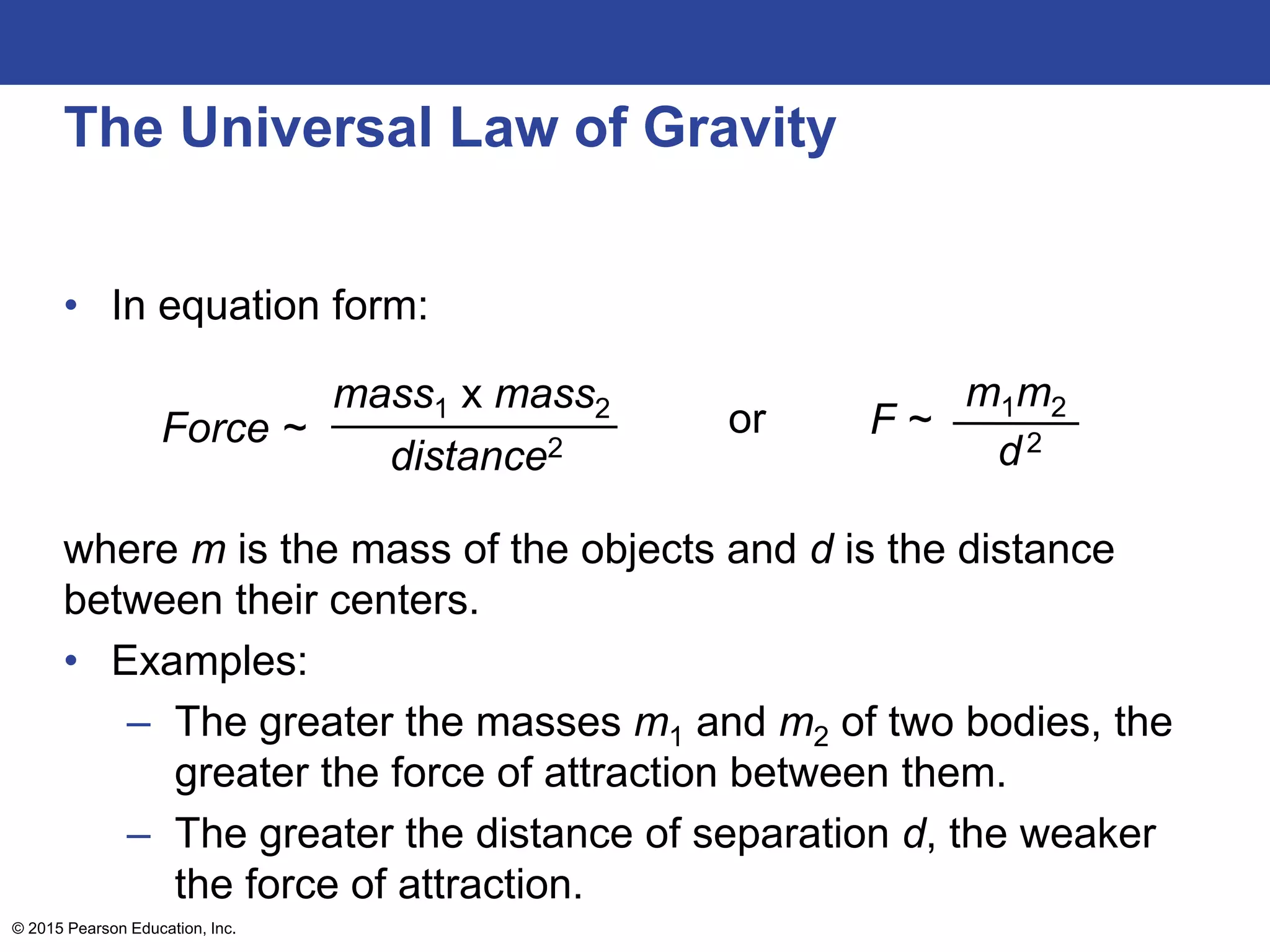
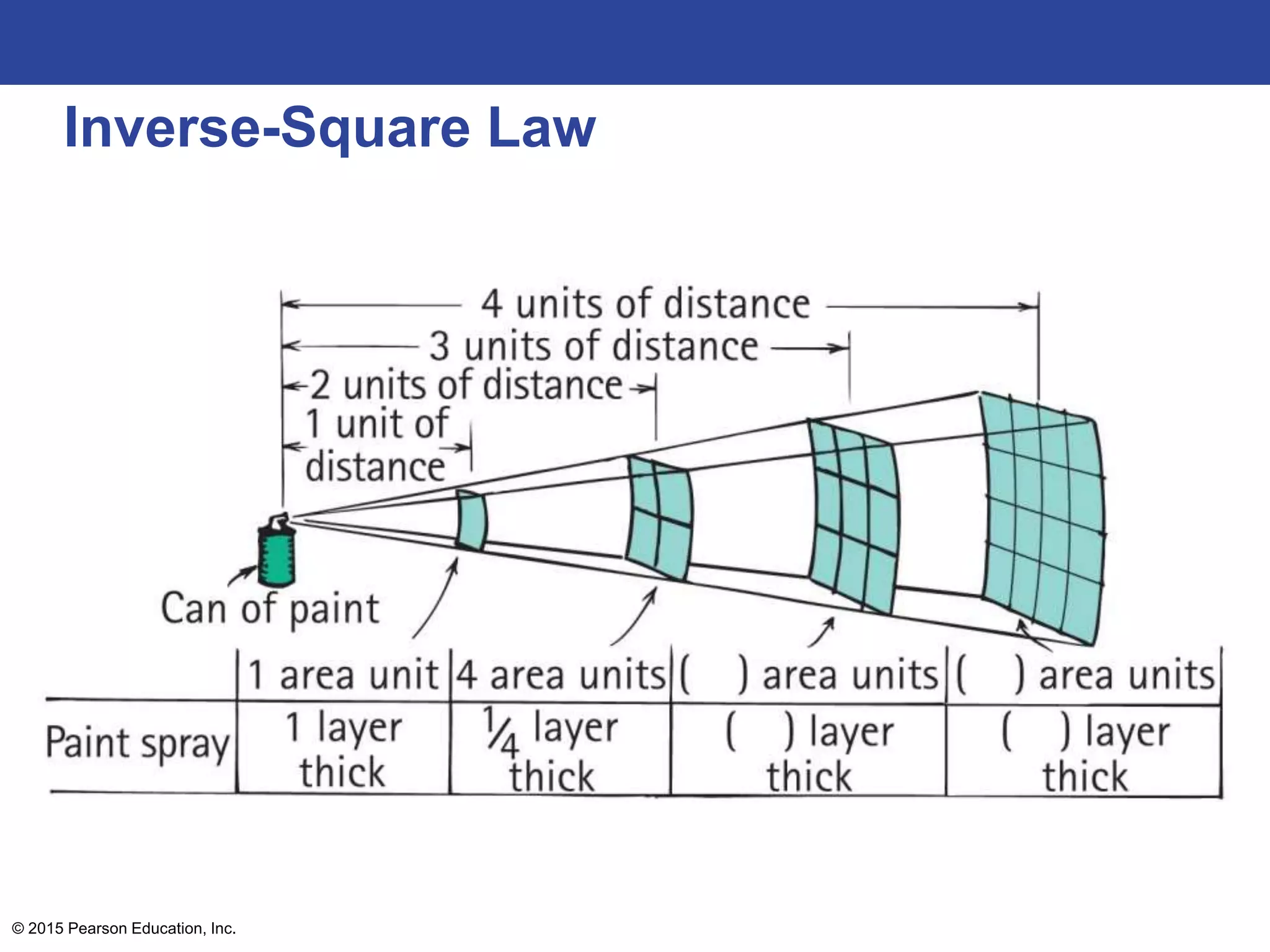
