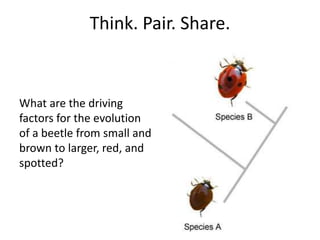
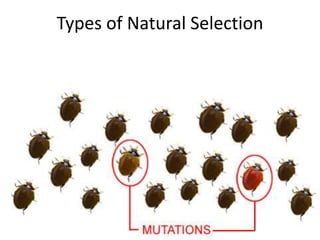
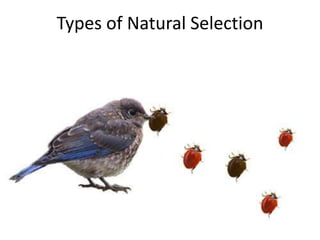
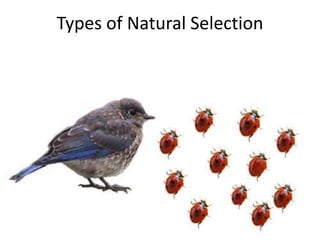
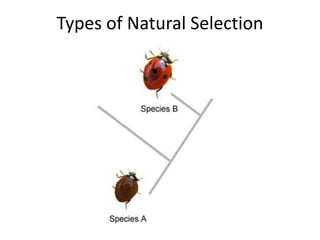
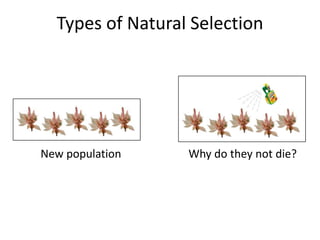
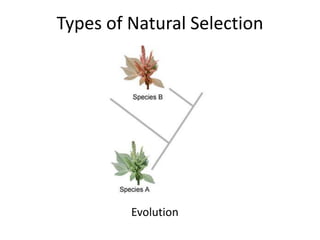
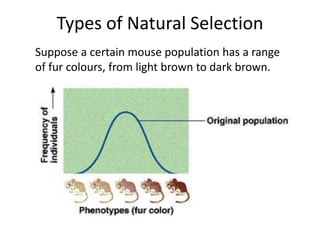
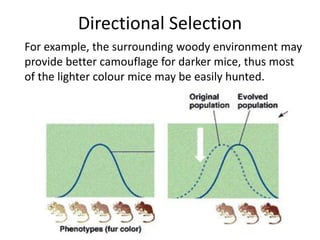
There are four types of natural selection: 1) Directional selection which favors an extreme variation of a trait, 2) Stabilizing selection which favors the average phenotype, 3) Disruptive selection which favors extreme traits while the average declines, and 4) Sexual selection which favors traits that increase success in finding a mate and reproducing. Examples are given for each type of selection.