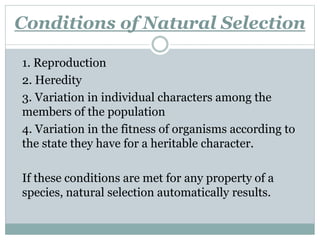
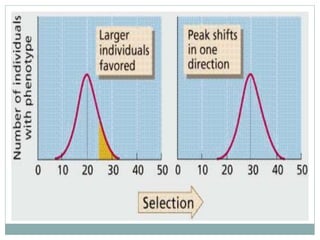
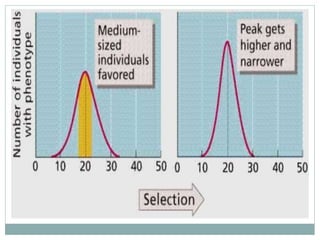
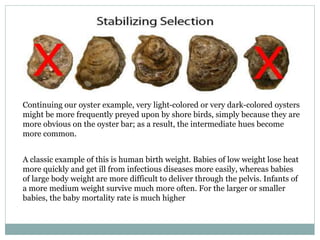
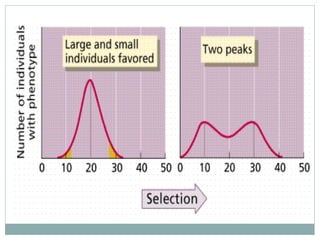
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution that explains how species arise and develop through natural selection, which favors individuals with advantageous traits that enhance their survival and reproduction. Natural selection can occur under three types: directional, stabilizing, and disruptive selection, each characterized by different outcomes in trait distributions within a population. The document provides examples illustrating these types, including the survival of thicker-shelled oysters and the effects of varying birth weights in humans.