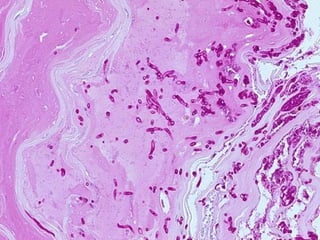
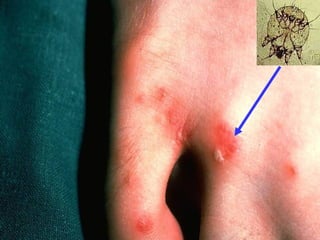
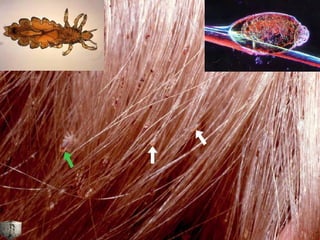
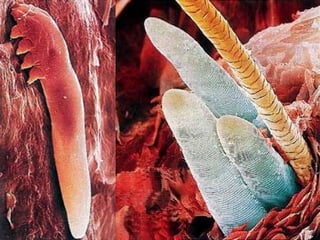
This document provides definitions and descriptions of terms related to normal skin anatomy and pathology. It begins with labeling diagrams of normal skin structures from the macroscopic to microscopic level. It then covers various skin conditions including pigmentation disorders, benign and malignant epidermal and dermal tumors, dermatoses, bullae, appendage disorders, panniculitis, and infections/infestations. For each condition, it lists key characteristics and histologic findings to aid in identification and diagnosis.