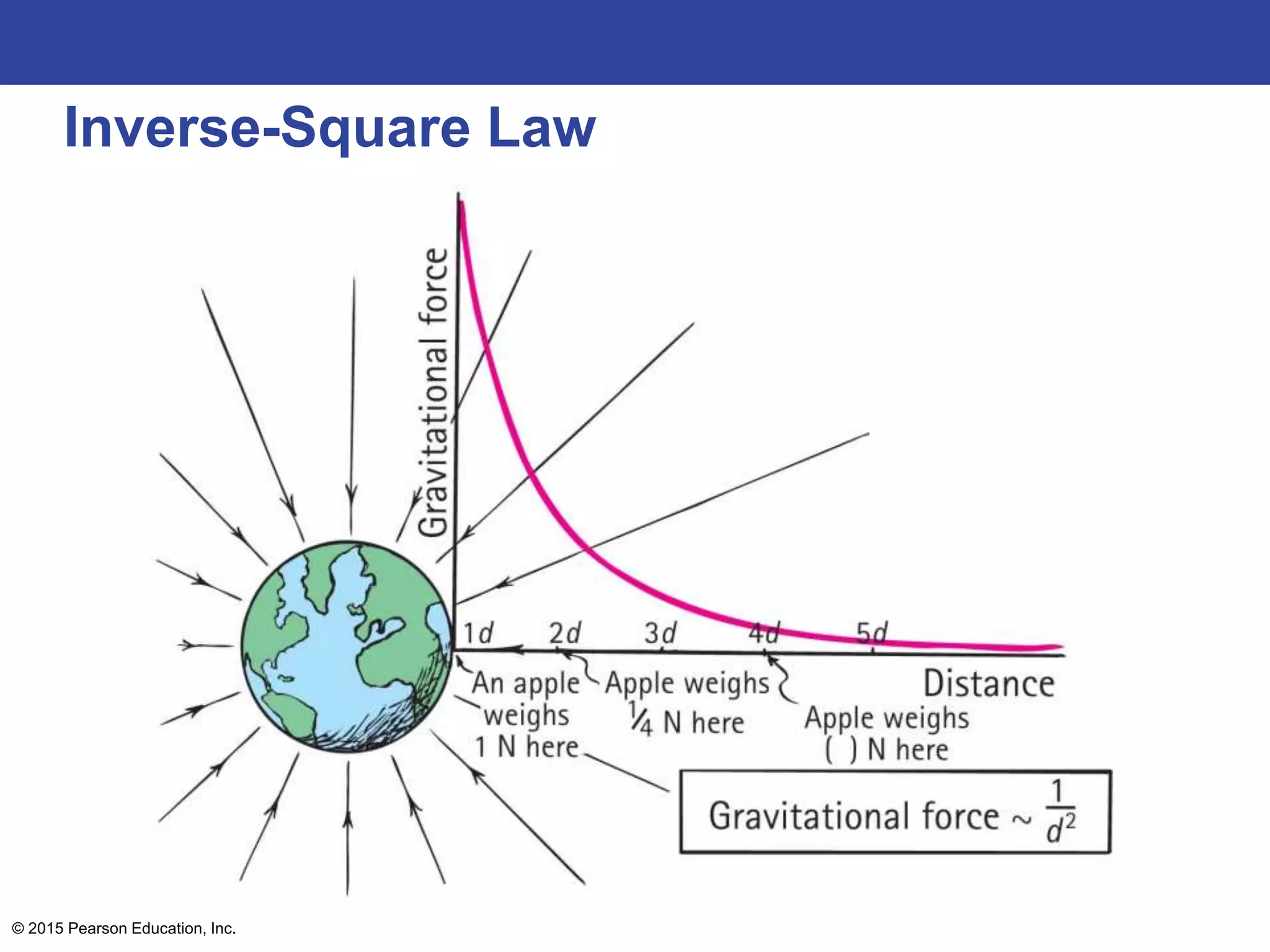
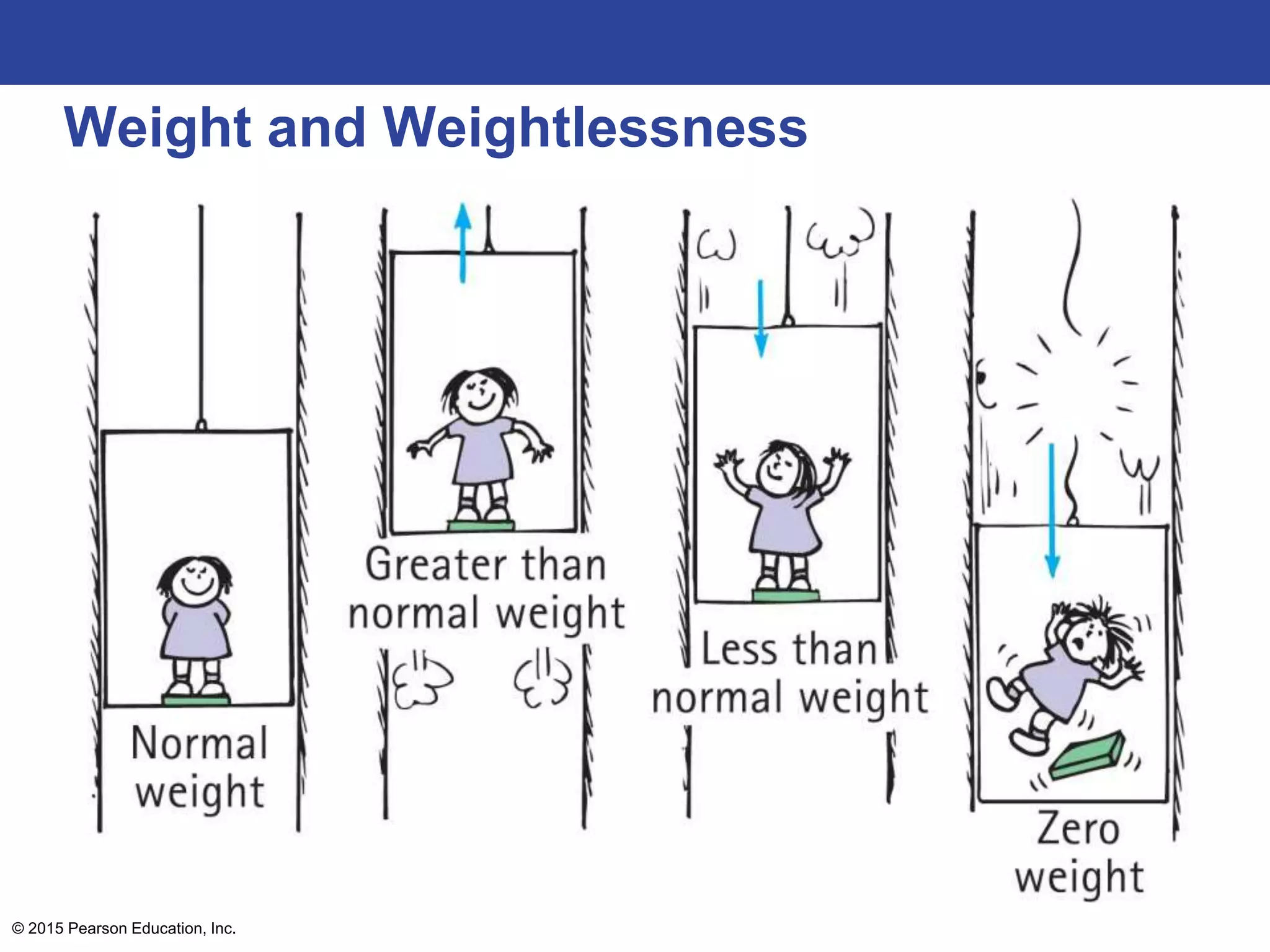
