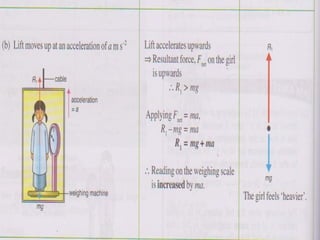
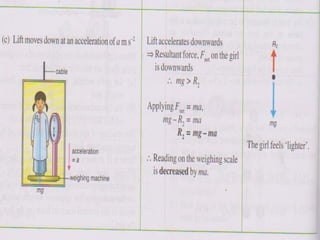
1. A box of mass 1.6 kg is suspended in a lift and its readings are taken at different lift accelerations. When stationary, the reading is 16N. When accelerating up at 2m/s^2, the reading is 19.2N. When accelerating down at 3m/s^2, the reading is 11.2N.
2. A student's weight on Earth is 450N. On the Moon, where gravity is 6 times weaker, the student's weight would be 75N.
3. A ball is thrown up at 20m/s. It reaches a maximum height of 20m and takes 4 seconds to return to the starting point.











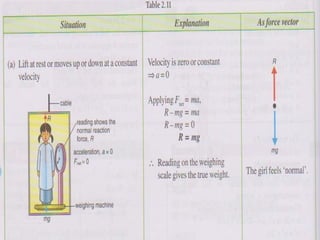

![1 A box of mass 1.6 kg is suspended from a spring balance
hanging from the ceiling of a lift
What is the reading on the spring balace if :
(a) The lift is stationary
(b) The lift moves upwards at an acceleration of 2 ms-2?
(c) The lift moes downwards at an acceleration of 3ms-2
[take g = 10 ms-2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gravity-121105051537-phpapp01/85/Gravity-Form-4-20-320.jpg)





