Embed presentation
Downloaded 347 times



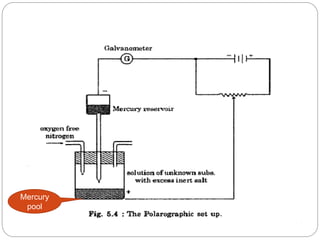




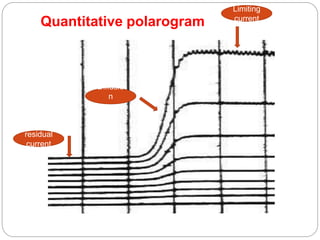


Polarography is a type of voltammetry where the working electrode is a dropping mercury electrode (DME). A polarographic cell contains a solution of interest, a reference electrode like calomel, a small DME indicator electrode, and an auxiliary electrode. Mercury is dropped from the DME at a stable rate, and current versus potential is recorded as voltage is applied gradually. The DME allows for analysis of very small sample volumes due to its narrow capillary. However, polarography is limited to potentials between +0.4 and -2 V, and the small capillary can become blocked. The diffusion current in polarography depends on factors like analyte concentration, diffusion coefficient, mercury drop flow rate, and drop lifetime