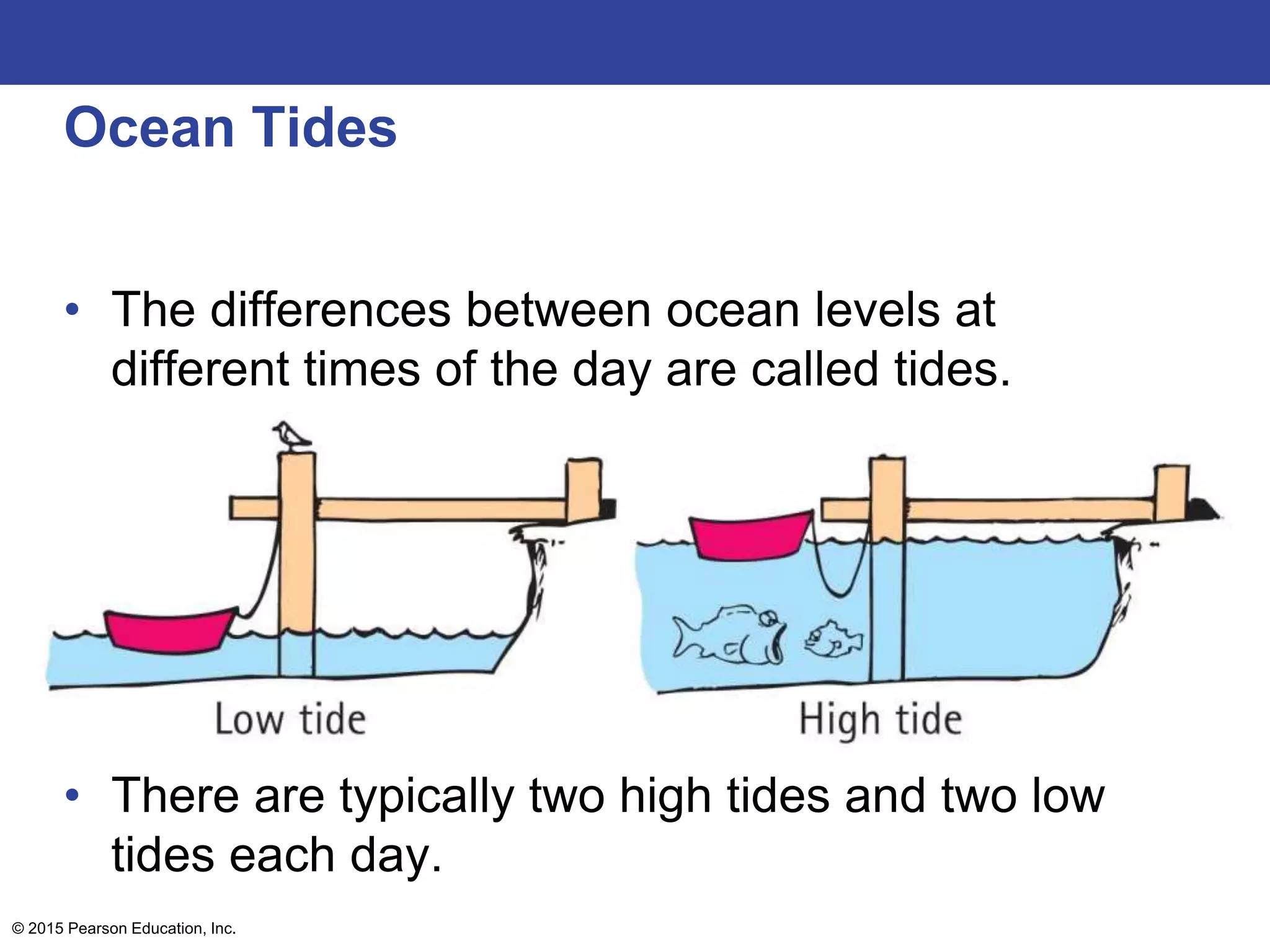
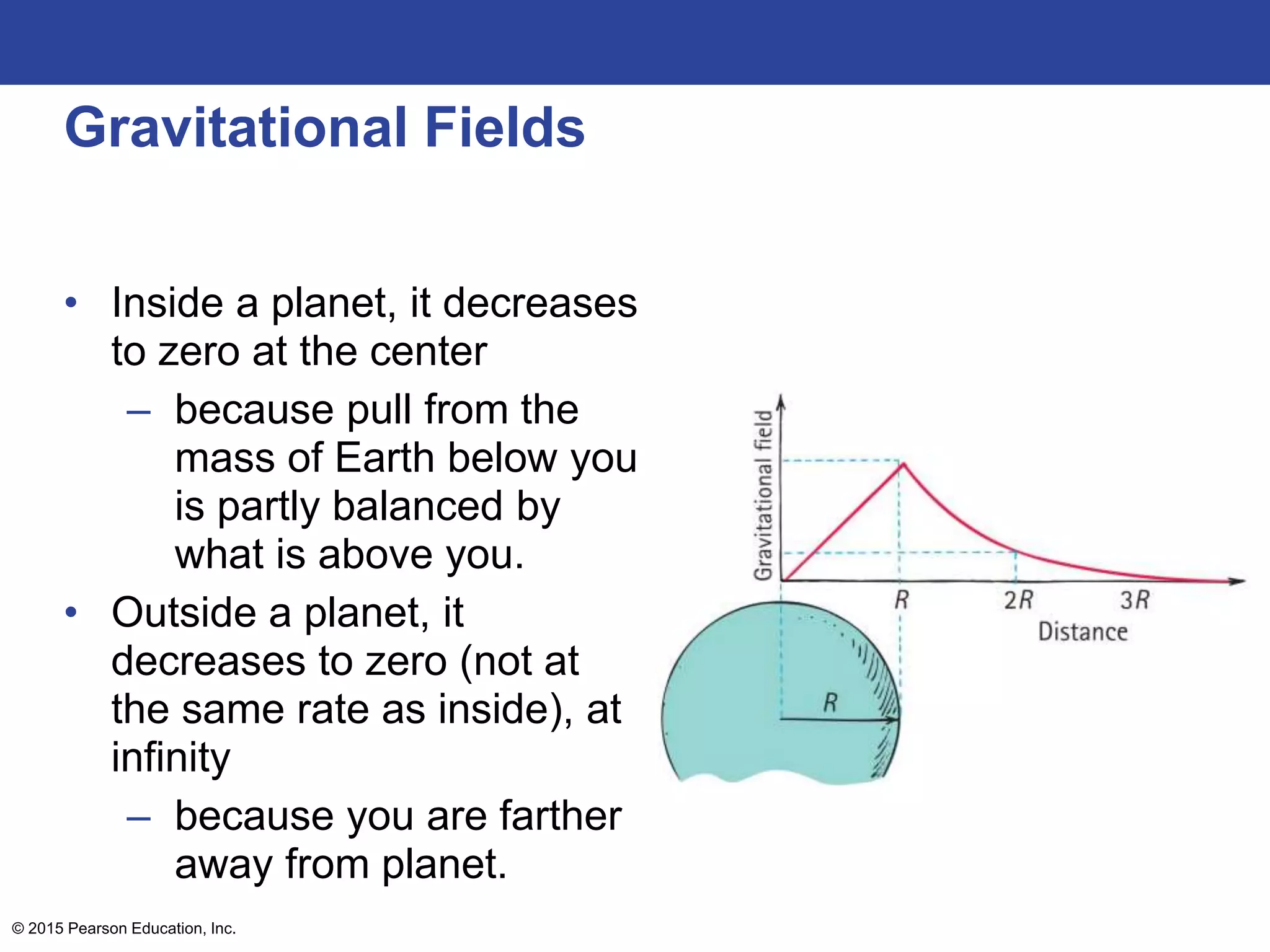
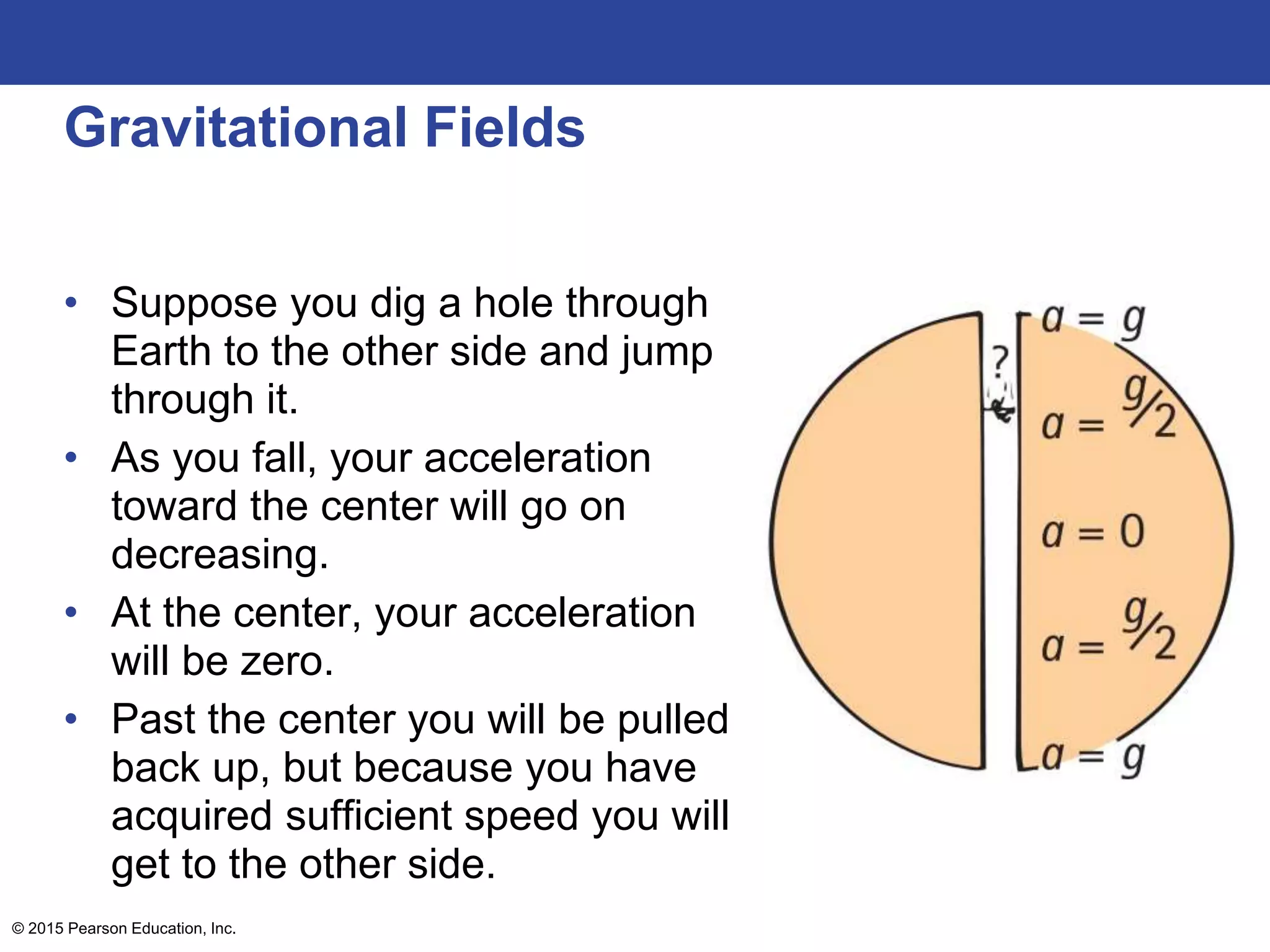
