Embed presentation
Downloaded 337 times


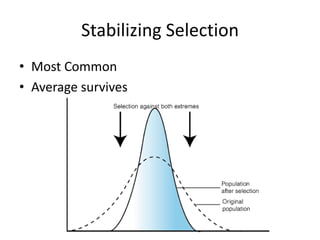

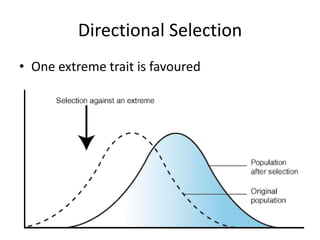

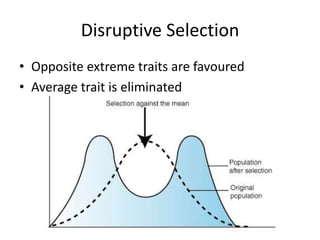


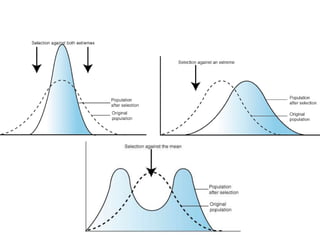

There are three main types of natural selection: stabilizing selection, directional selection, and disruptive selection. Stabilizing selection favors average traits so that medium-sized or medium-weight individuals are most likely to survive. Directional selection favors individuals with one extreme trait, like long-necked giraffes or large horses. Disruptive selection favors individuals with opposite extreme traits, so average or intermediate individuals die out while the extremes survive, like with camouflaged light or dark rabbits.










