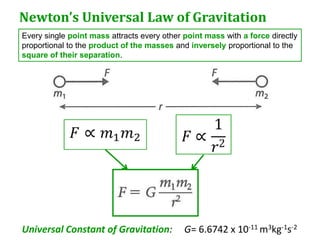
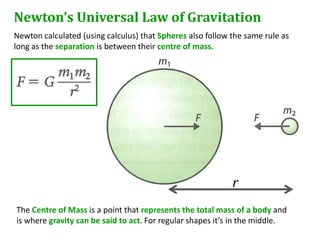
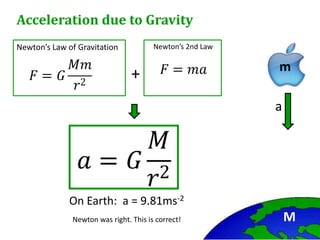
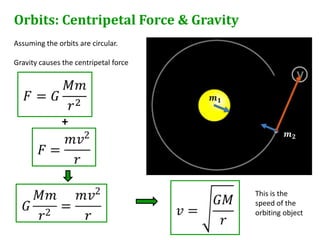
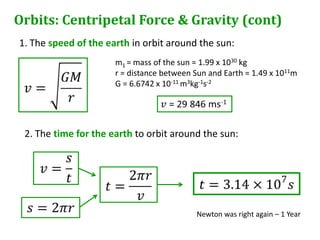
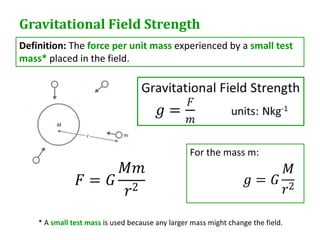
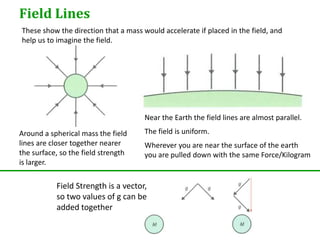
Newton's universal law of gravitation states that every point mass in the universe attracts every other point mass with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The gravitational field strength is defined as the gravitational force per unit mass experienced by a small test mass in the field. Field lines illustrate the direction of acceleration due to gravity and indicate that the field strength is greater nearer the surface of spherical masses.