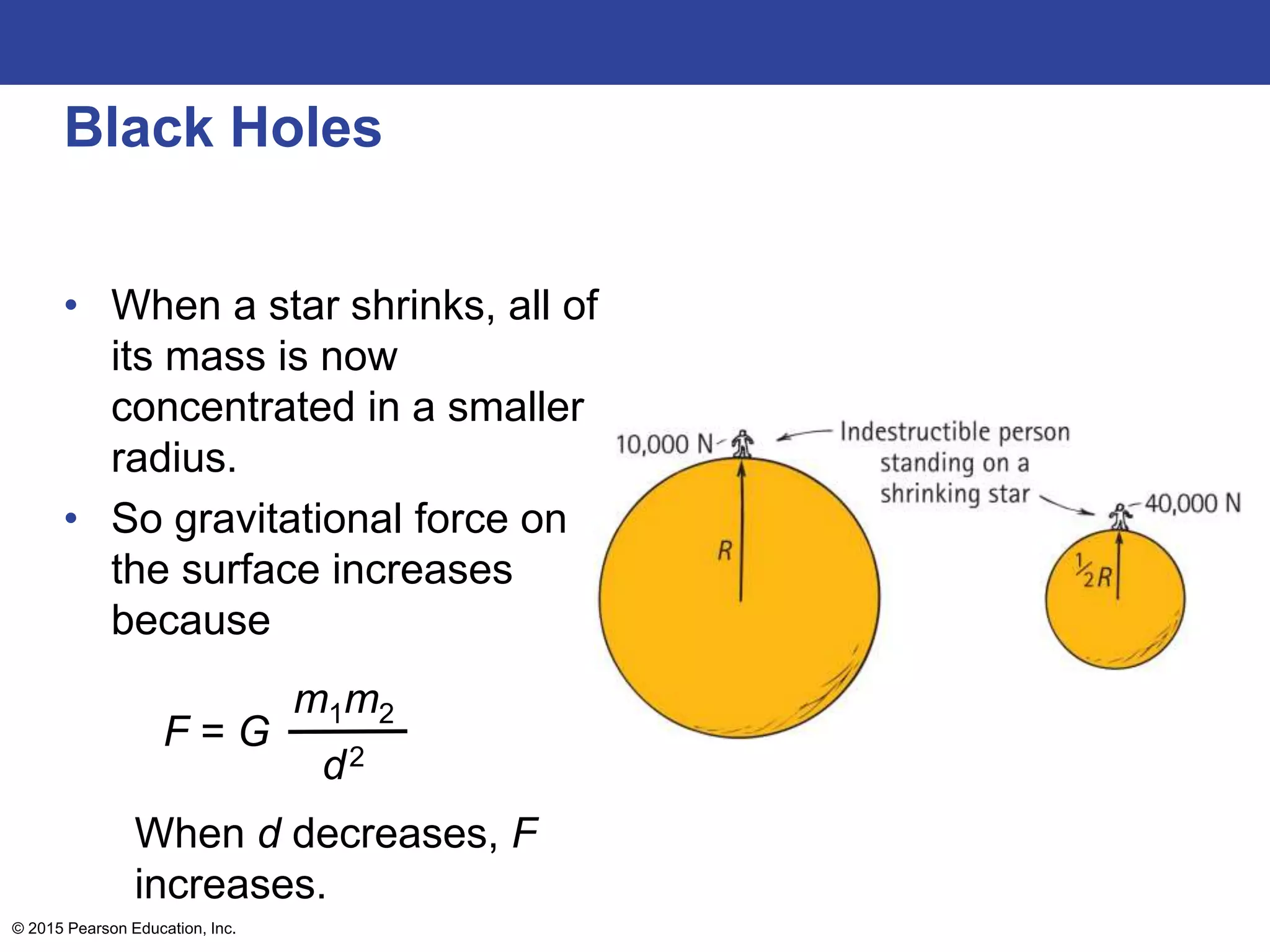
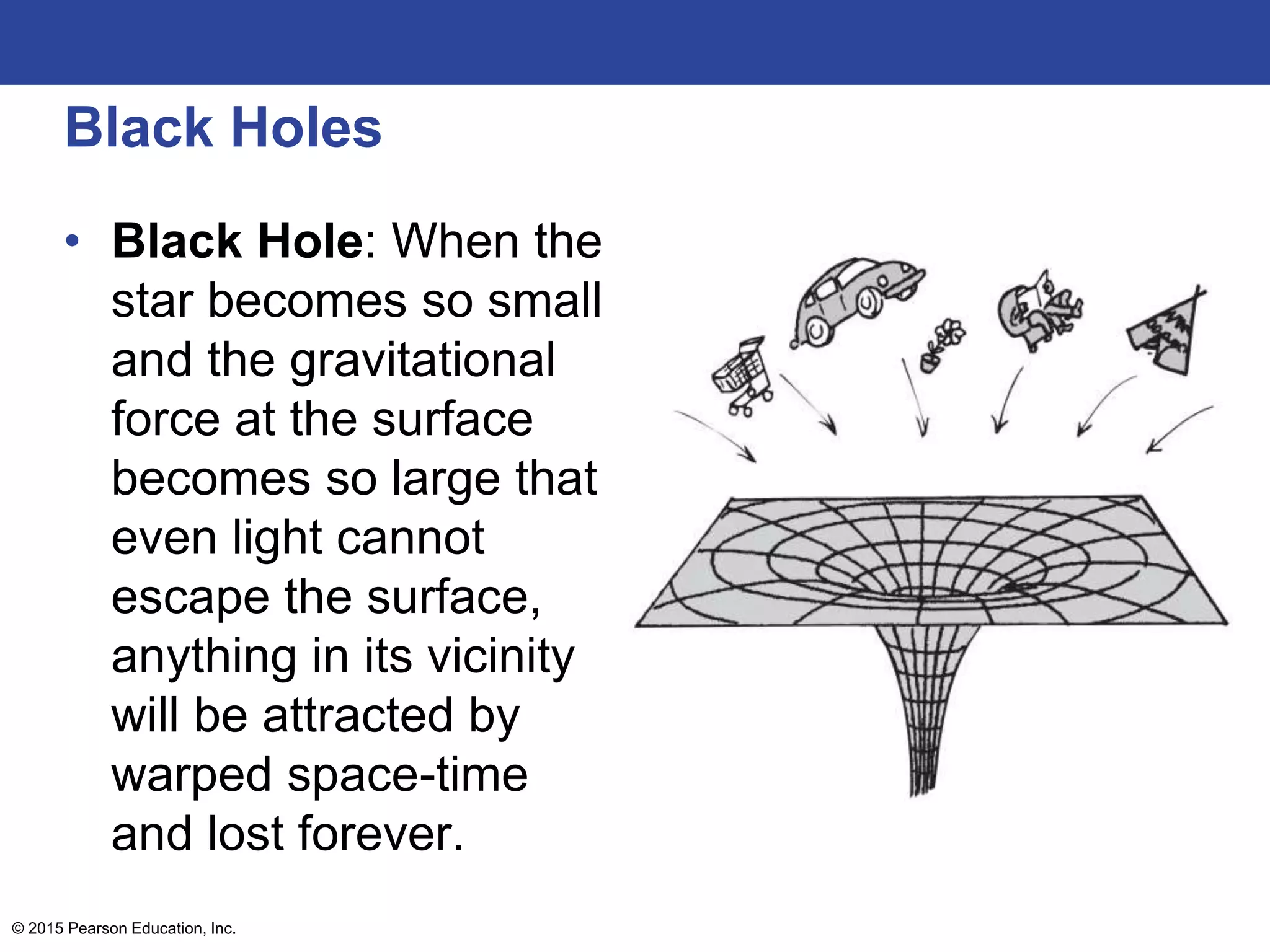
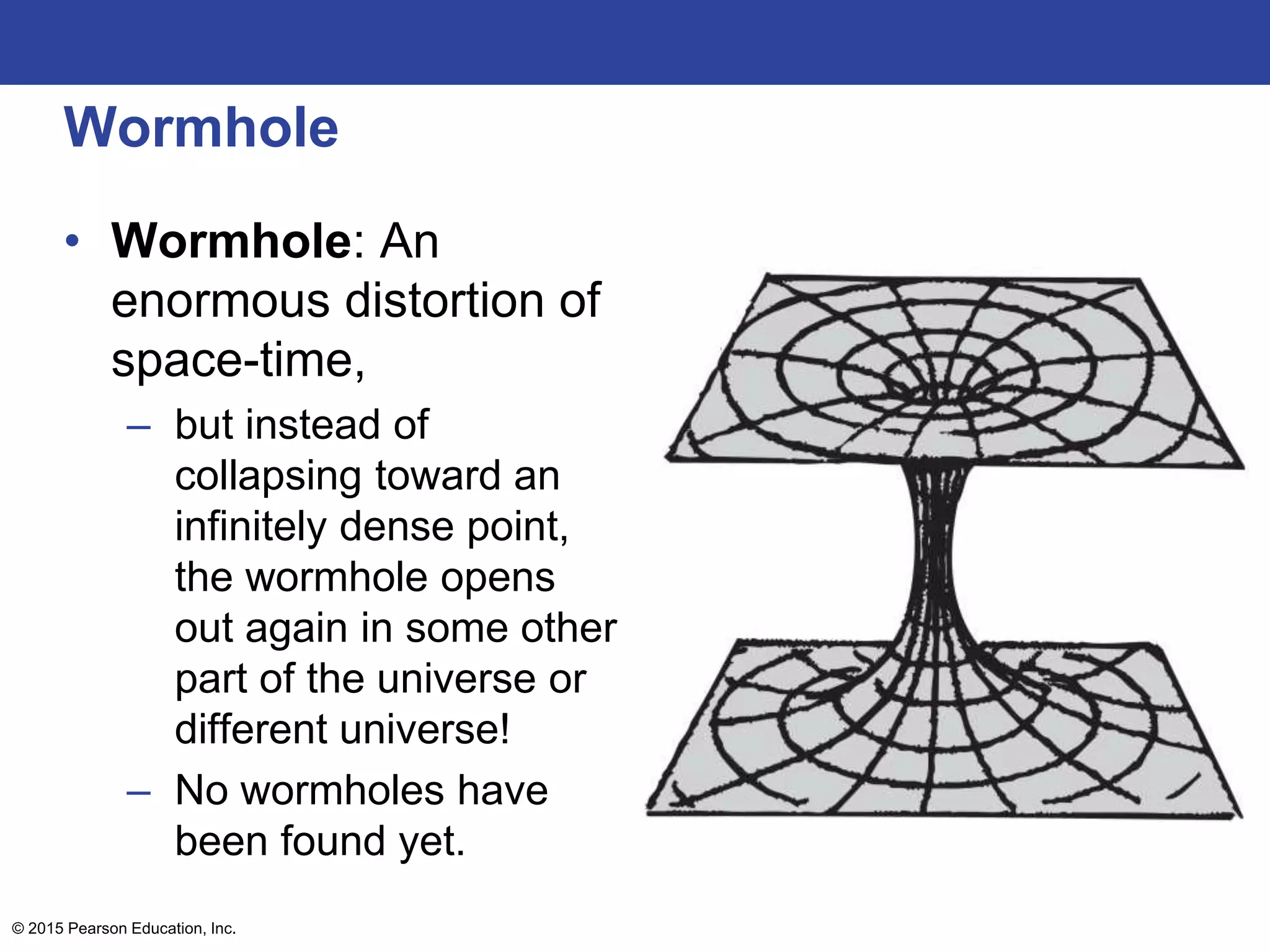
This lecture outline covers key concepts of gravity including Newton's universal law of gravity, the inverse square law, gravitational fields, weight and weightlessness, ocean tides, black holes, and Einstein's theory of gravitation. The key topics are explained through definitions, equations, diagrams, and examples.